Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times



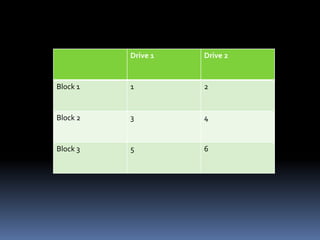

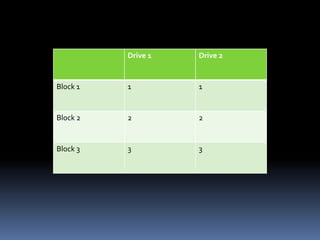

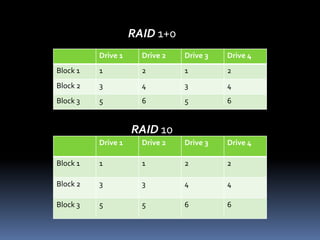


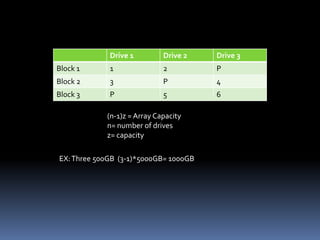



RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) uses multiple hard drives for performance and reliability. RAID 0 uses striping to increase performance but provides no data redundancy. RAID 1 uses mirroring to provide full data redundancy but offers no performance increase. RAID 5 uses parity to provide redundancy across 3 or more drives while also increasing performance. Newer RAID technologies like RAID n offer more flexibility and reliability than standard RAID levels. The G-SPEED eS PRO XL RAID system provides fast, high capacity storage optimized for video workflows.













