This document provides an overview of the TECH2002 Studies in Digital Technology course. The course will cover topics such as digital technology, new media, social media, participatory culture, and online video. Assessments will include individual and group presentations, research papers, and a YouTube video. Key concepts that will be examined include Web 2.0, participatory culture, social media, blogs, and how technology is integrated into everyday life. Students will complete weekly tasks to gain participation points, including creating audio mixes, playlists, research citations, and using social media platforms like Twitter and YouTube.








![Academic Study
Darley, A. (2000) Visual Digital Culture, London,
Routledge.
Flew, T. (2008) New Media: An Introduction (3rd
Edition), South Melbourne, Oxford University
Press.
Mayfield, A. (2007) What is social media? [WWW].
Available from:
http://www.icrossing.co.uk/fileadmin/uploads/eBooks/
(Accessed 24/09/08).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech2002lecweekone0910-091008053408-phpapp01/85/Tech2002lecweekone0910-11-320.jpg)

![Assessment
• Coursework [50%] – YouTube
Research Project
– Component 1 (10%) Presentation
– Component 2 (15%) Research Paper
– Component 3 (25%) YouTube Video
• Component 4 Exam [50%] – 2 hour
unseen exam](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech2002lecweekone0910-091008053408-phpapp01/85/Tech2002lecweekone0910-13-320.jpg)



![New media (Flew 2008)
• Convergence of
computing,
communications
and content
(media)
[‘three Cs’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech2002lecweekone0910-091008053408-phpapp01/85/Tech2002lecweekone0910-17-320.jpg)




















![Week 1 Tasks
• Research Task [3 annotated citations in a Word doc]
(50)
• One minute YouTube video documentary about
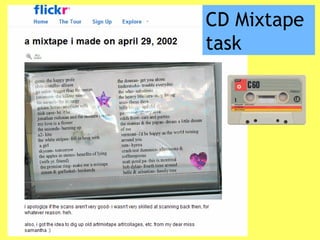
audiocassettes and/or mixtapes (50)
• Creating a research study blog on Wordpress.com (50)
• Creating a CD mixtape lasting 60 minutes with art work
and tracklist (50)
• Joining Spotify (50)
• Producing a Spotify playlist posted on
Sharemyplaylists.com (50)
•
• Current Participation Points Total (300)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech2002lecweekone0910-091008053408-phpapp01/85/Tech2002lecweekone0910-38-320.jpg)


![Bibliography
Burgess, J. and Green, J. (2009) YouTube: Online Video and Participatory Culture, Cambridge,
Polity.
Flew, T. (2008) New Media: An Introduction (3rd
Edition), South Melbourne, Oxford University
Press.
Kusek, D. and Leonhard, G. (2005) The Future of Music, Boston, Berklee Press.
Leadbeater, C. (2008) We Think [WWW] Available at
http://www.charlesleadbeater.net/cms/xstandard/Rev%20Ch%20Two.pdf
(Accessed 3/10/08)
Lilley, A. (2007) ‘The Me in Media: Participation, Interactivity and the Rise of the People
formerly known as the audience’, The Royal Television Society Huw Wheldon Memorial
Lecture 2007.
Mayfield, A. (2007) What is social media? [WWW] Available at
http://www.icrossing.co.uk/fileadmin/uploads/eBooks/
What_is_social_media_Nov_2007.pdf (Accessed 24/09/08).
Moores, S. (2005) Media/Theory: Thinking About Media and Communications, London and New
York, Routledge.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech2002lecweekone0910-091008053408-phpapp01/85/Tech2002lecweekone0910-41-320.jpg)