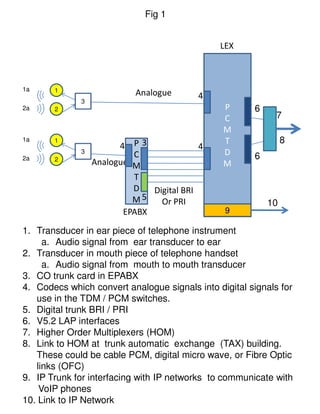
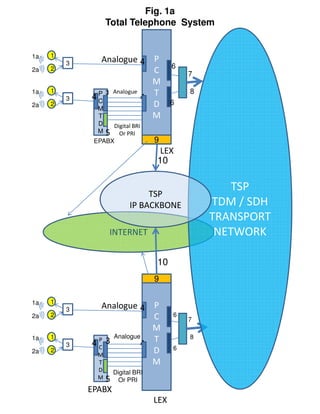
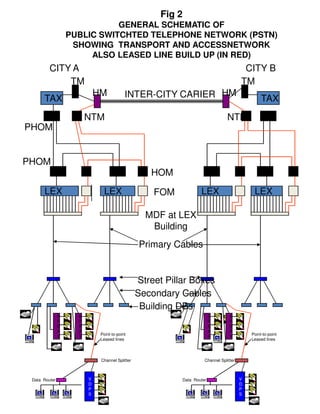
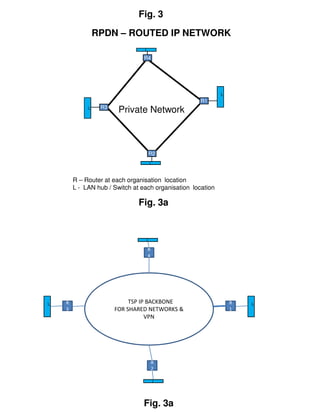
Circuit switched telephone networks transmit digitized voice signals over dedicated circuits, while packet switched networks divide voice signals into packets which are transmitted over shared networks. In circuit switched networks, a connection is established end-to-end for each call, while in packet switched networks multiple communications share network bandwidth through packetization. Packetization allows better utilization of bandwidth for bursty data traffic as in computer networks, while circuit switched networks ensure utilization through traffic engineering. Voice can be transmitted over packet networks by digitizing it and transmitting the voice packets alongside data packets.