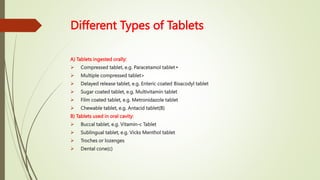
The document provides an overview of tablet formulations used in industrial pharmacy, defining tablets as compressed solid dosage forms containing active substances and excipients. It categorizes various types of tablets, including those ingested orally, used in the oral cavity, and administered via other routes, and explains the role of different excipients such as diluents, binders, disintegrants, lubricants, coloring agents, flavoring agents, and sweetening agents in tablet manufacturing. Key characteristics and examples of these excipients are discussed, emphasizing their importance in the effectiveness and stability of the final product.