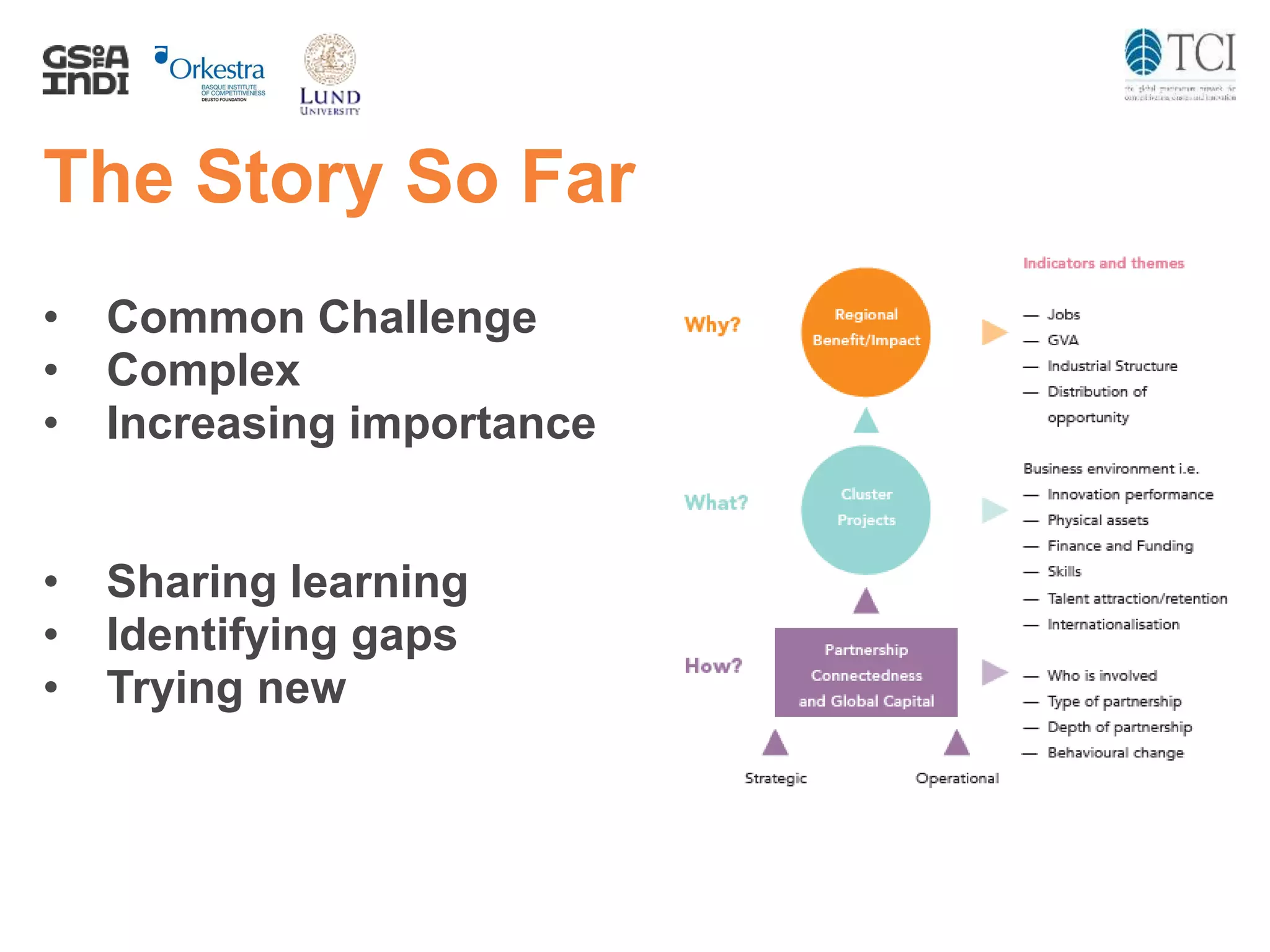
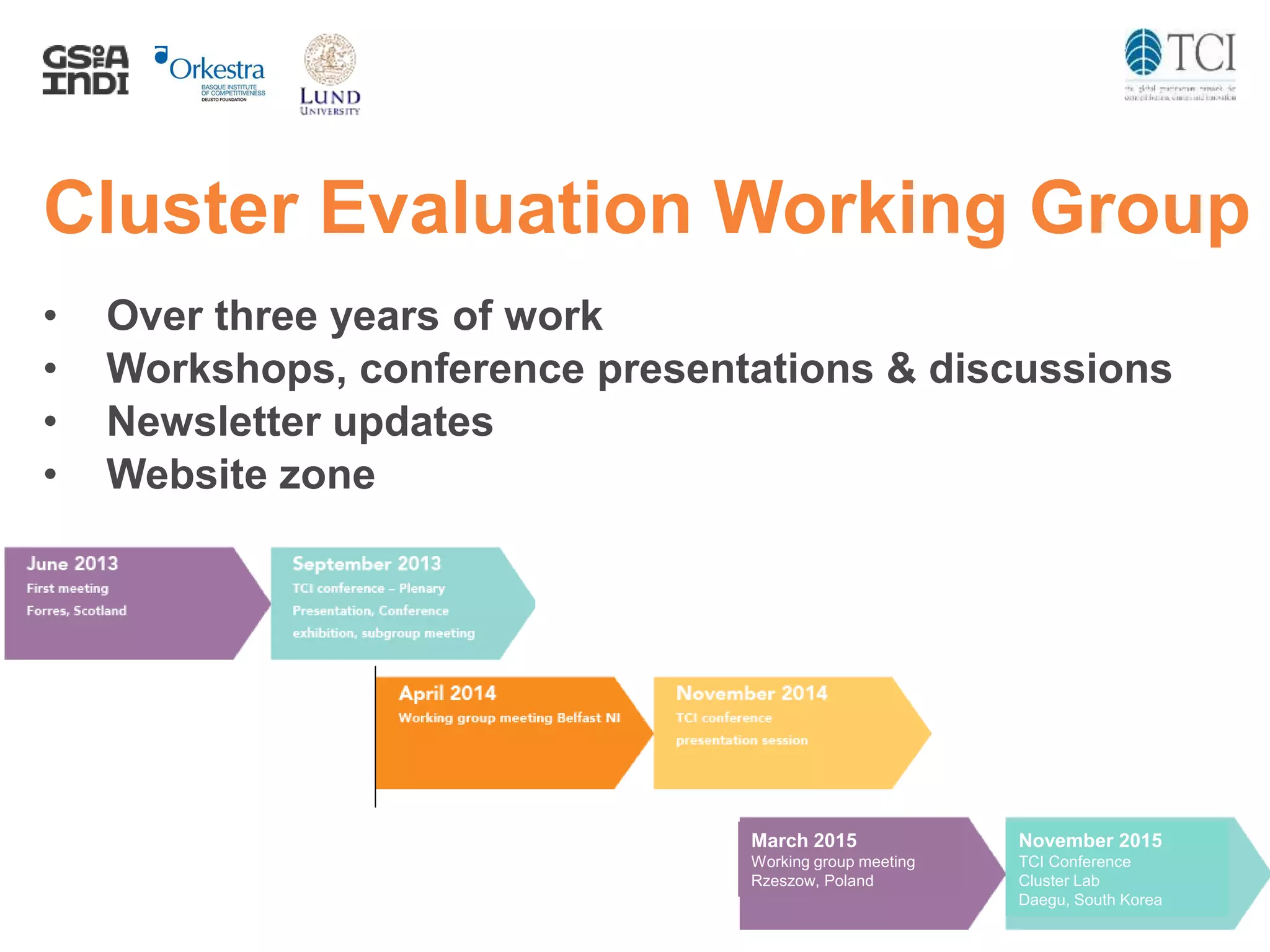
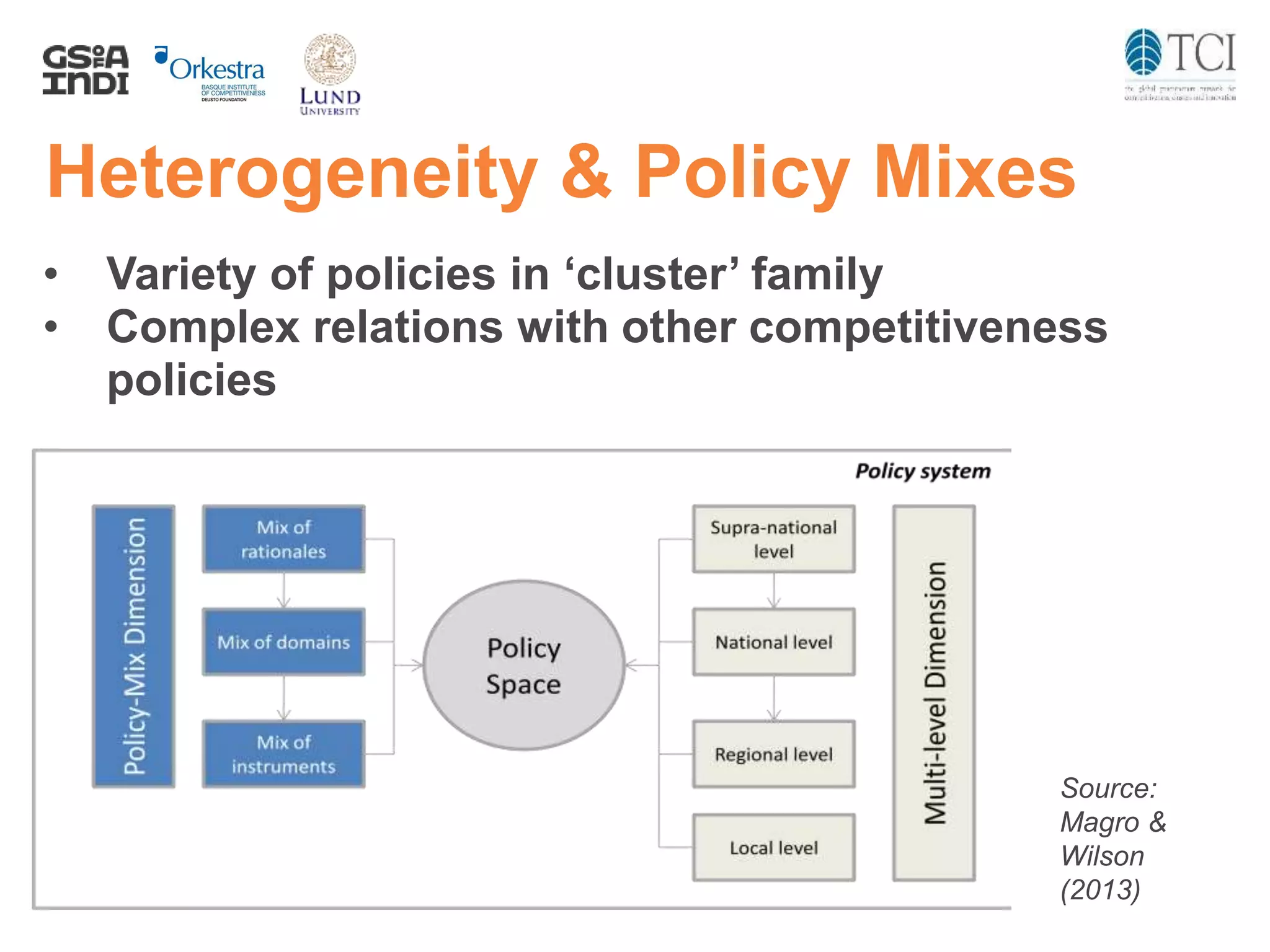
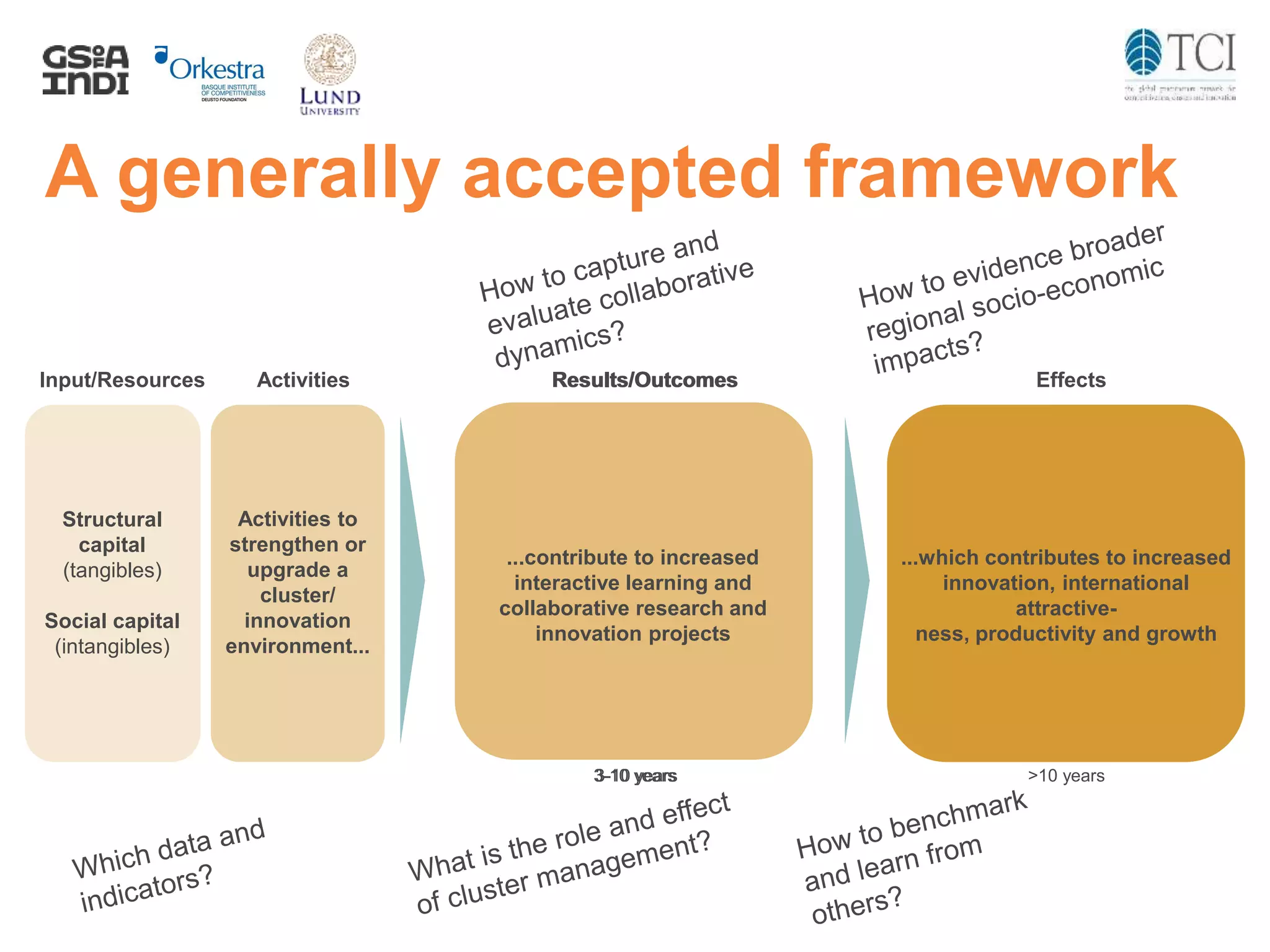
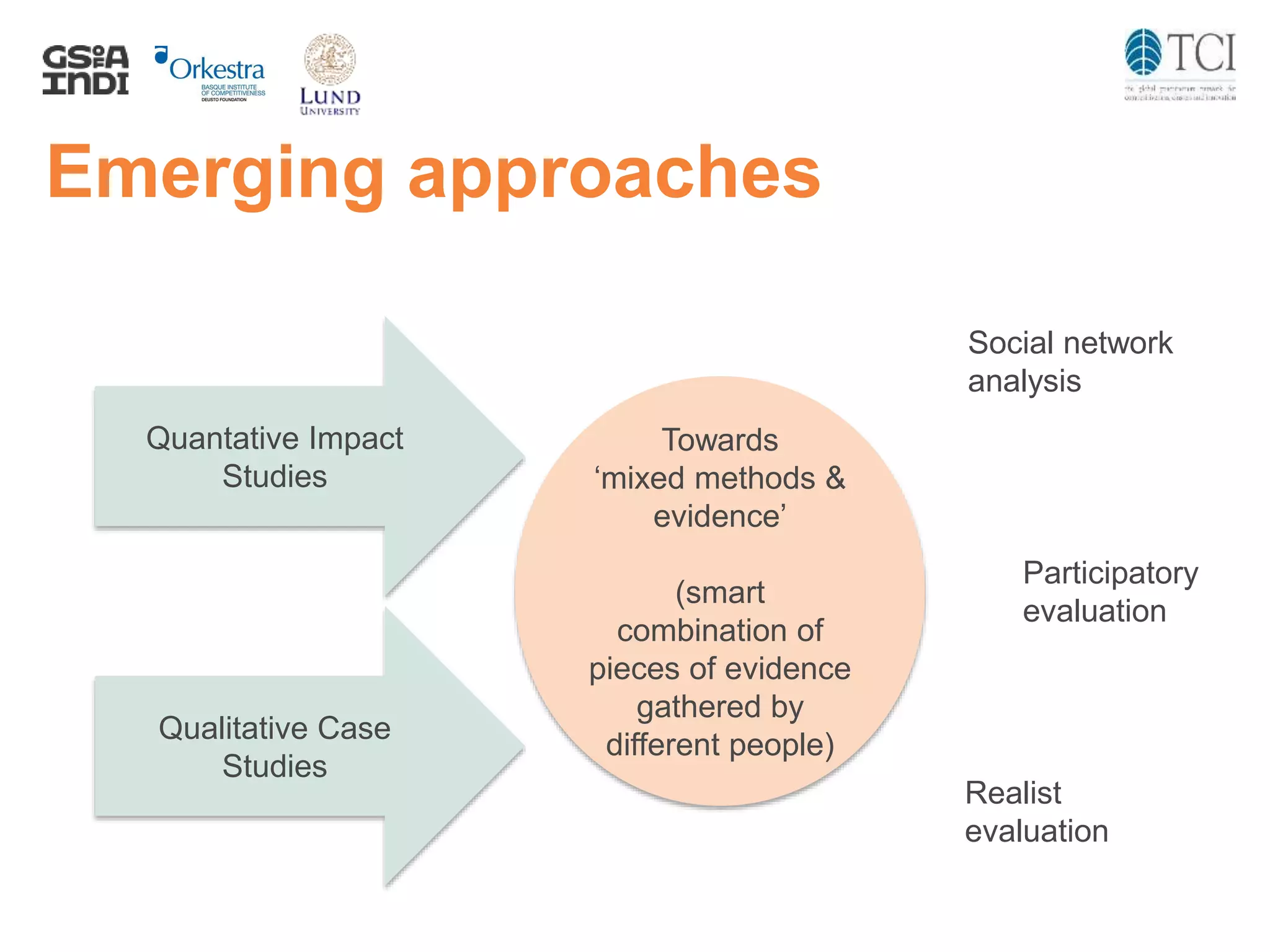
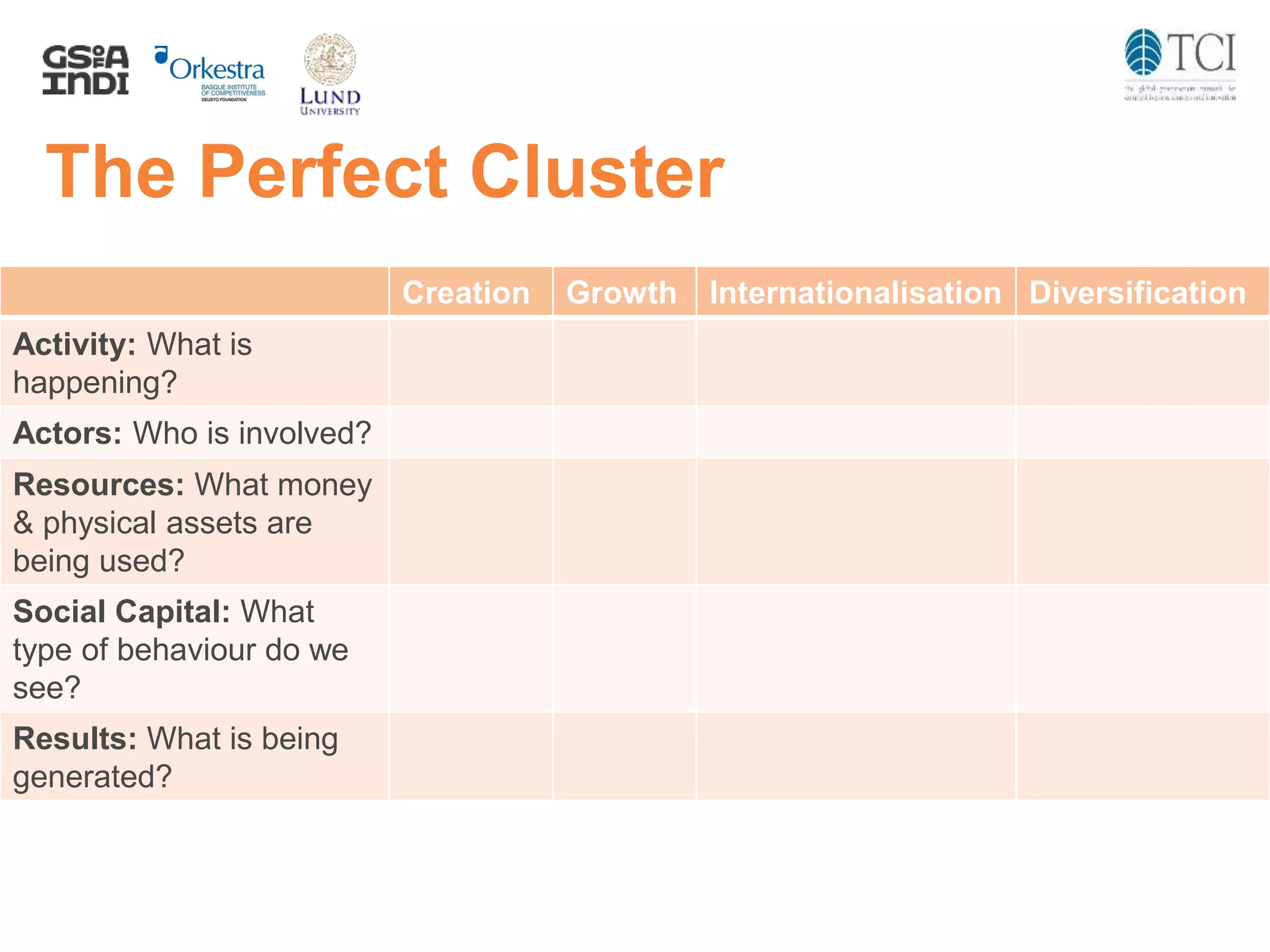
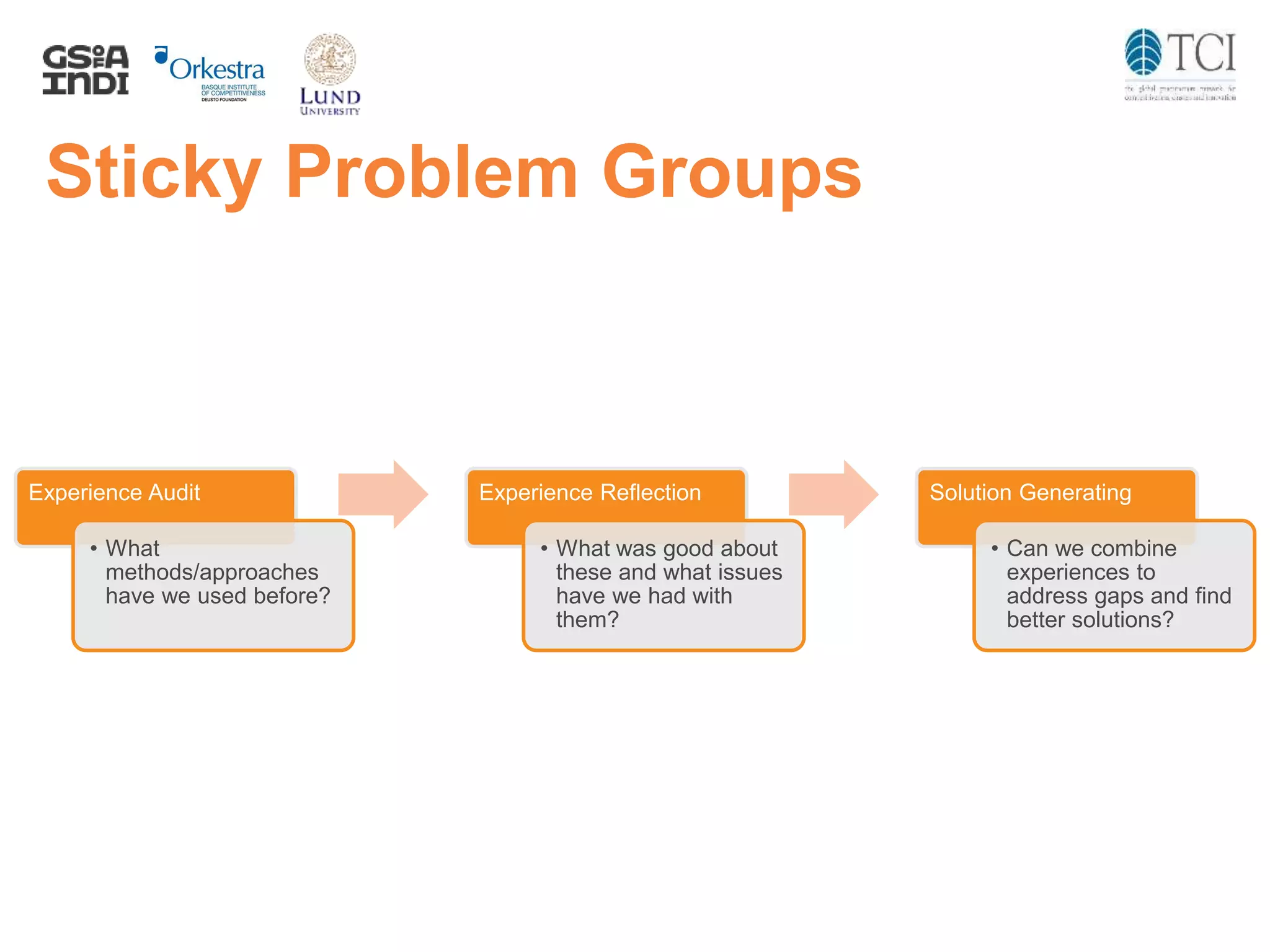
The document discusses the challenges and progress in cluster policy evaluation, highlighting the importance of collaborative learning and sharing experiences among stakeholders. It emphasizes the need for improved methodologies to capture the impact of cluster policies, addressing issues such as intangible outcomes and the complexity of policy mixes. The document aims to foster discussions on effective evaluation practices that enhance trust, social capital, and actionable insights for policymakers.