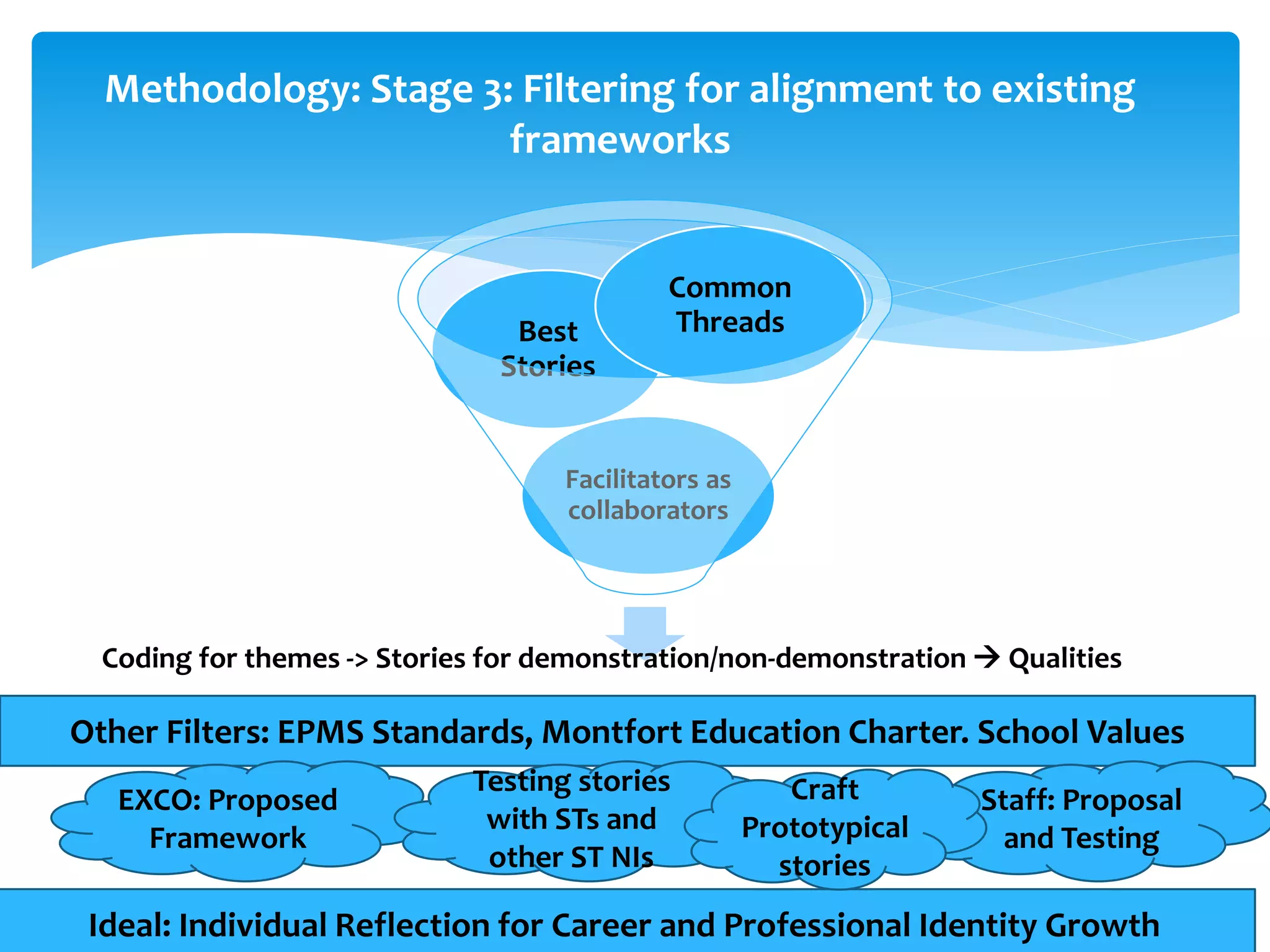
The document proposes a framework for teacher leader development consisting of three domains:
1. Professional Mastery (skill-based), focusing on experience, effective classroom teaching, and openness to learning.
2. Effective Collaborator (personal qualities), emphasizing trustworthiness, willingness to help others, nurturing attitude, approachability, and empathy.
3. Organizational Excellence (culture-builder), highlighting being positive-minded, leading by example, providing clarity, and being proactive and reflective.
The framework is intended to guide career development, performance reviews, and the cultivation of teacher leadership qualities beyond individual classrooms to benefit student learning.