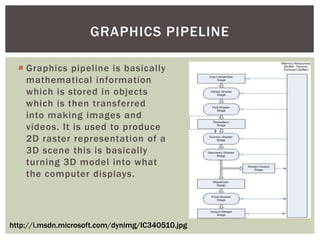
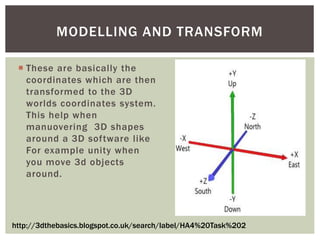
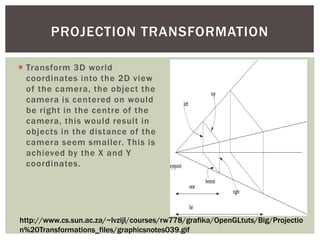
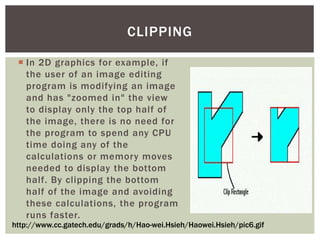
The document discusses the key concepts and stages involved in displaying 3D polygon animations, including application programming interfaces (APIs) like Direct3D and OpenGL that help programmers develop 3D programs. It then covers the graphics pipeline which involves transforming 3D models into 2D images through steps like modeling, camera transformations, lighting, projection, clipping, rasterization, texturing and fragment shading before final display.