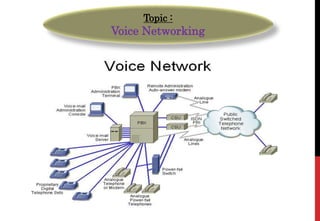
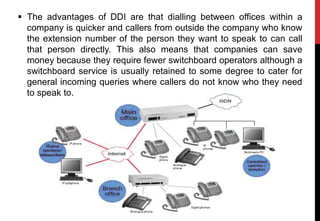
A private voice network can save companies money on telephone bills and ensure callers can reach the desired extension on the first call. Designing such a network involves choosing between direct inward dialing (DID), private leased circuits, public switched telephone network (PSTN) overflow, or virtual private networks (VPN). The optimal solution depends on factors like call volumes, number of sites, and whether a wide area data network exists that could incorporate voice services. Numbering plans are also important to integrate different sites on a private network or VPN.