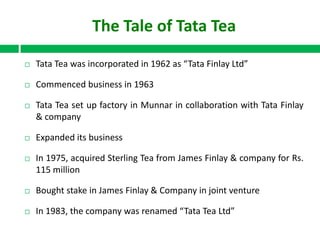
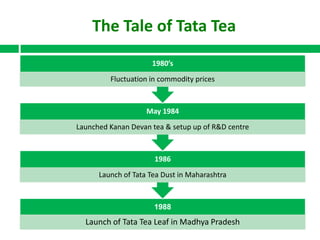
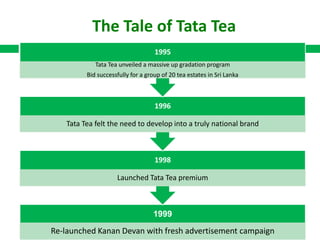
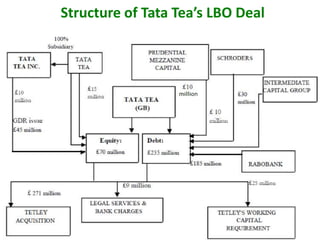
In 2000, Tata Tea made a landmark move by acquiring the UK brand Tetley for ₤271 million, marking the first leveraged buy-out (LBO) by an Indian company and positioning Tata Tea as the world's second-largest tea producer. The acquisition showcased Tata Tea's transformation and ambition on the global stage, backed by a strategic financial structure that protected its balance sheet. The document details Tata Tea's evolution and prior successes leading up to the LBO, emphasizing the significance of this deal in Indian corporate history.