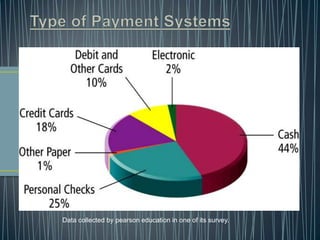
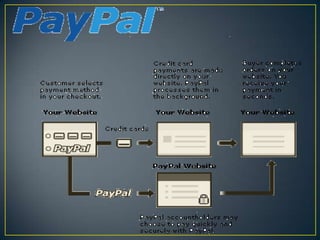
This document provides an overview of payment systems in banking in India. It discusses the history of payment instruments from coins to paper money to modern systems like cheques and electronic funds transfer. It outlines some key milestones in the evolution of payment systems in India such as the introduction of magnetic ink character recognition for cheque processing and real-time gross settlement. The document also describes the role played by the Reserve Bank of India in payment systems as a user, service provider, and regulator. It discusses the organizational structure established by RBI to oversee reforms to the national payment system, including the Payment Systems Group, Payment Systems Advisory Committee, and National Payments Council.