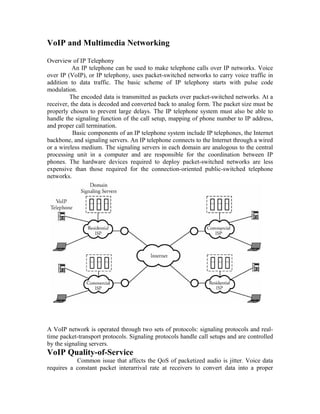
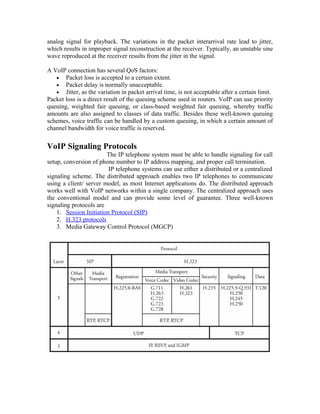
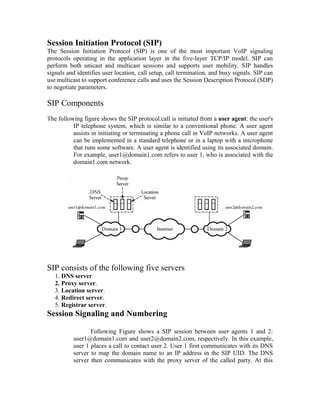
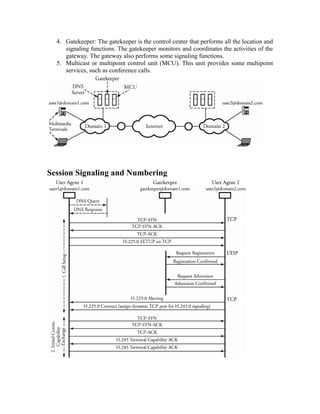
VoIP uses packet networks to carry voice calls in addition to data. It works by converting analog voice signals to digital data packets which are transmitted over IP networks and reconverted to analog at the receiving end. Key components include IP phones, signaling servers, and protocols like SIP and H.323 which handle call setup and signaling. Quality of service for VoIP depends on factors like packet loss, delay, and jitter which can be managed through queuing and reserving bandwidth for voice traffic.