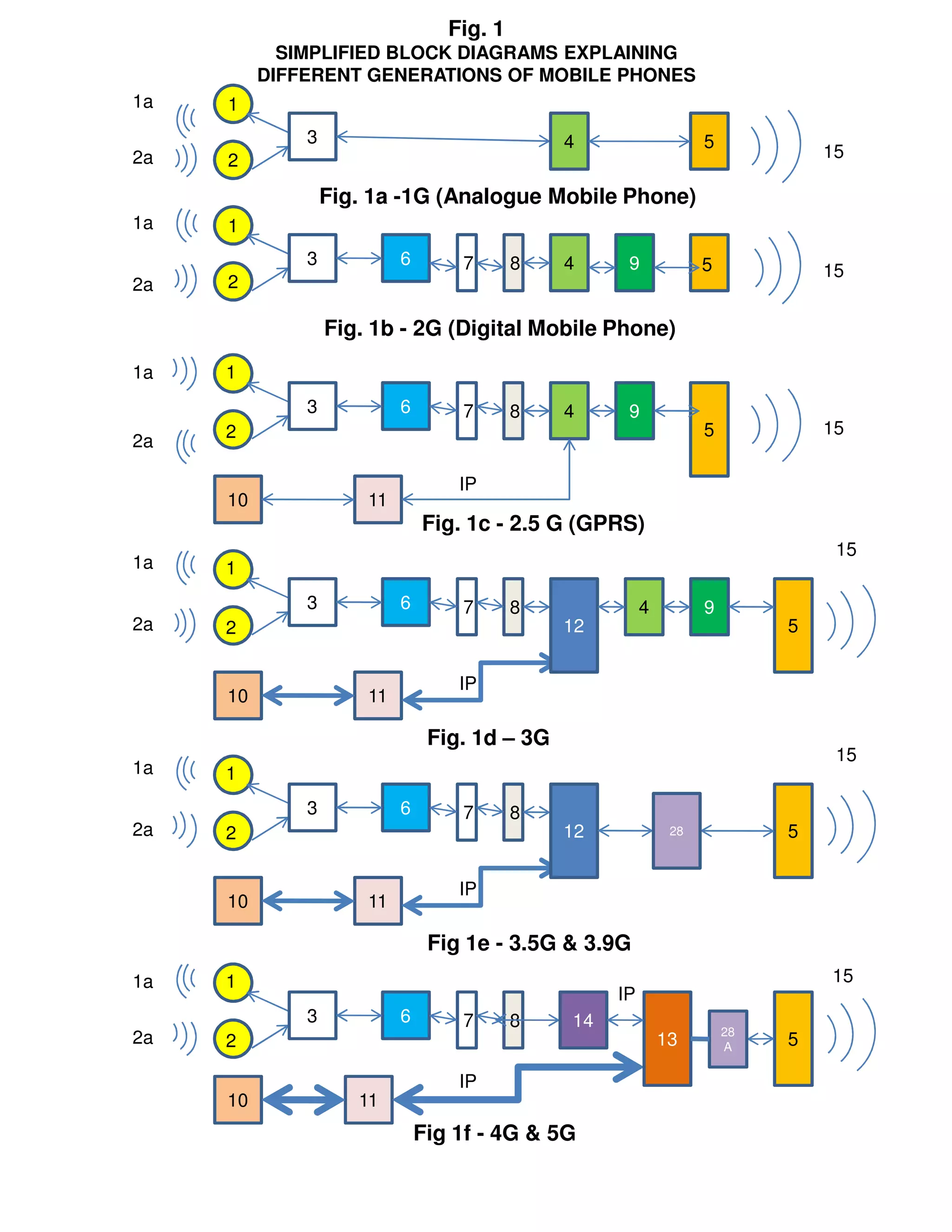
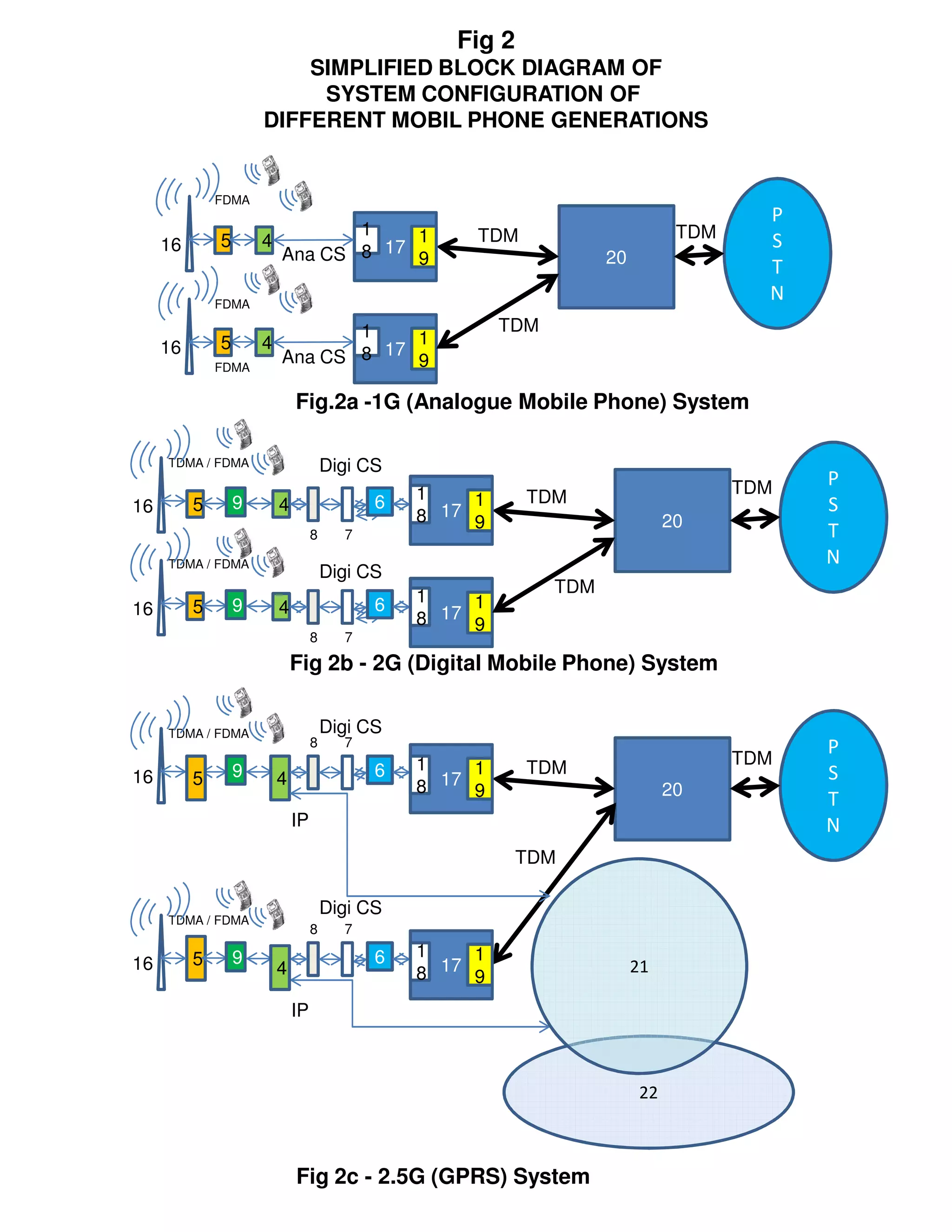
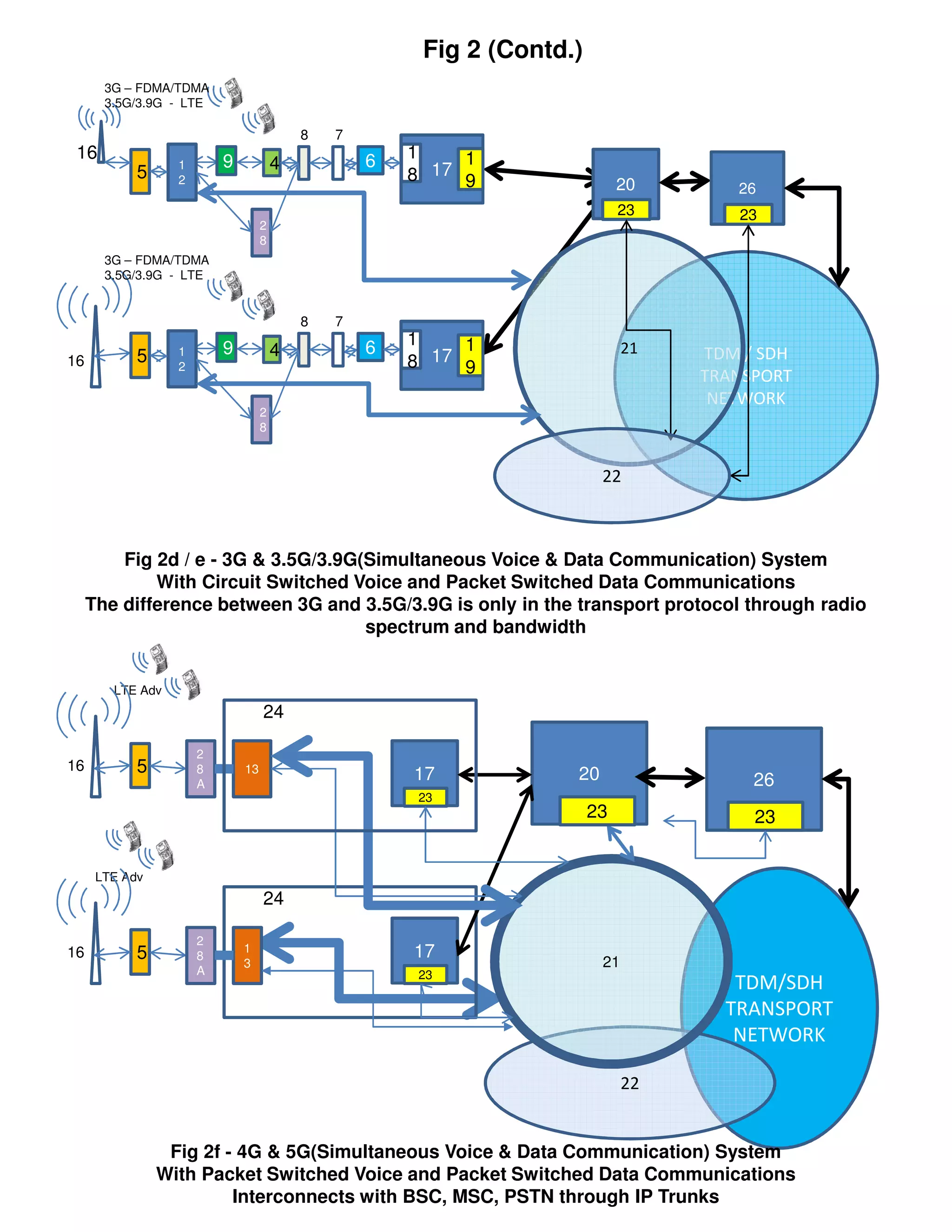
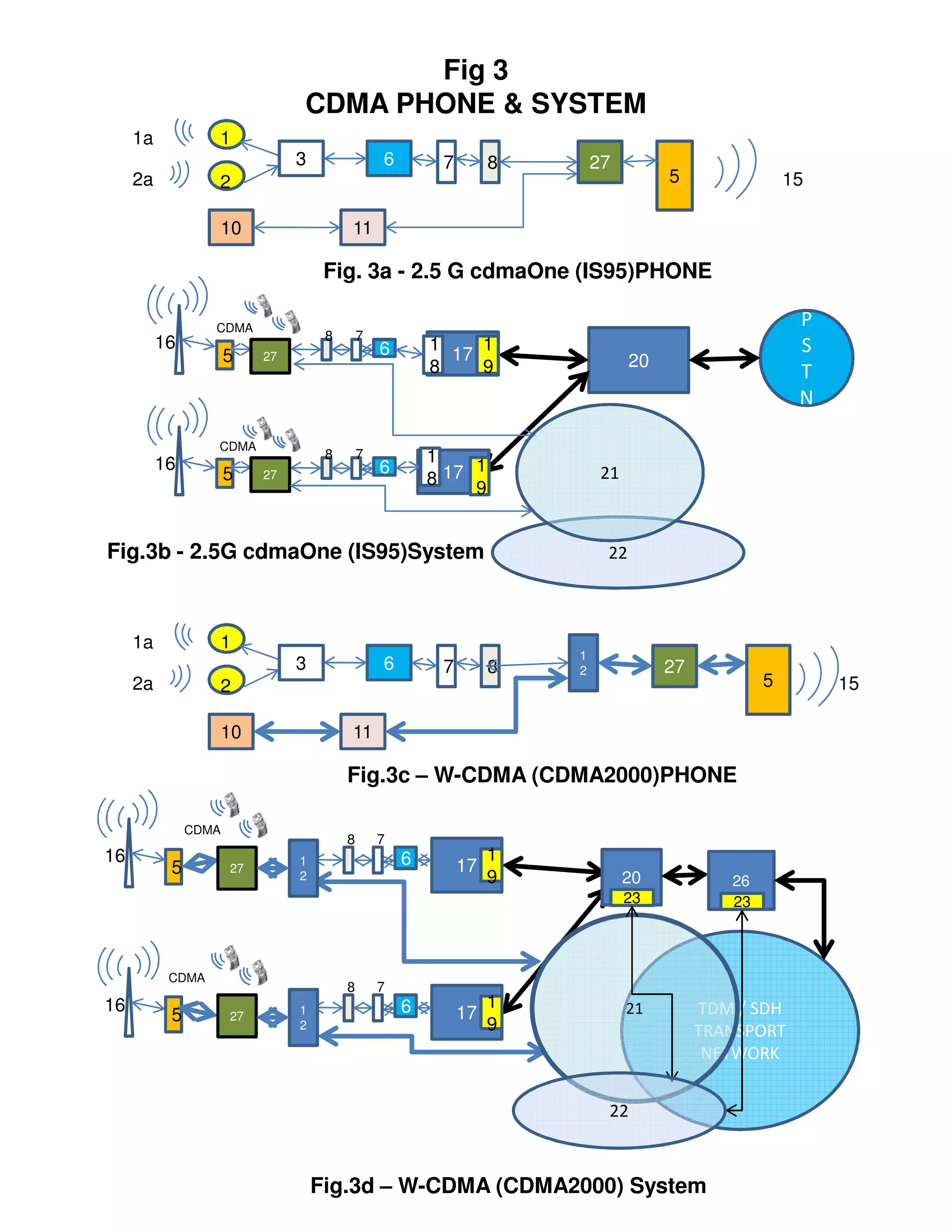
This document compares different generations of mobile phones and systems through block diagrams. It shows the evolution from 1G analog phones using FDMA to 5G phones using LTE Advanced. Key differences include how voice and data are transmitted over radio channels (circuit switched vs packetized), increasing bandwidths enabling higher speeds, and transitioning from circuit switched to packetized voice delivery.