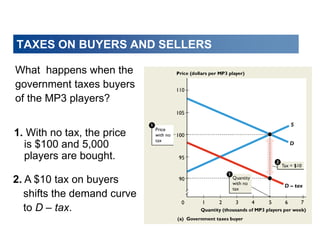
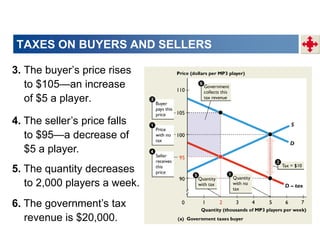
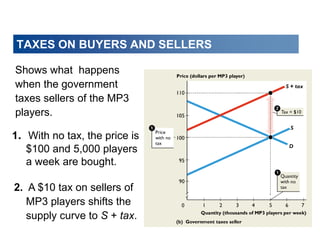
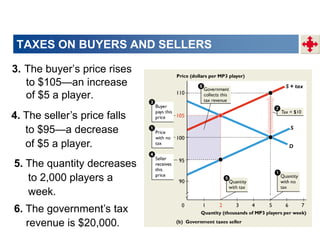
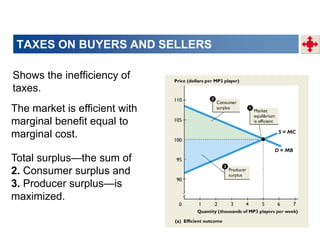
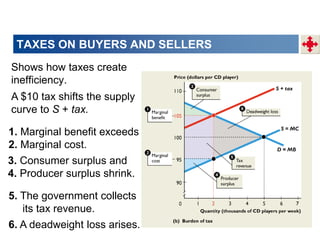
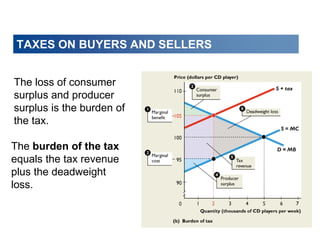
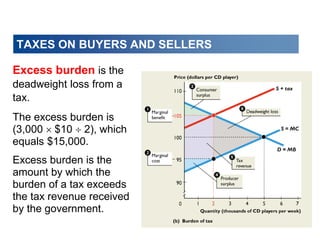
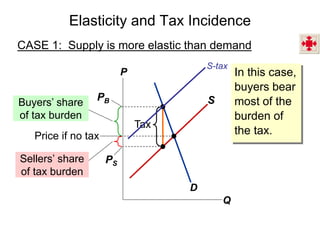
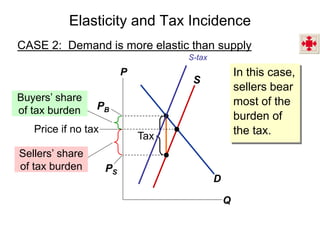
This document discusses tax incidence and how taxes create inefficiencies in markets. It contains the following key points:
1. Tax incidence refers to how the burden of a tax is divided between buyers and sellers. A tax places a wedge between the price buyers pay and sellers receive.
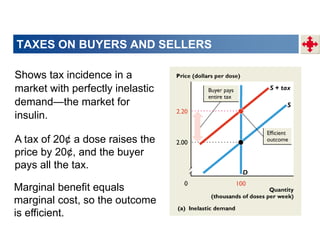
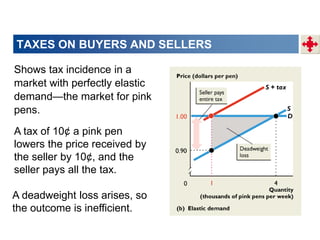
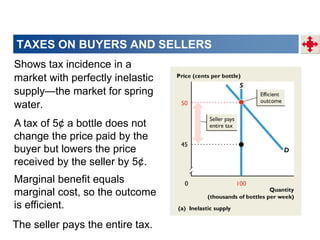
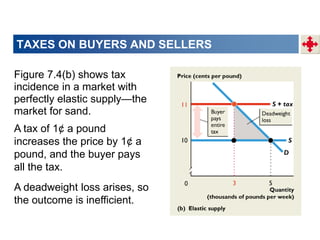
2. When demand is perfectly inelastic, buyers bear the entire burden of the tax. When supply is perfectly inelastic, sellers bear the entire burden.
3. Taxes result in deadweight losses by creating a wedge between the price buyers are willing to pay and the price sellers are willing to accept. This leads to an inefficient outcome where quantity traded is below the efficient level.