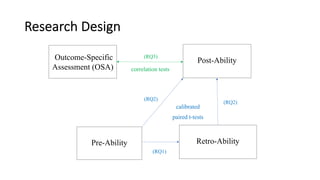
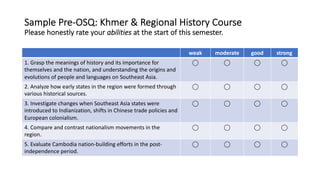
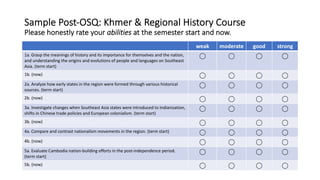
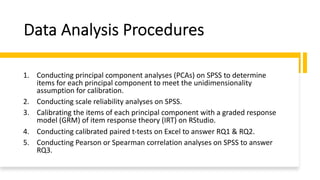
1) The document outlines a study that assessed the reliability and validity of students' self-reported learning outcomes against stated course learning outcomes.
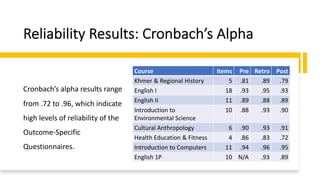
2) Preliminary results found the outcome-specific questionnaires to have high reliability. Most courses saw significant increases in student self-ratings from beginning to end.
3) Further analysis is still needed to determine if end-of-course self-ratings correlate with assessments of student task performance against learning outcomes.