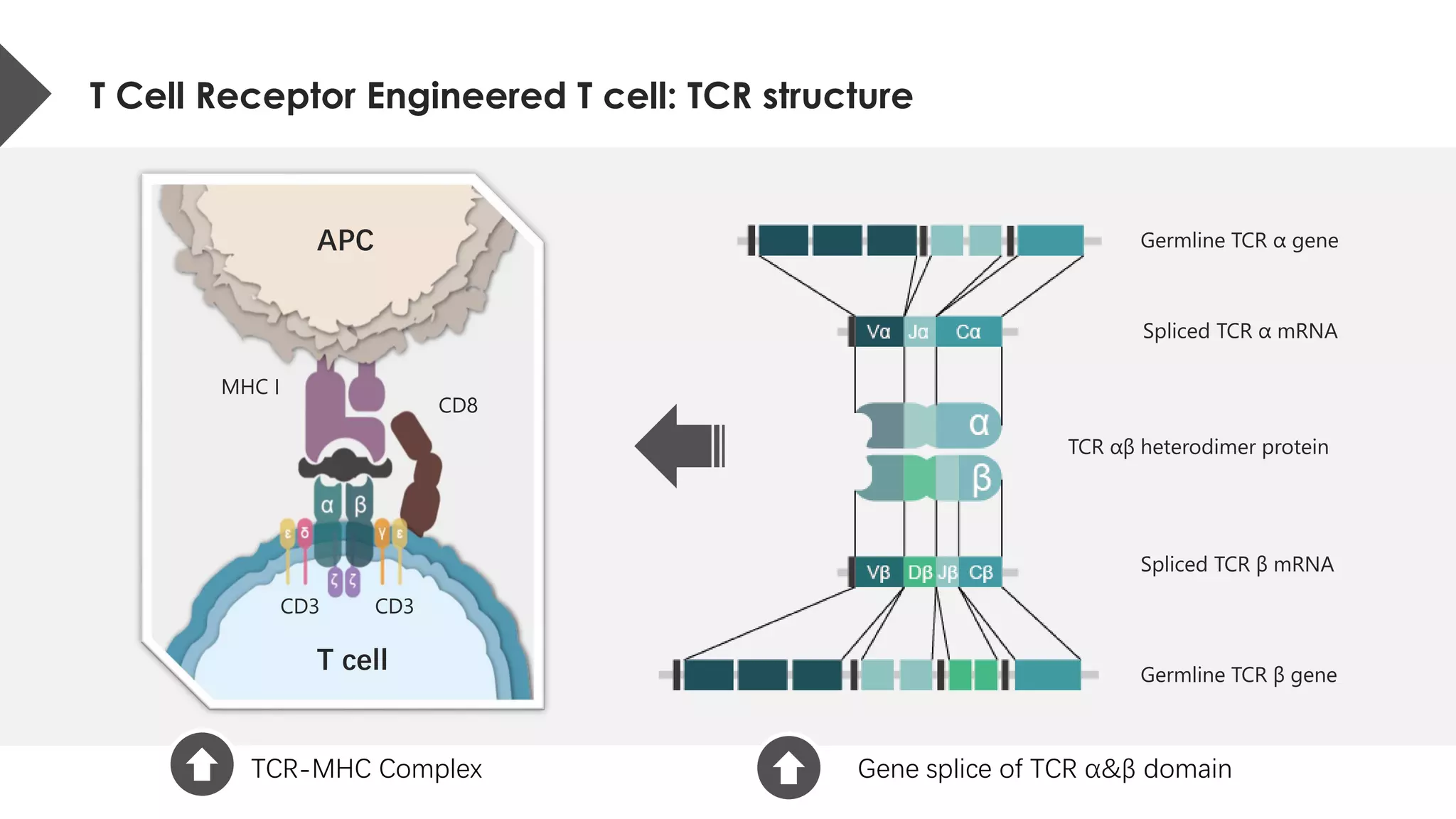
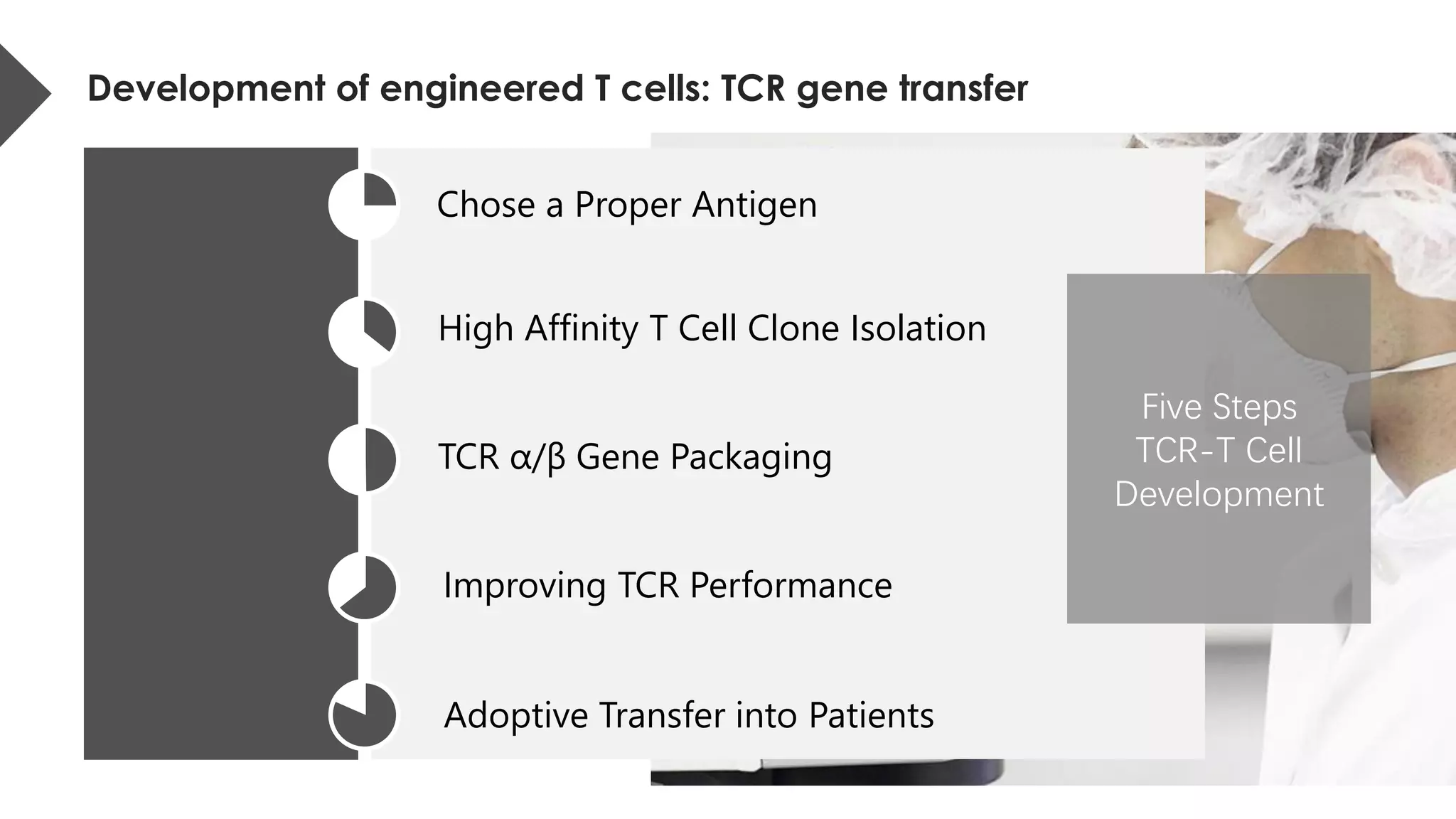
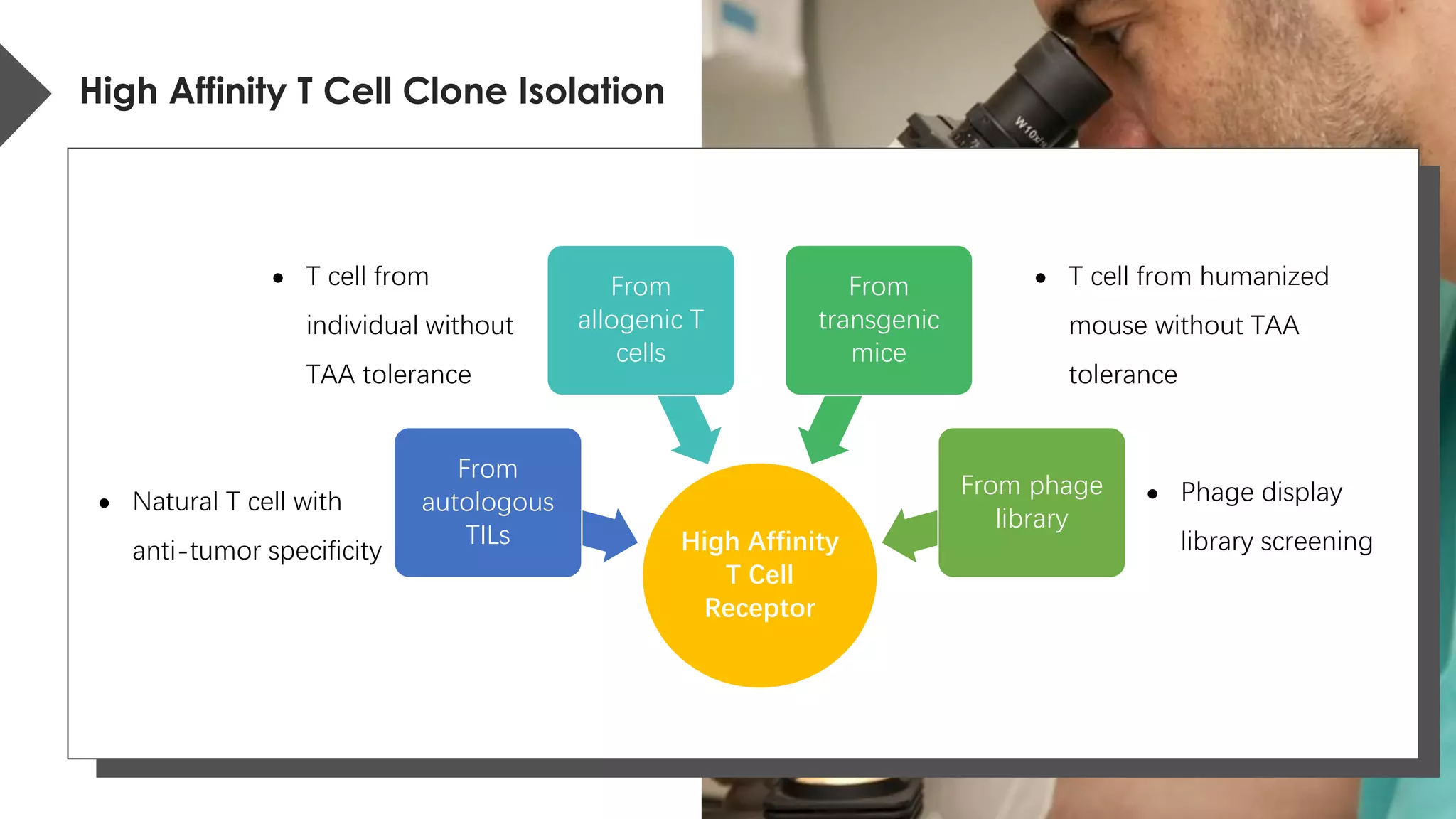
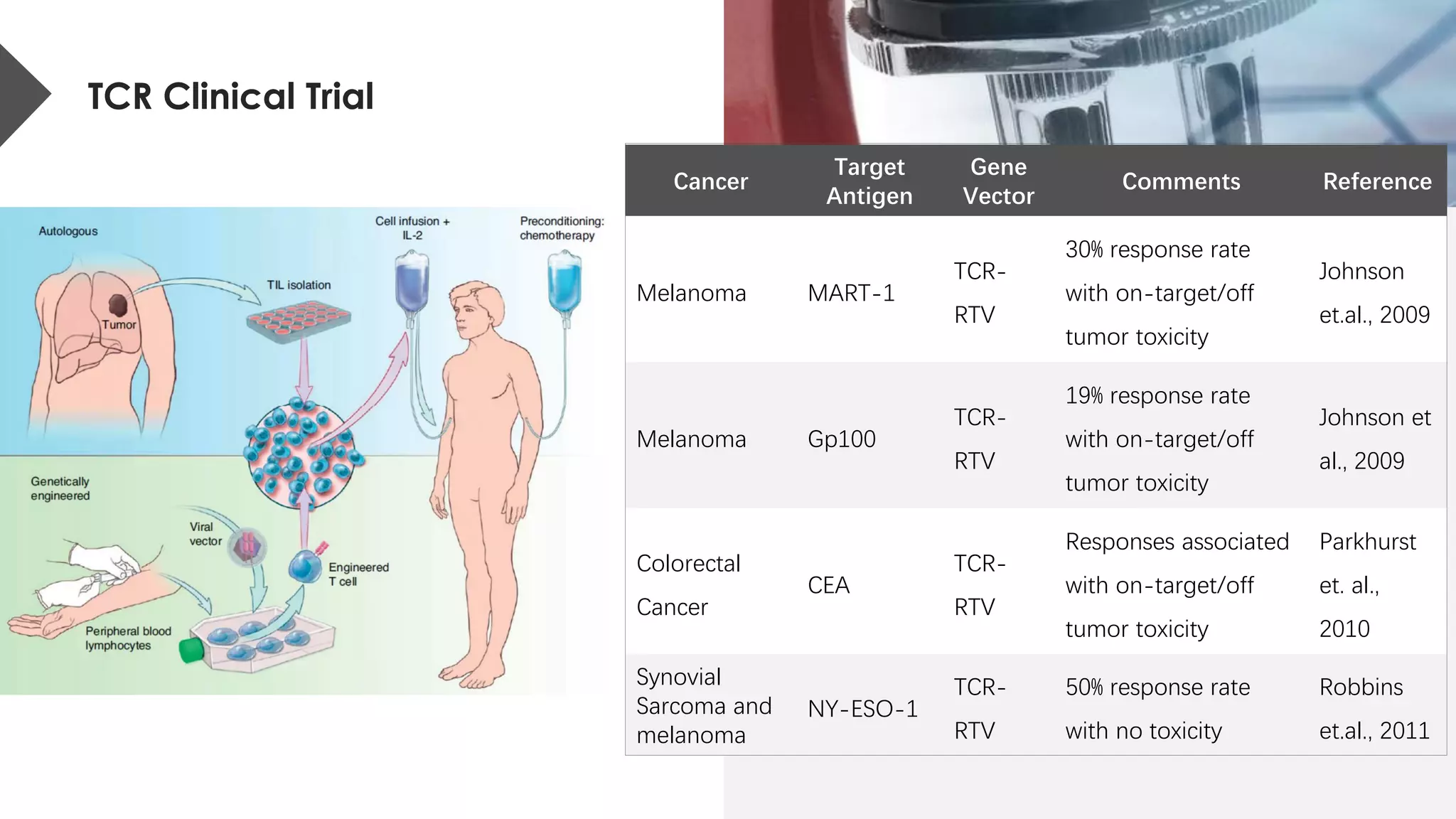
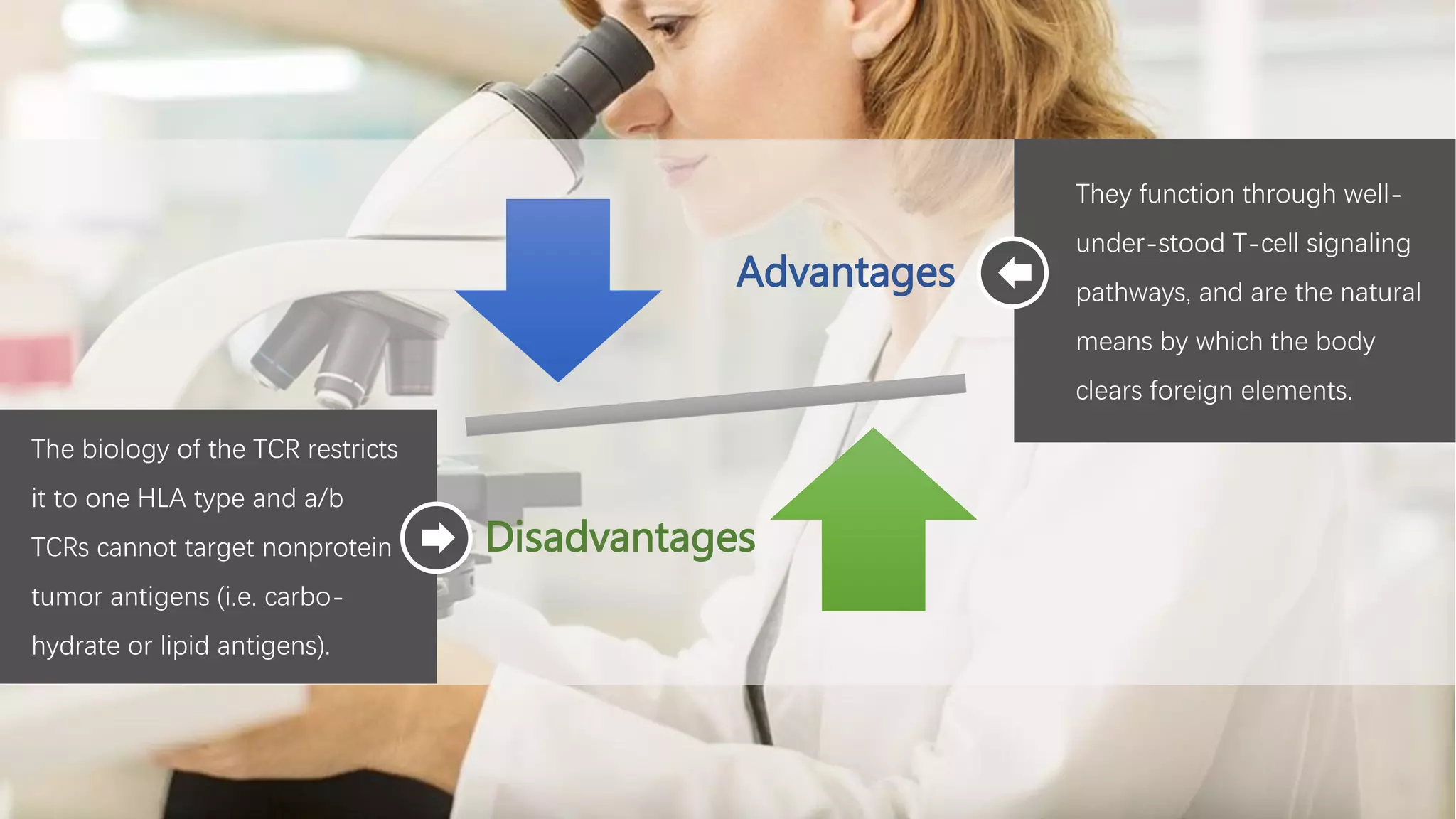
The document provides an overview of engineered T cell technology for anti-tumor therapy, highlighting T cell receptor (TCR) structure, gene transfer methods, and various types of engineered T cells such as chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T) and TCR engineered T cells (TCR-T). It discusses the steps involved in developing high-affinity TCRs, including antigen selection and performance improvements, as well as clinical applications and challenges of TCR technology. Additionally, it includes references to TCR clinical trials and their outcomes, emphasizing the advantages and limitations of TCR-based therapies.