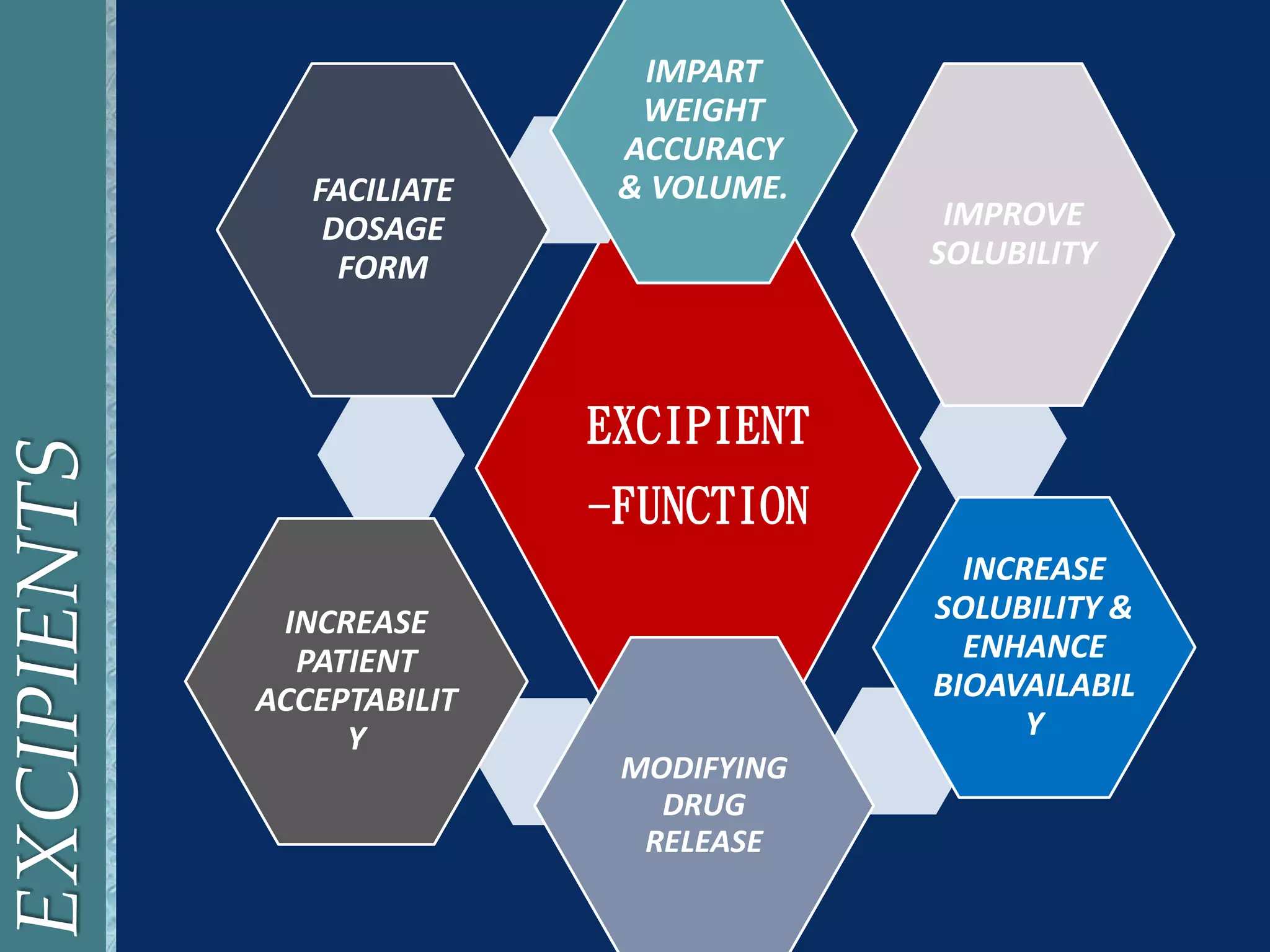
The document provides an overview of tablets as a solid dosage form in pharmacy, detailing their definition, types, excipients, and ingredients. It categorizes tablets based on their administration routes and outlines the advantages and disadvantages of using tablets as a pharmaceutical form. The discussion includes the role of various excipients in improving tablet characteristics and overall drug delivery.