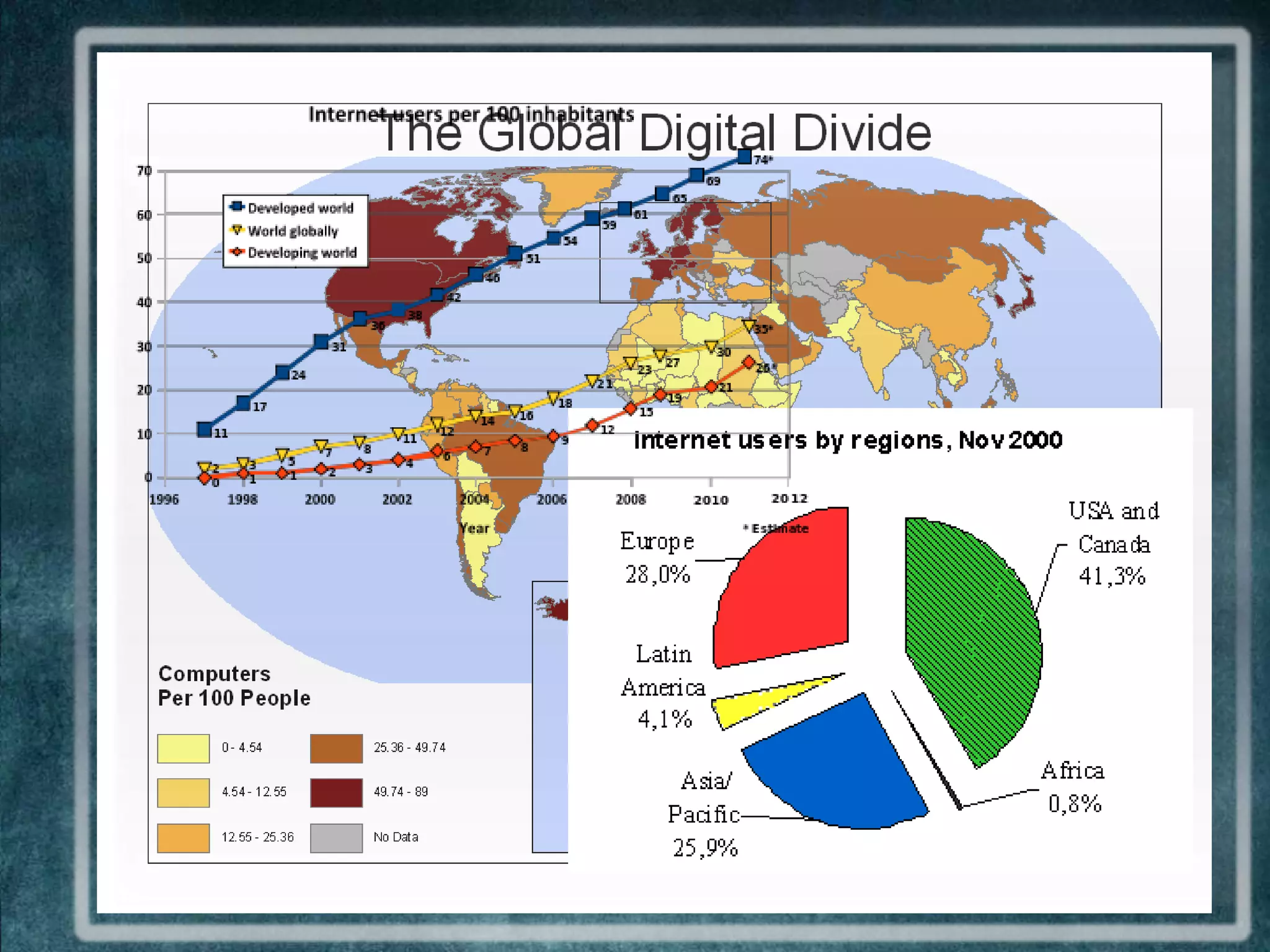
This presentation discusses the integration of educational technology in developing countries. It explores whether technology widens or narrows socioeconomic gaps, and if it is a tool of de-colonization or re-colonization. A brief history shows how educational technology has evolved from top-down radio/TV programs to bottom-up tools like audio/video tapes to today's interactive internet and mobile technologies. However, developing nations still face challenges like limited resources, infrastructure, and local content that contribute to a "digital divide". The One Laptop Per Child project and potential of m-learning are also examined.