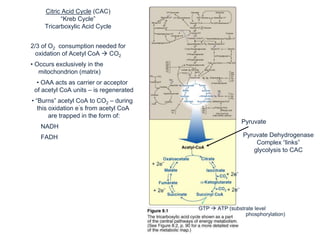
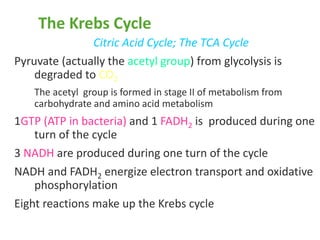
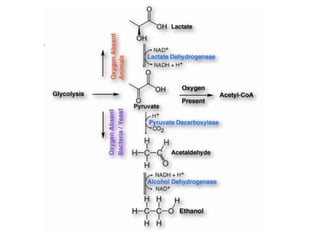
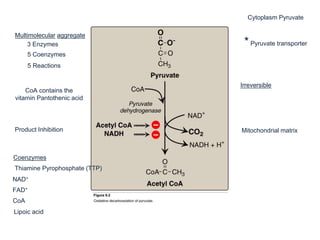
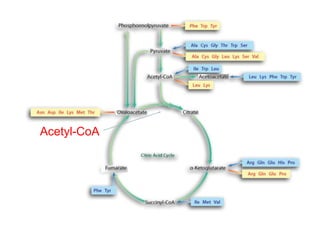
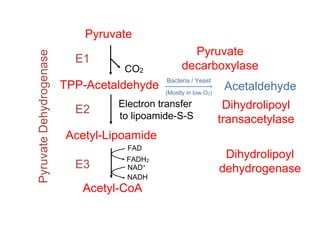
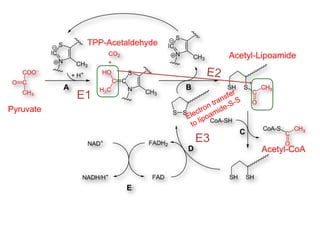
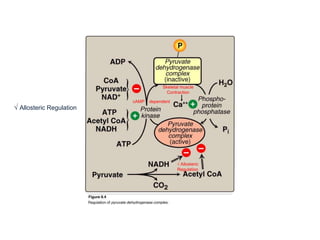
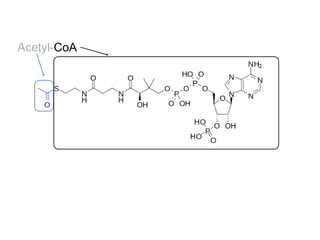
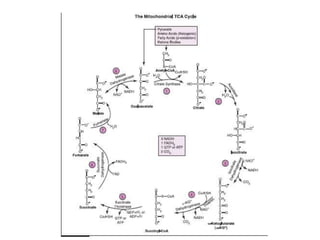
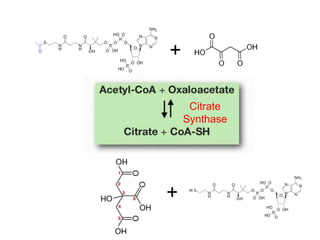
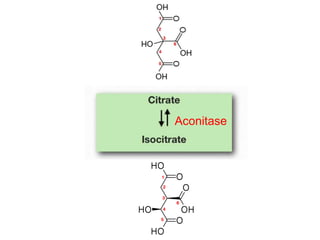
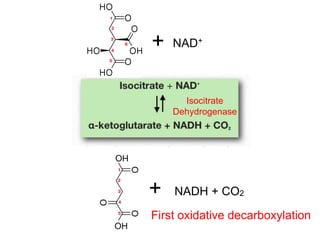
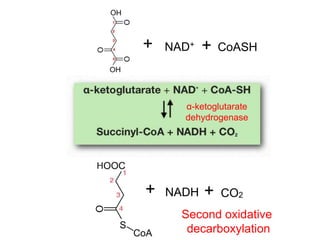
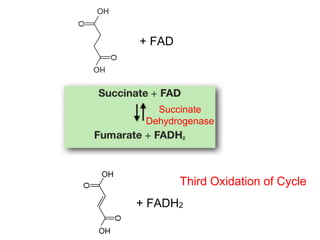
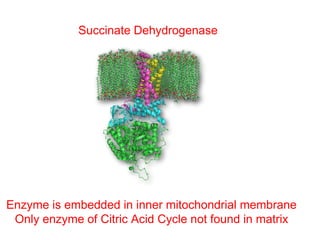
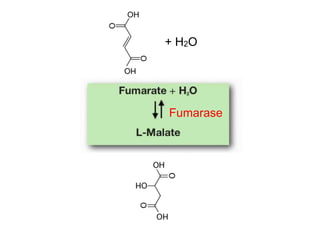
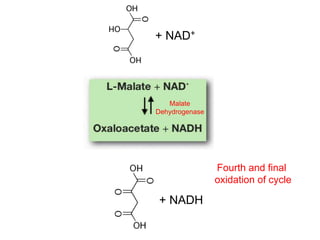
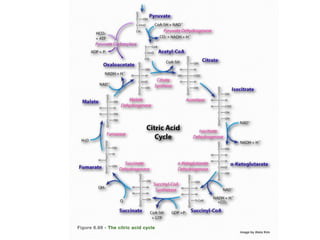
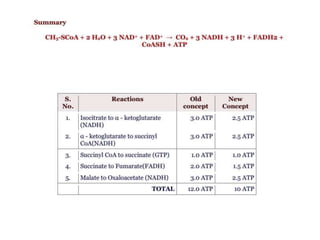
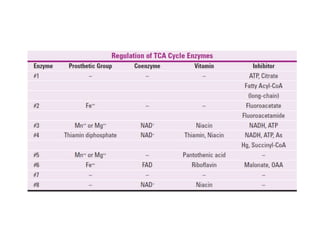
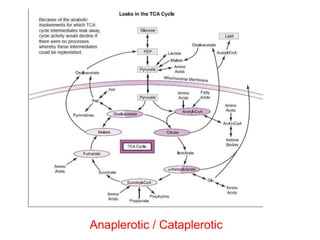
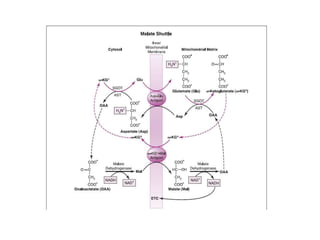
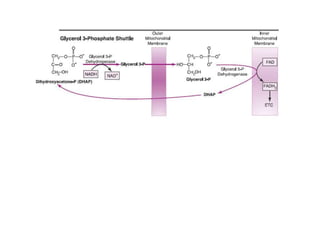
The citric acid cycle (CAC), also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The cycle consists of eight sequential reactions that generate high-energy electron carriers and carbon dioxide. Each turn of the cycle produces 3 NADH molecules, 1 FADH2, and 1 GTP that fuel oxidative phosphorylation and generate ATP. The cycle takes place exclusively in the mitochondrial matrix and is crucial for cellular respiration.