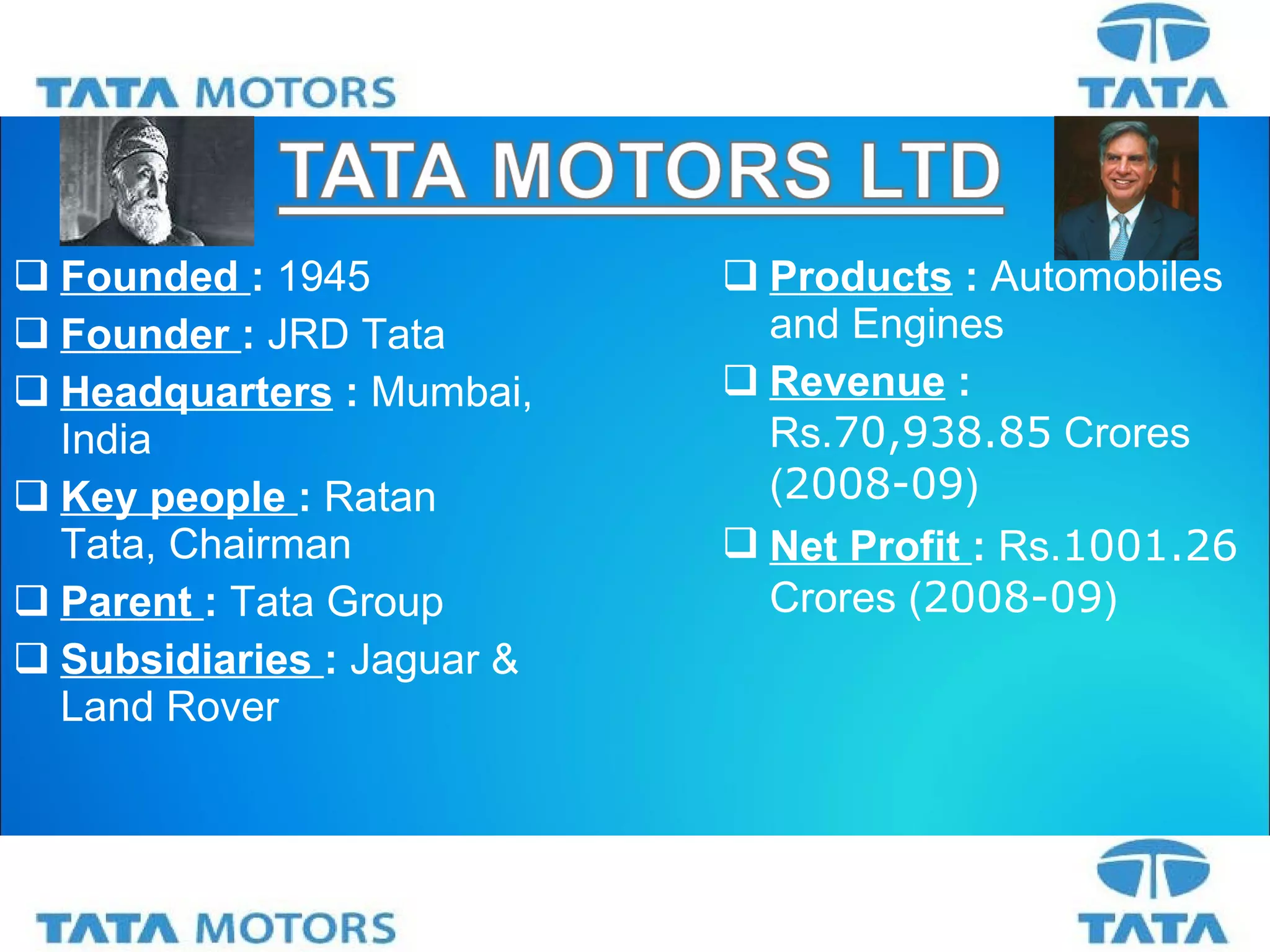
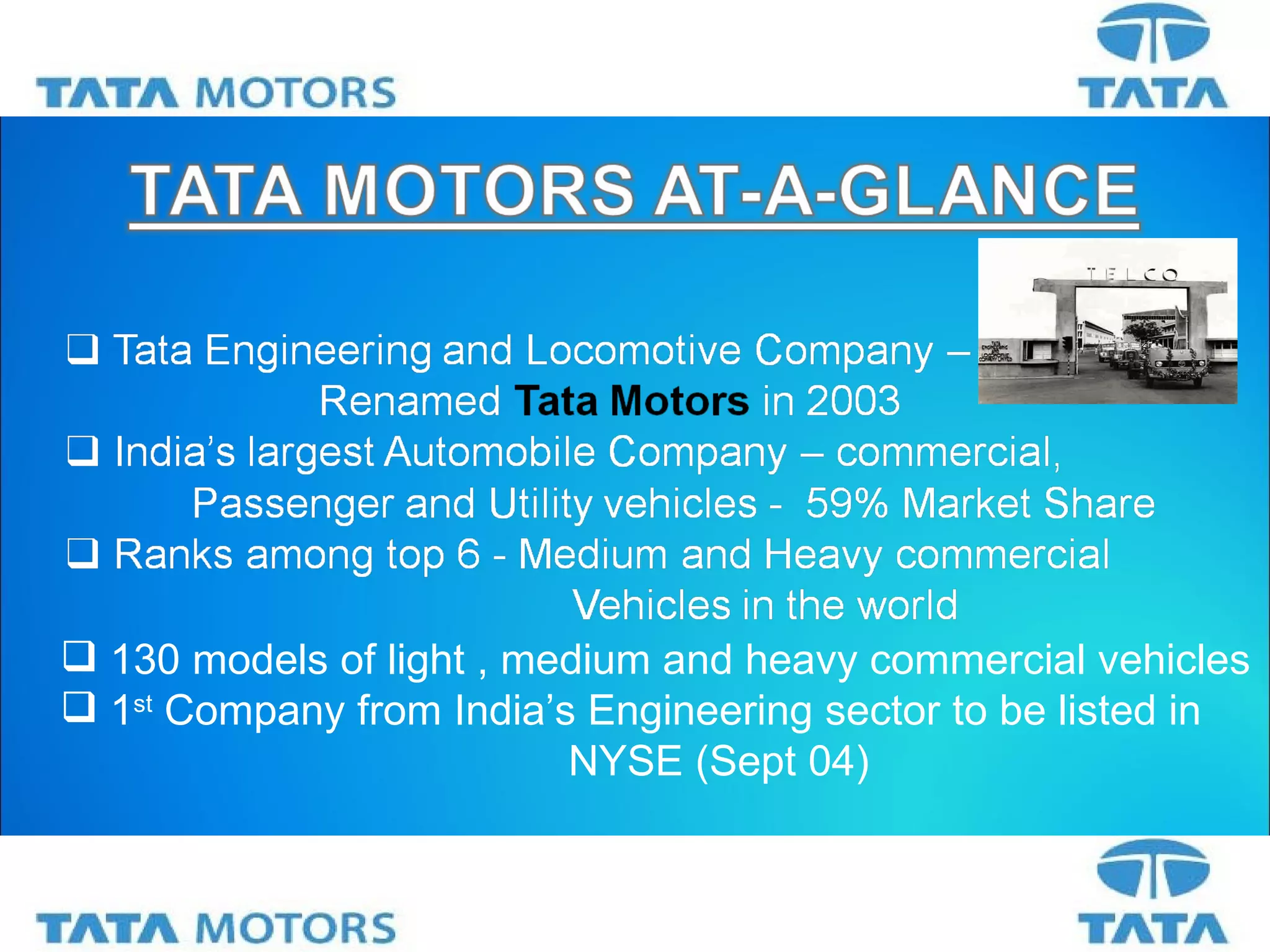
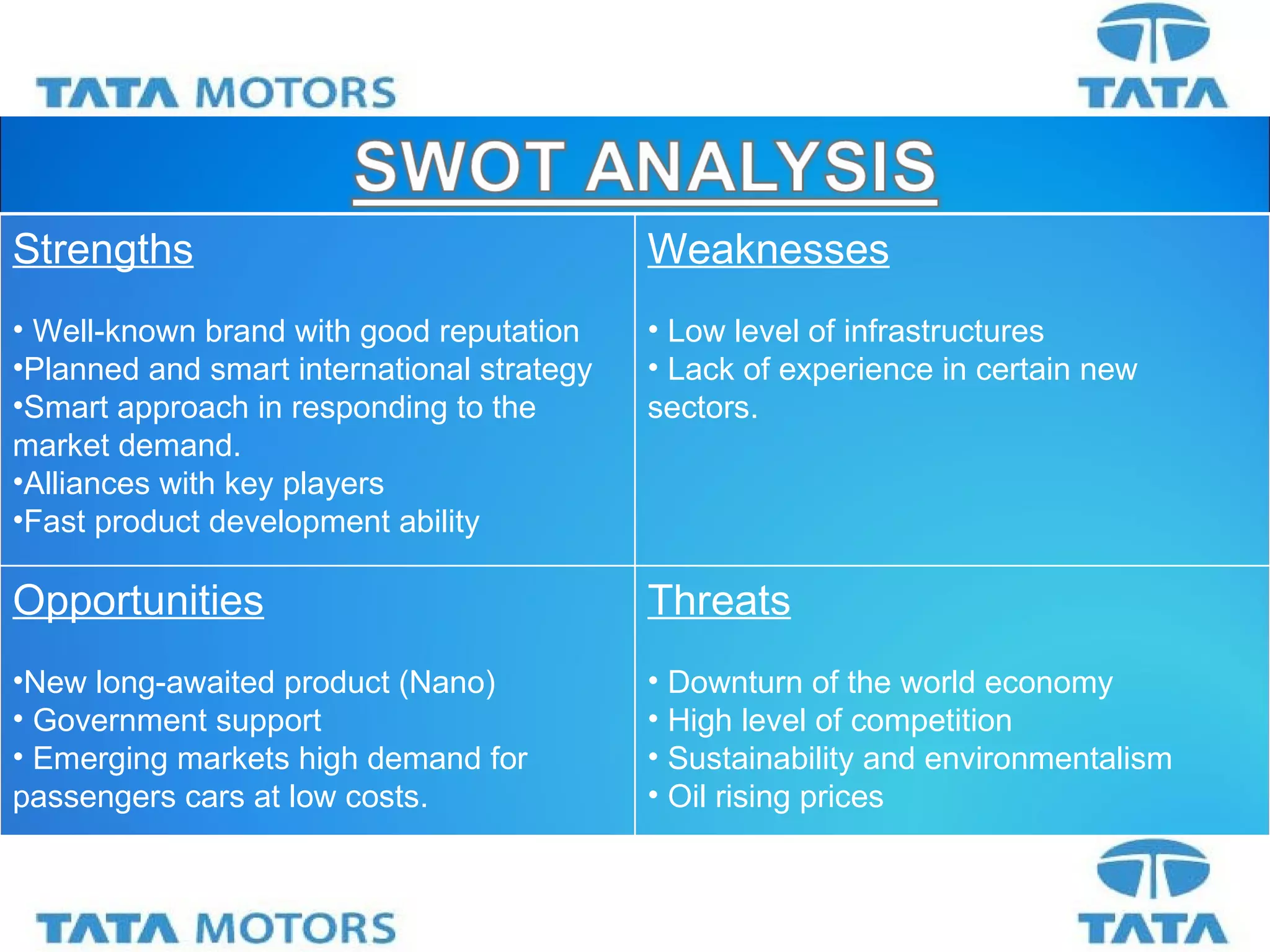
Tata Motors is an Indian multinational automotive manufacturing company founded in 1945 and headquartered in Mumbai, India. It has over 1400 engineers and scientists working across 6 R&D units in India, South Korea, Spain, and the UK. Some of Tata Motors' key accomplishments include developing India's first indigenous passenger car called the Tata Indica in 1998, and acquiring the British brands Jaguar and Land Rover from Ford Motors as part of its international expansion strategy. Looking ahead, Tata Motors aims to consolidate its position in India by capitalizing on opportunities from growing mobility needs and infrastructure development, and seeks growth from new products and emerging markets.