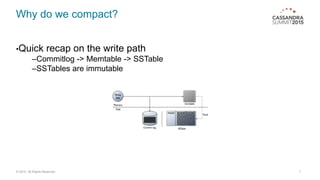
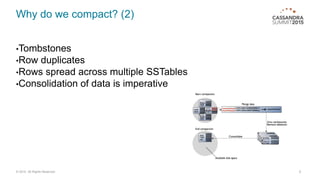
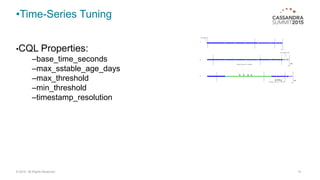
Manage your compactions before they manage you! This document discusses compaction in Cassandra databases. It covers why compaction is needed, different compaction strategies like size-tiered, levelled, and time-series, how to tune strategies, monitoring compactions, and disk tuning tips. The key messages are to select the right strategy for your usage, monitor compactions closely, and tune disk configuration, as compactions involve heavy I/O that must be well managed.