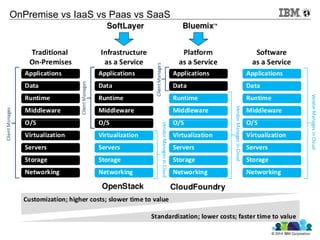
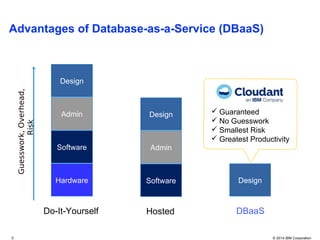
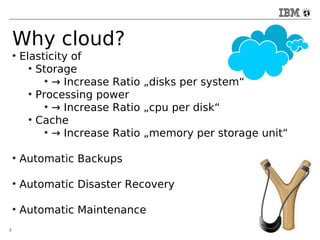
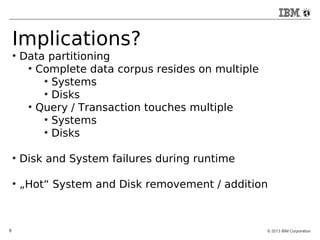
The document discusses databases in the cloud, including SQL and NoSQL options. It introduces IBM Bluemix, a cloud platform that provides database services. The advantages of database-as-a-service include reduced overhead and risk compared to self-hosted databases. Examples of companies using Cloudant database services are given. Reasons for using cloud databases include elasticity of storage and computing power as well as automatic backups and maintenance.