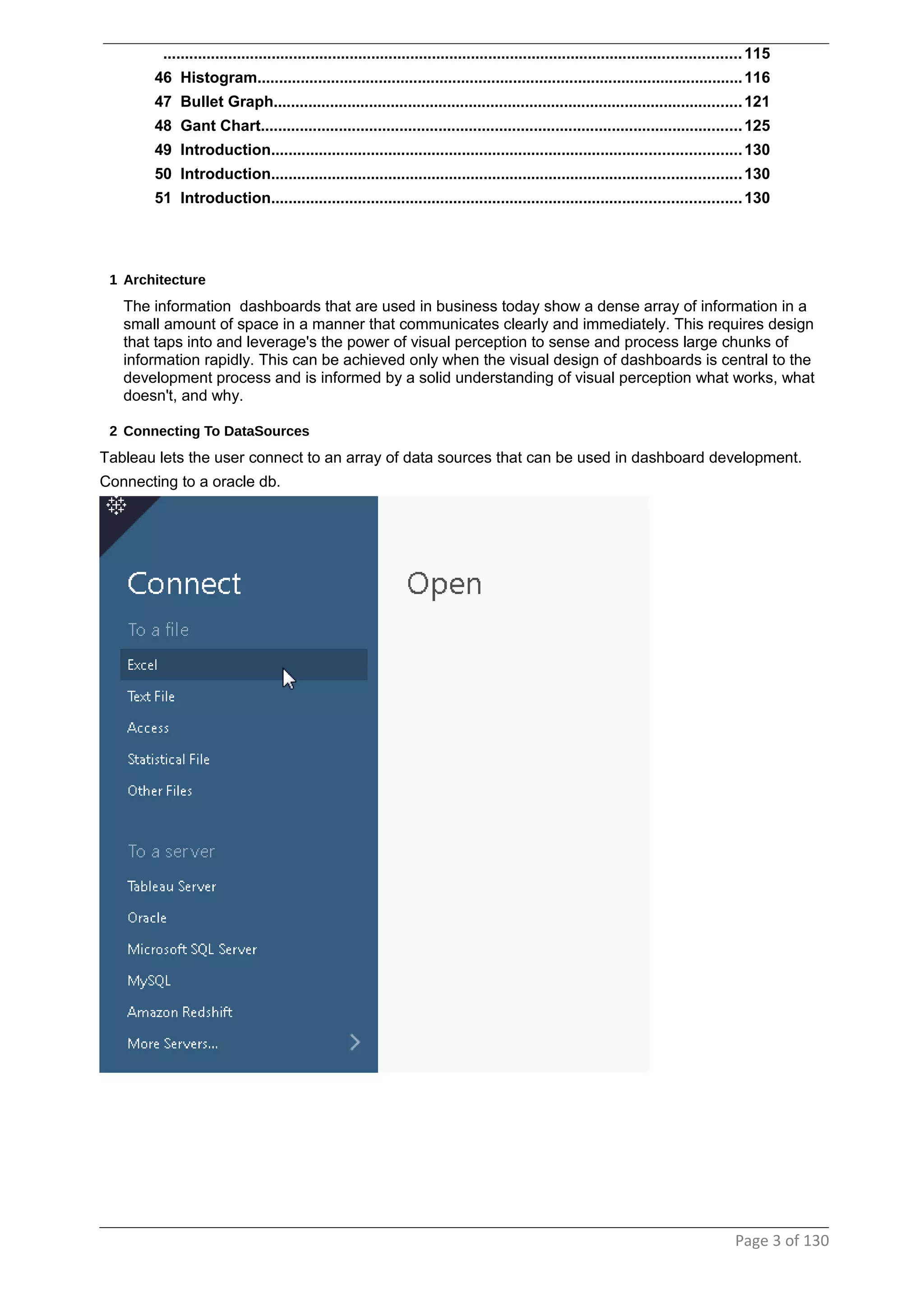
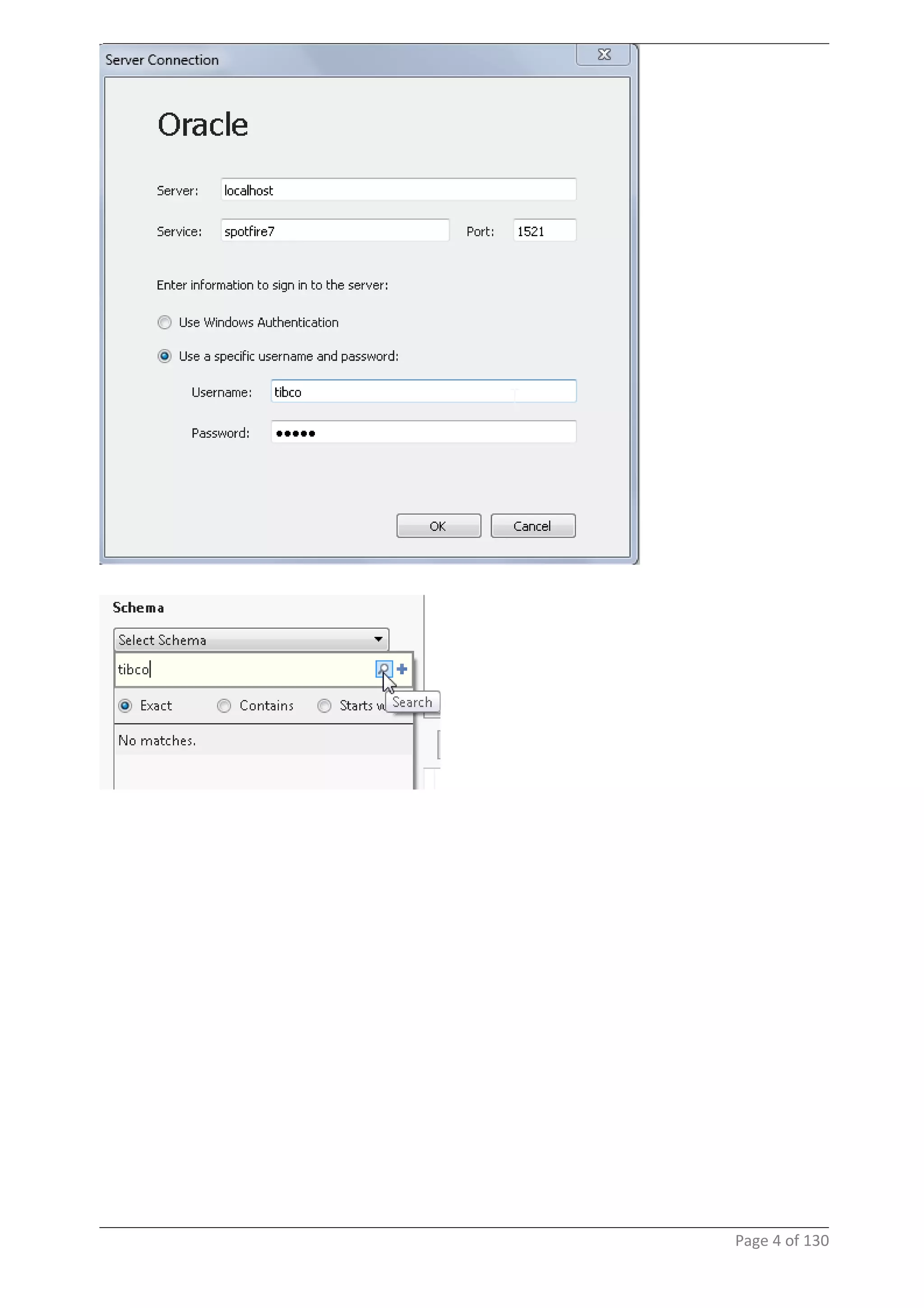
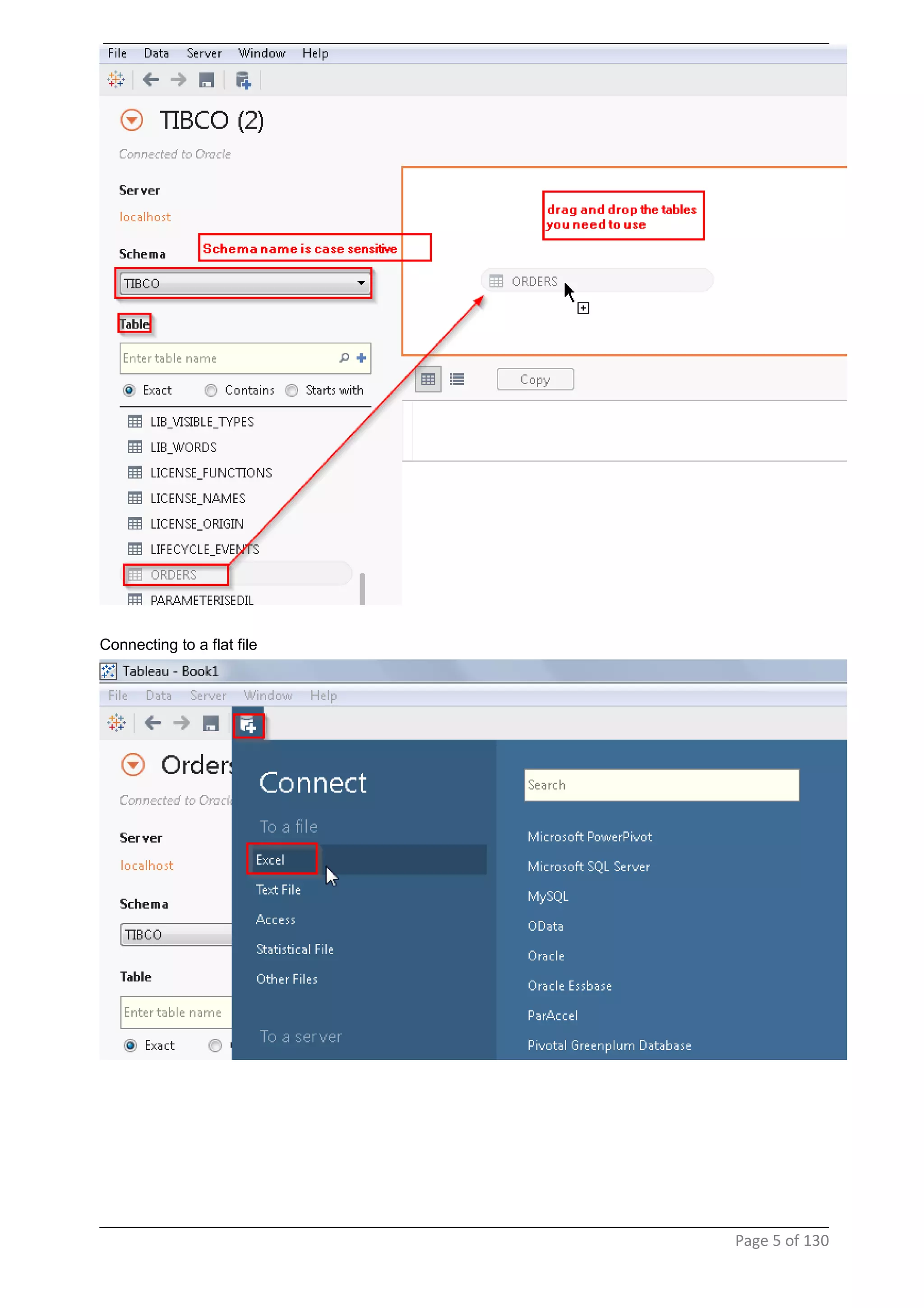
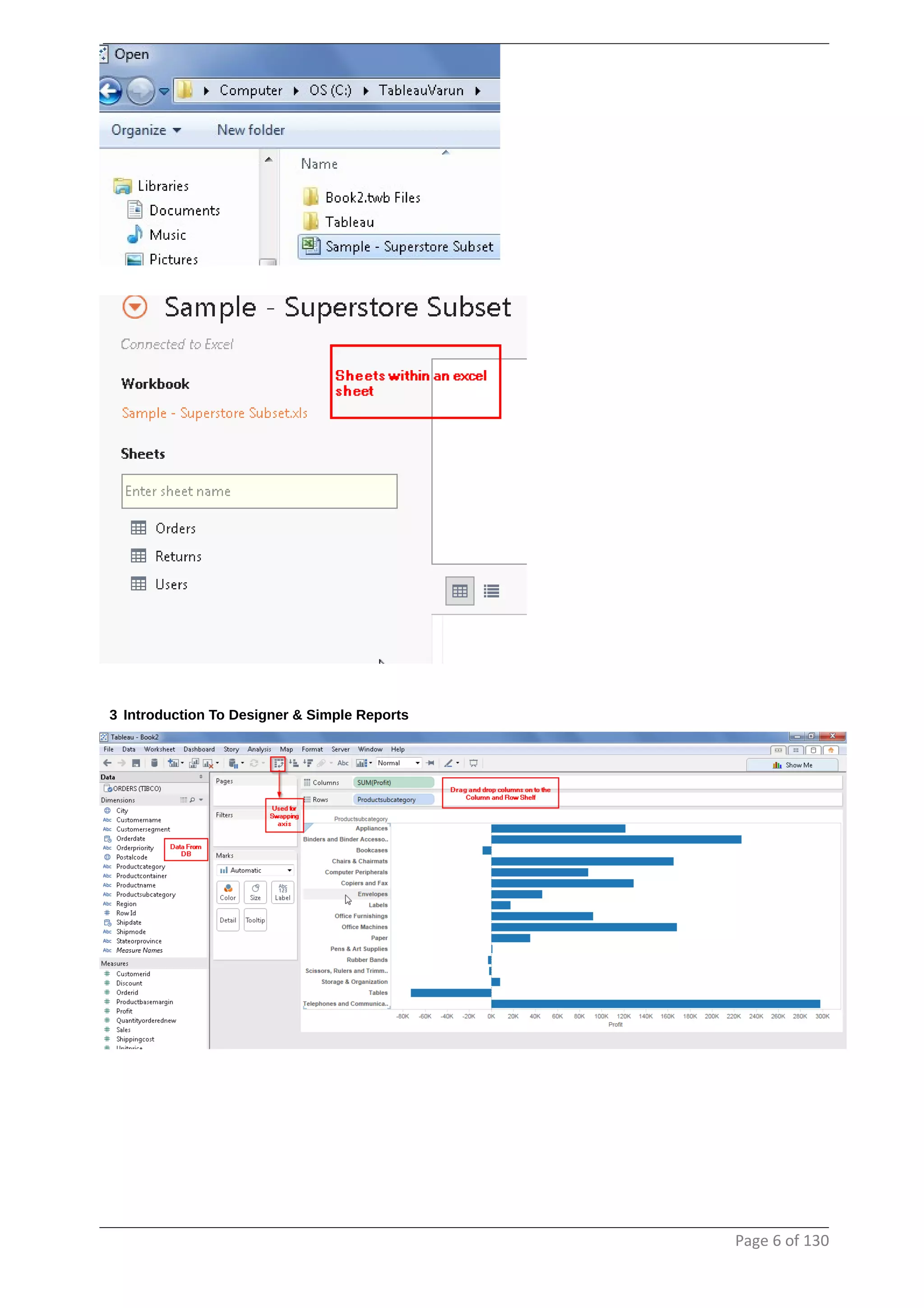
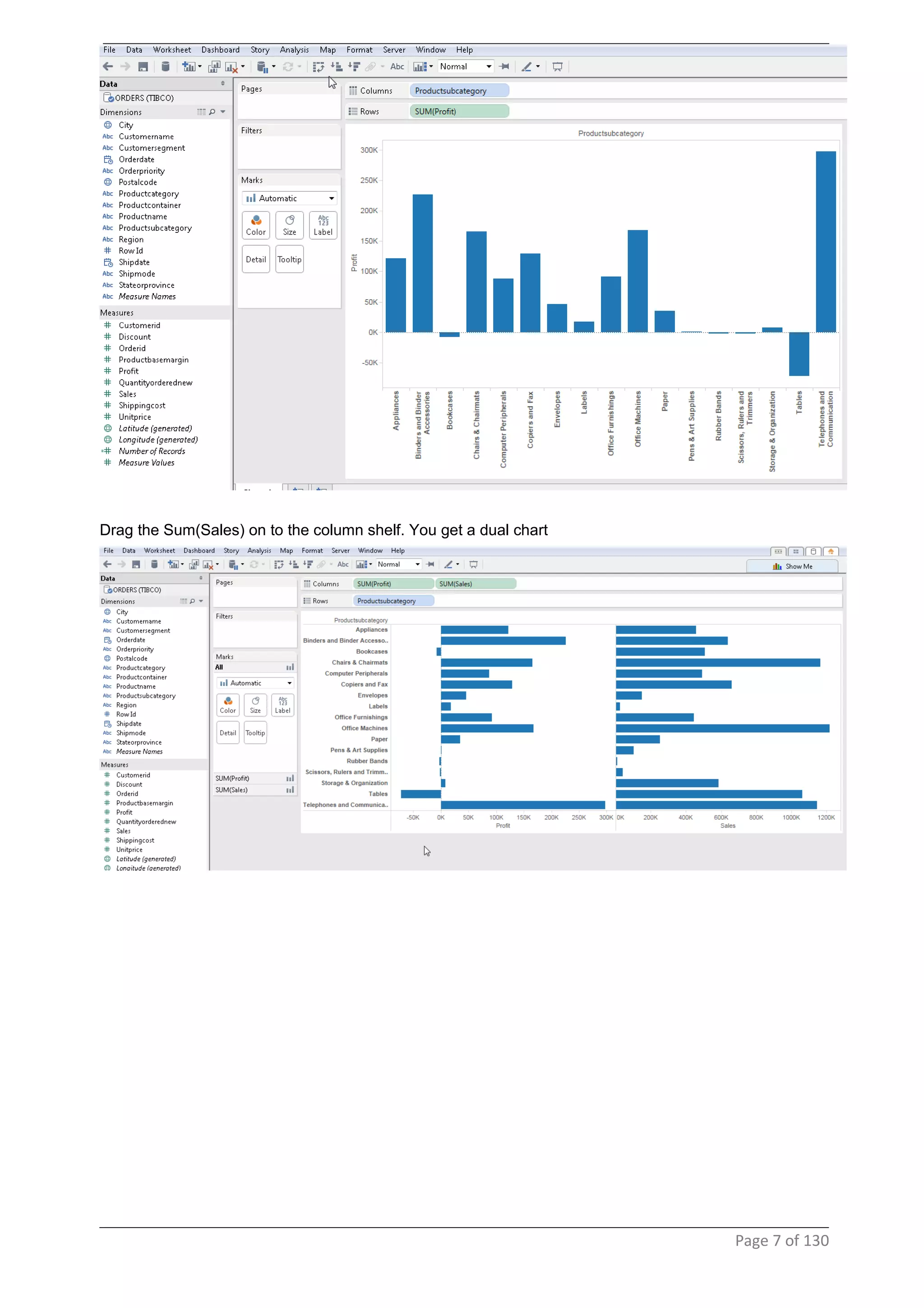
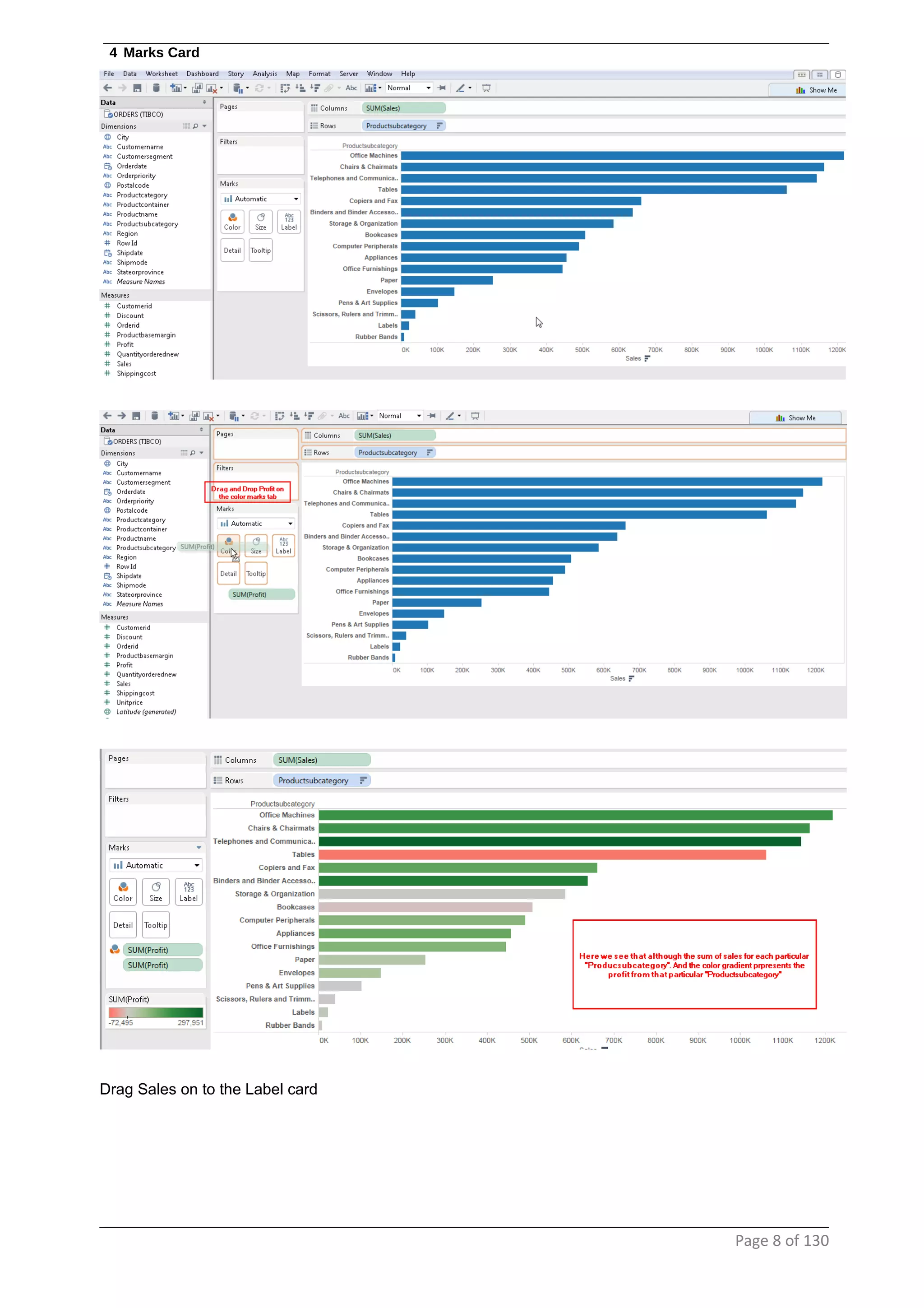
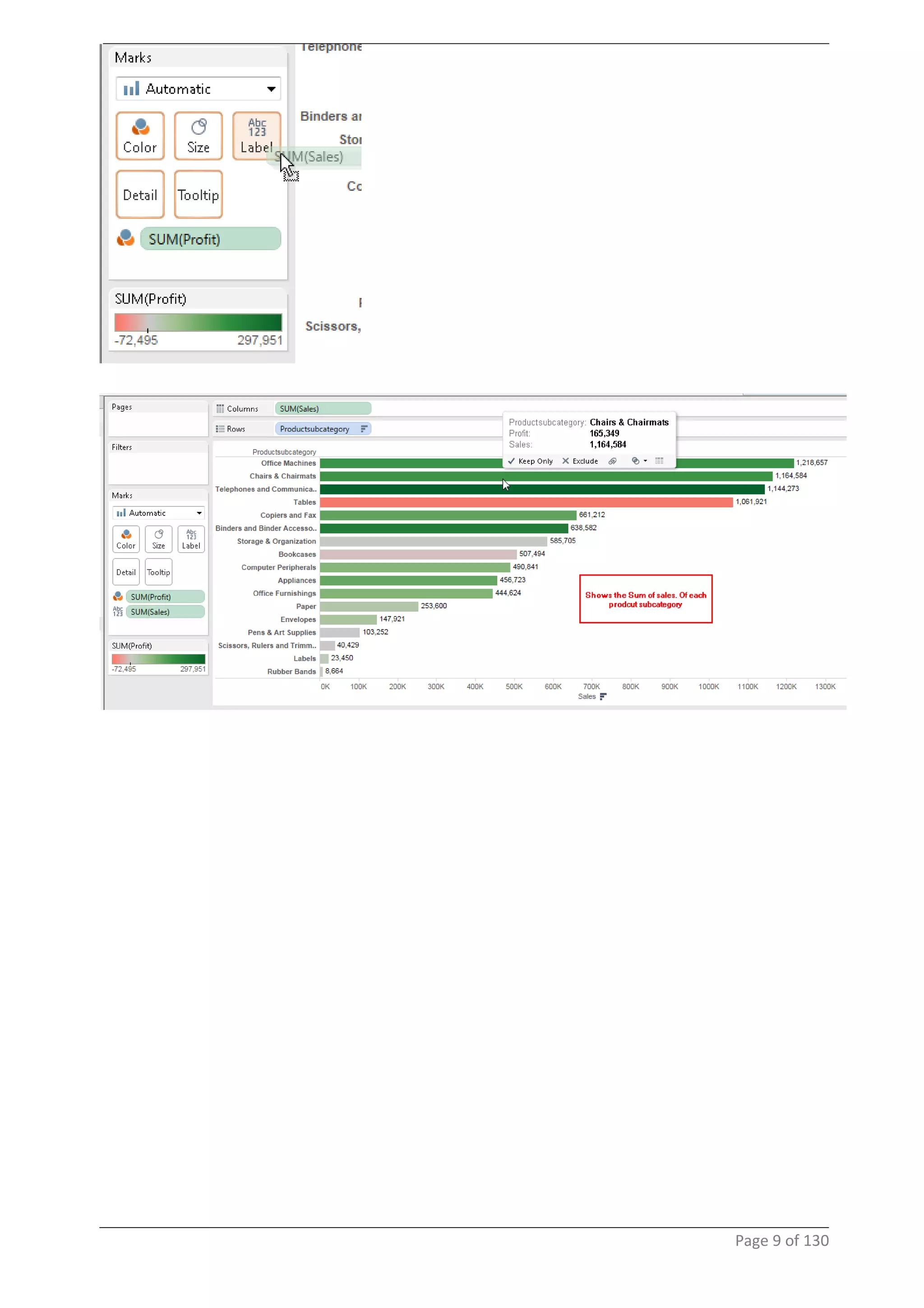
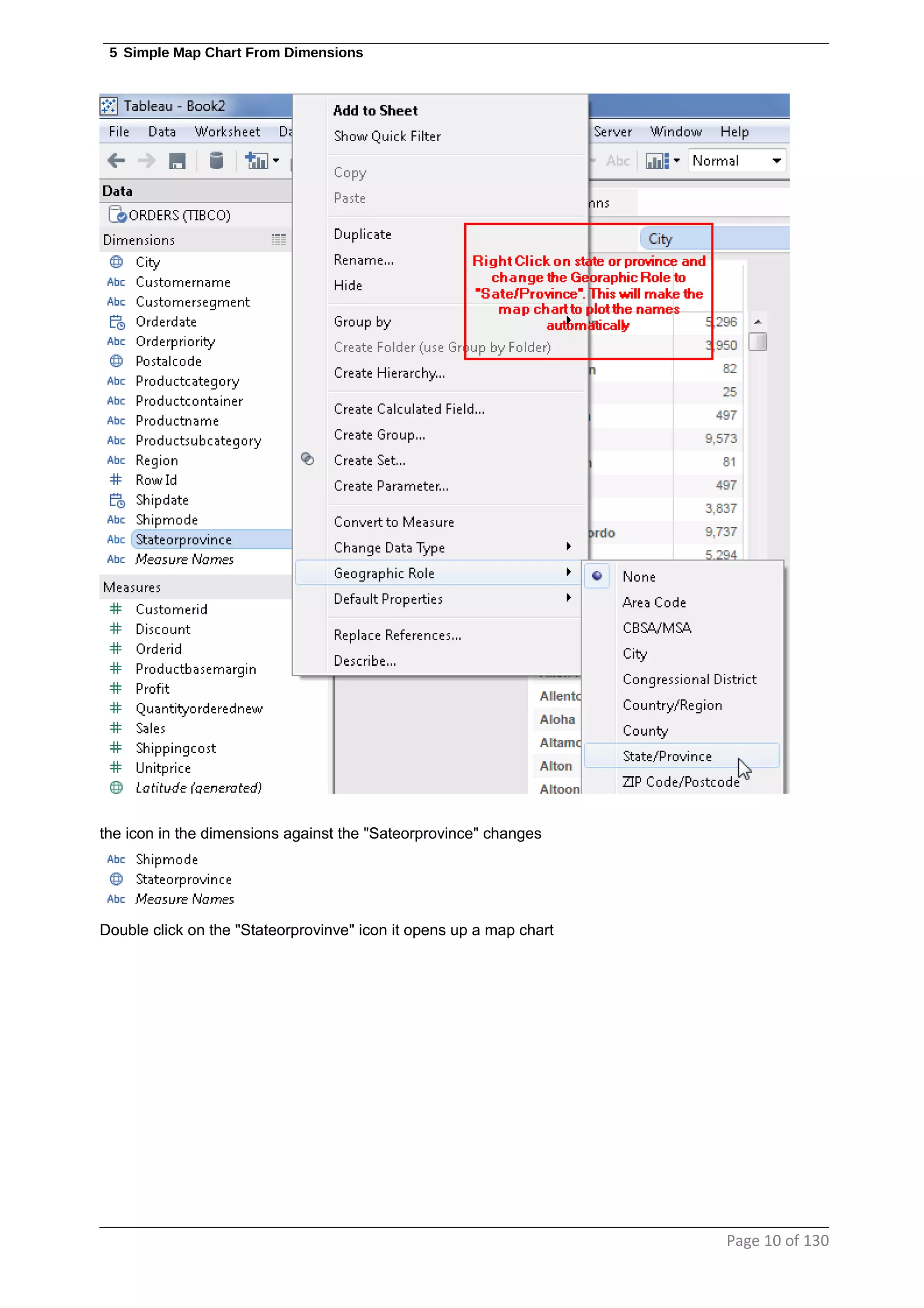
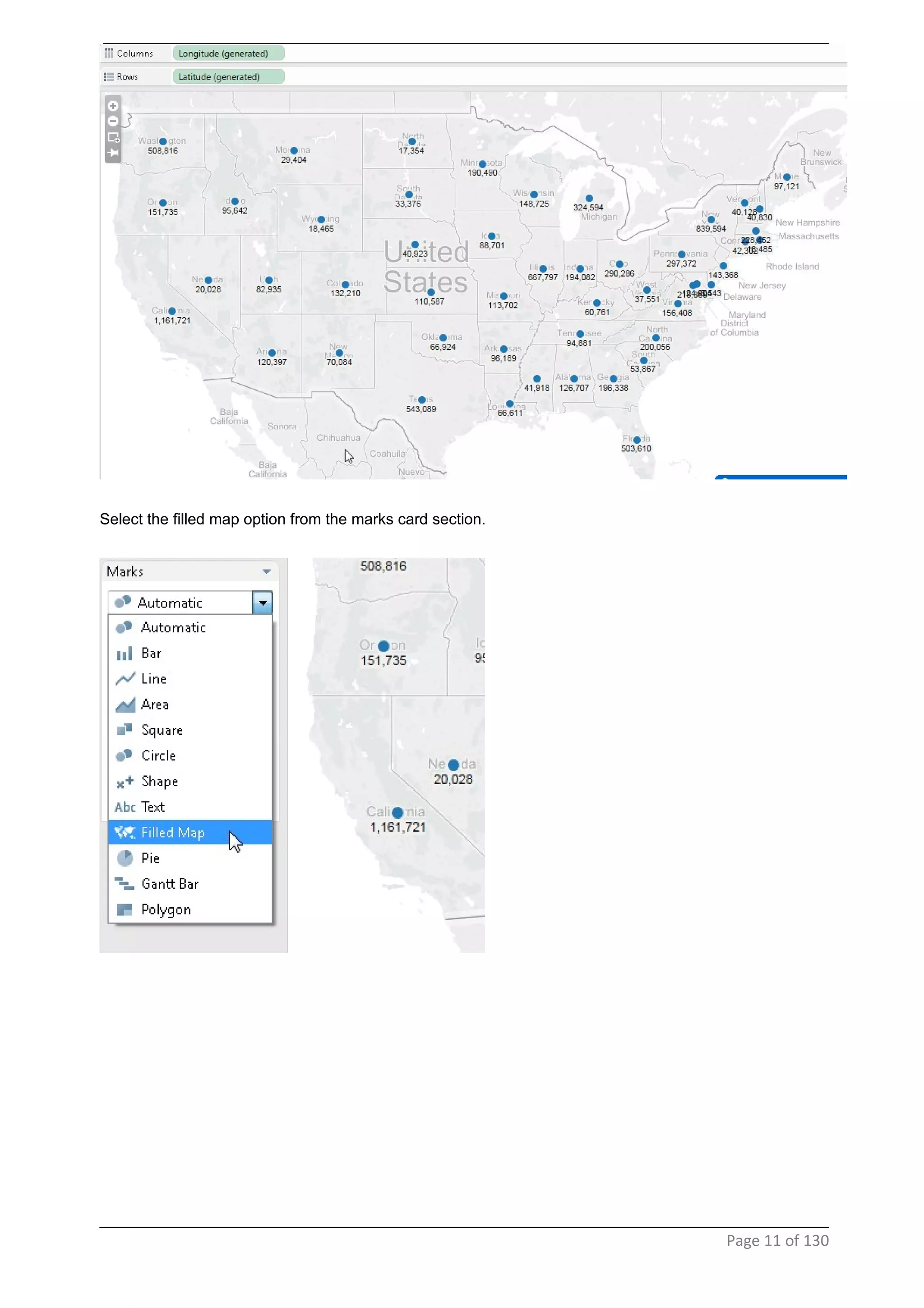
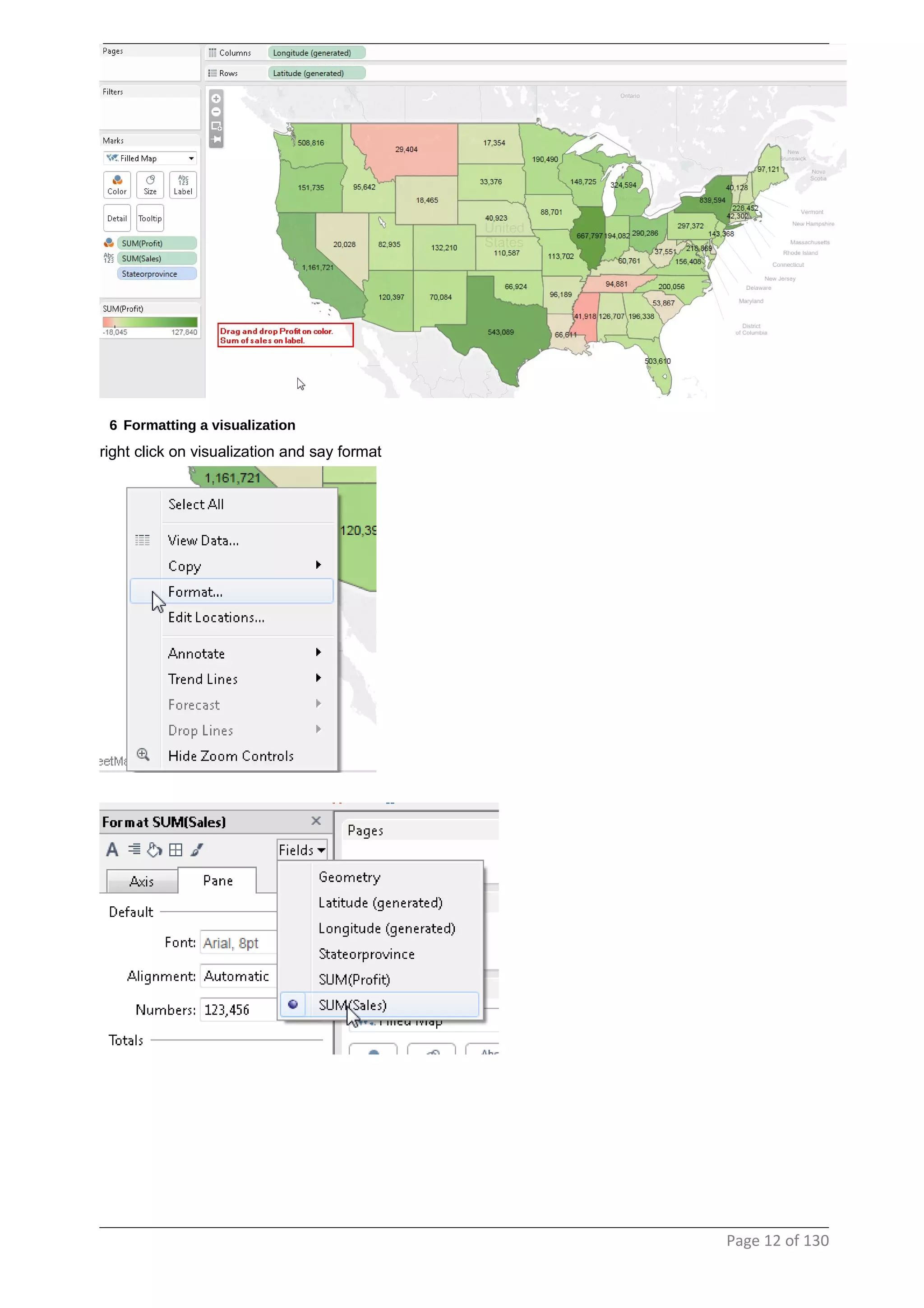
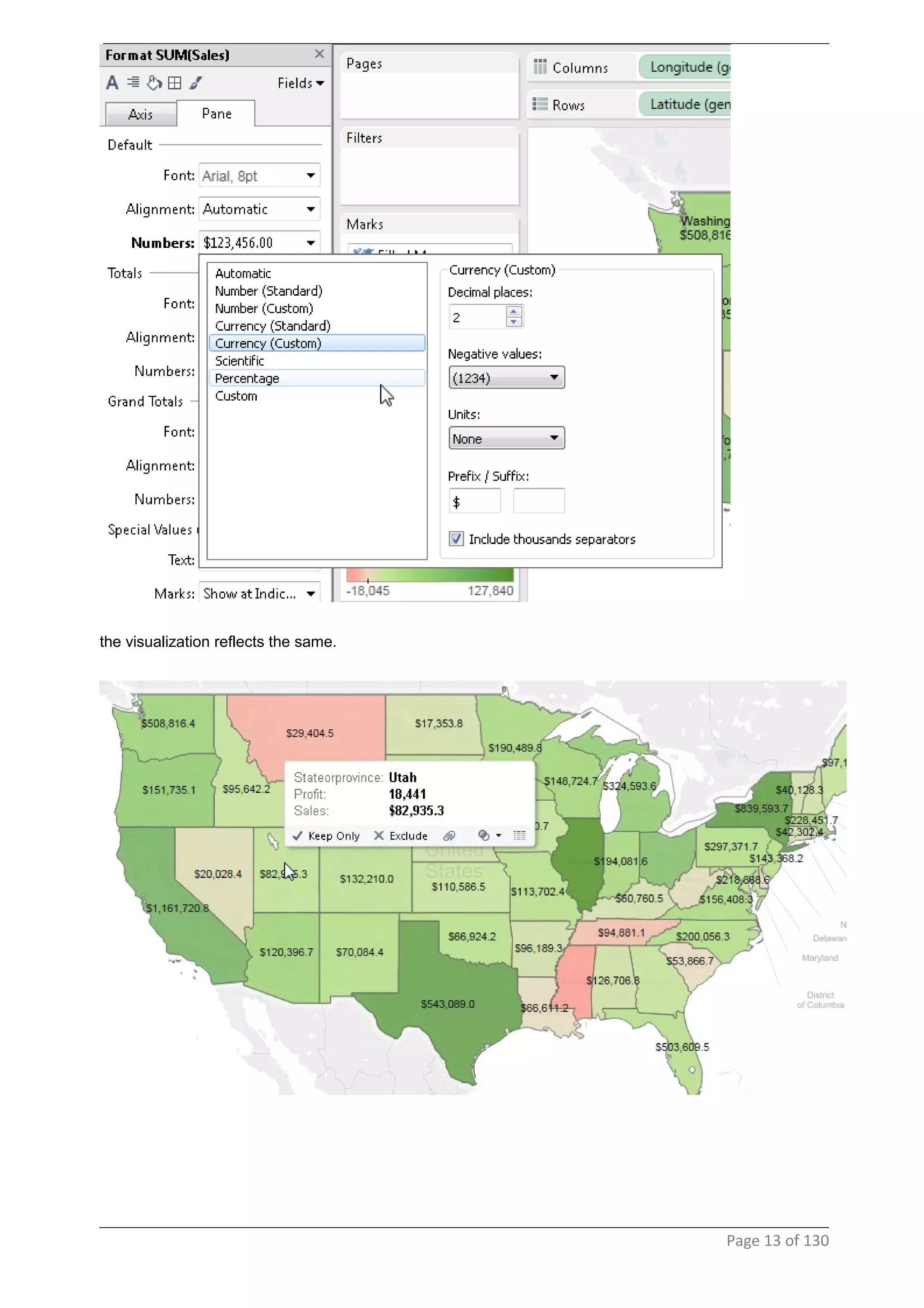
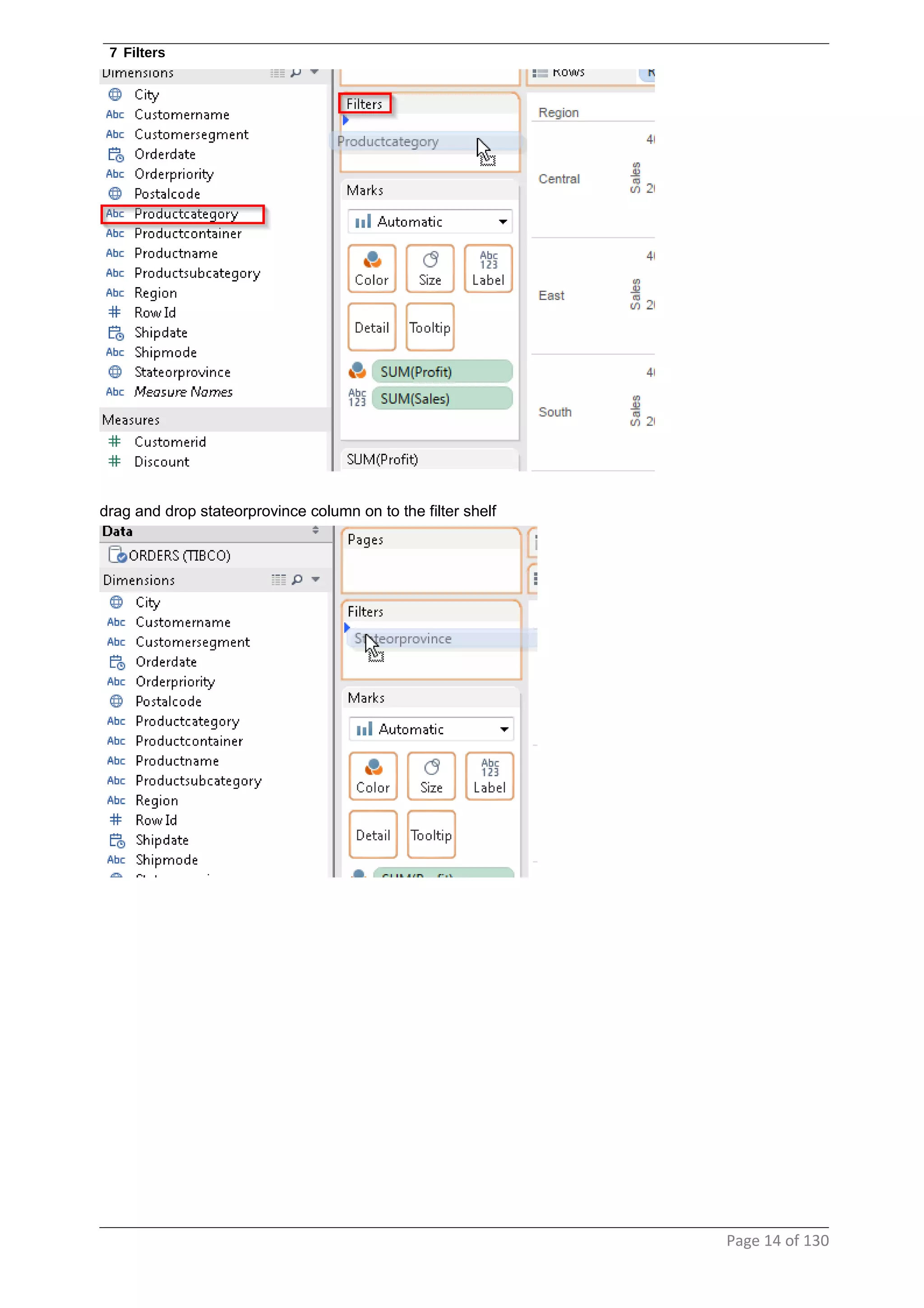
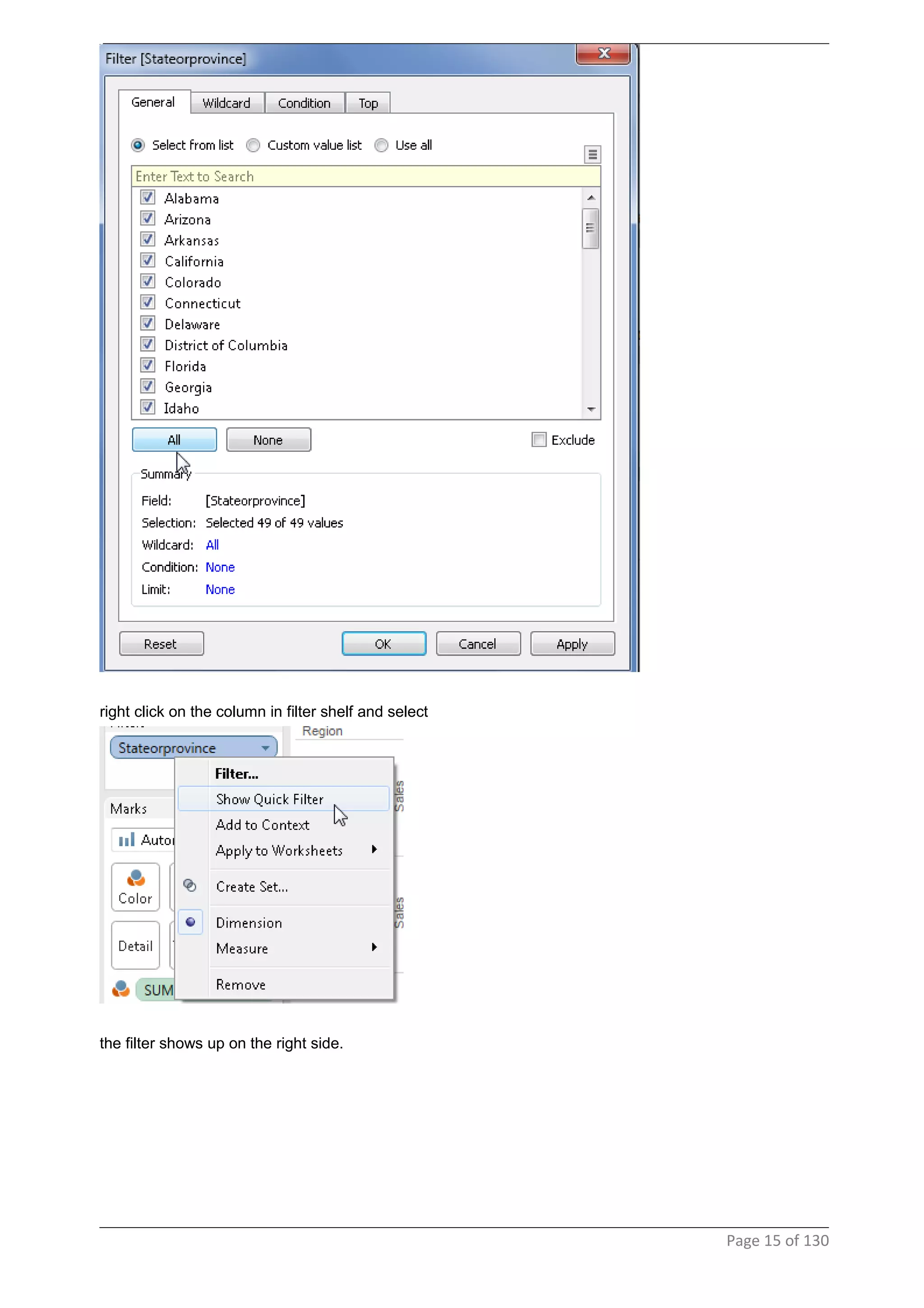
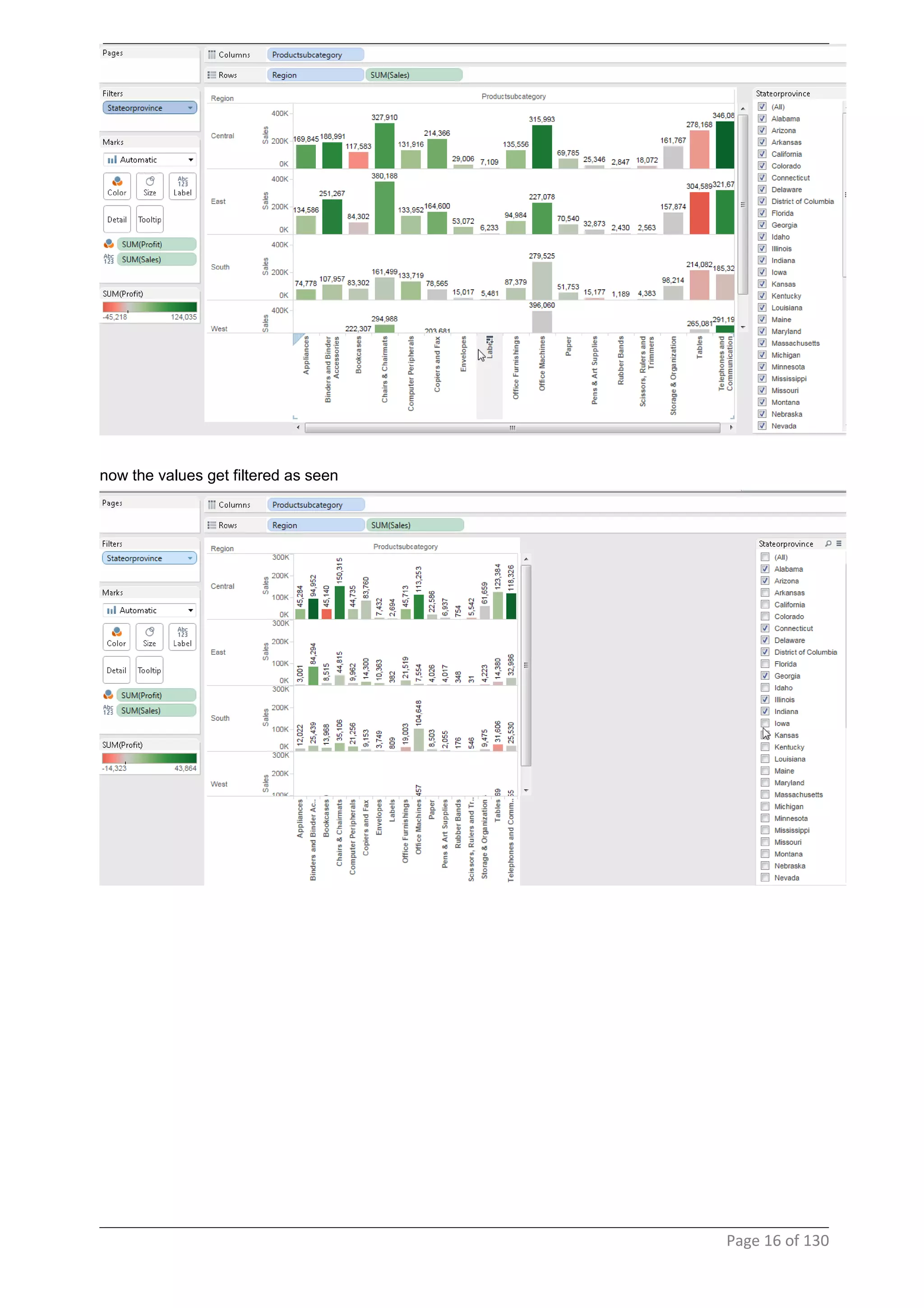
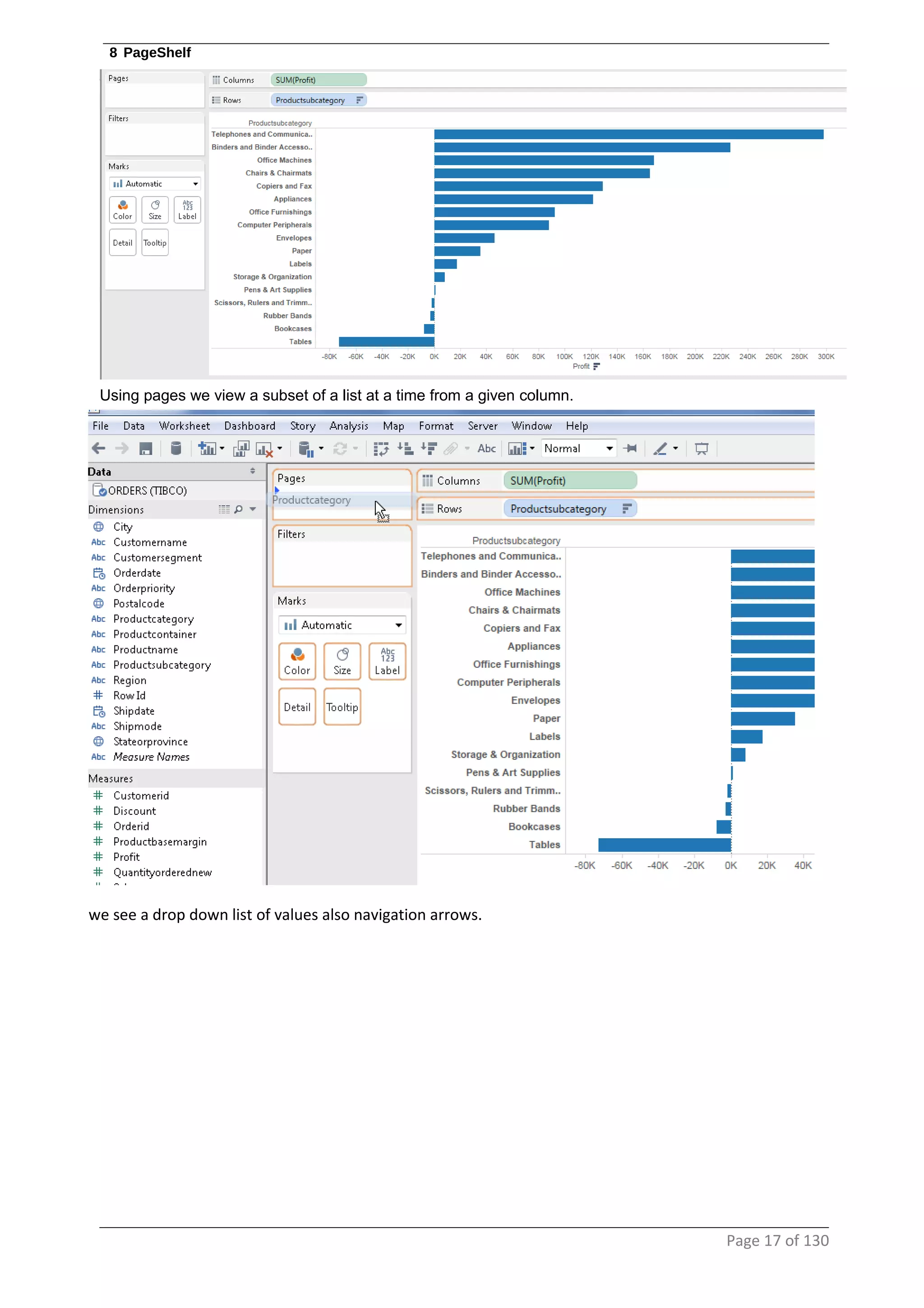
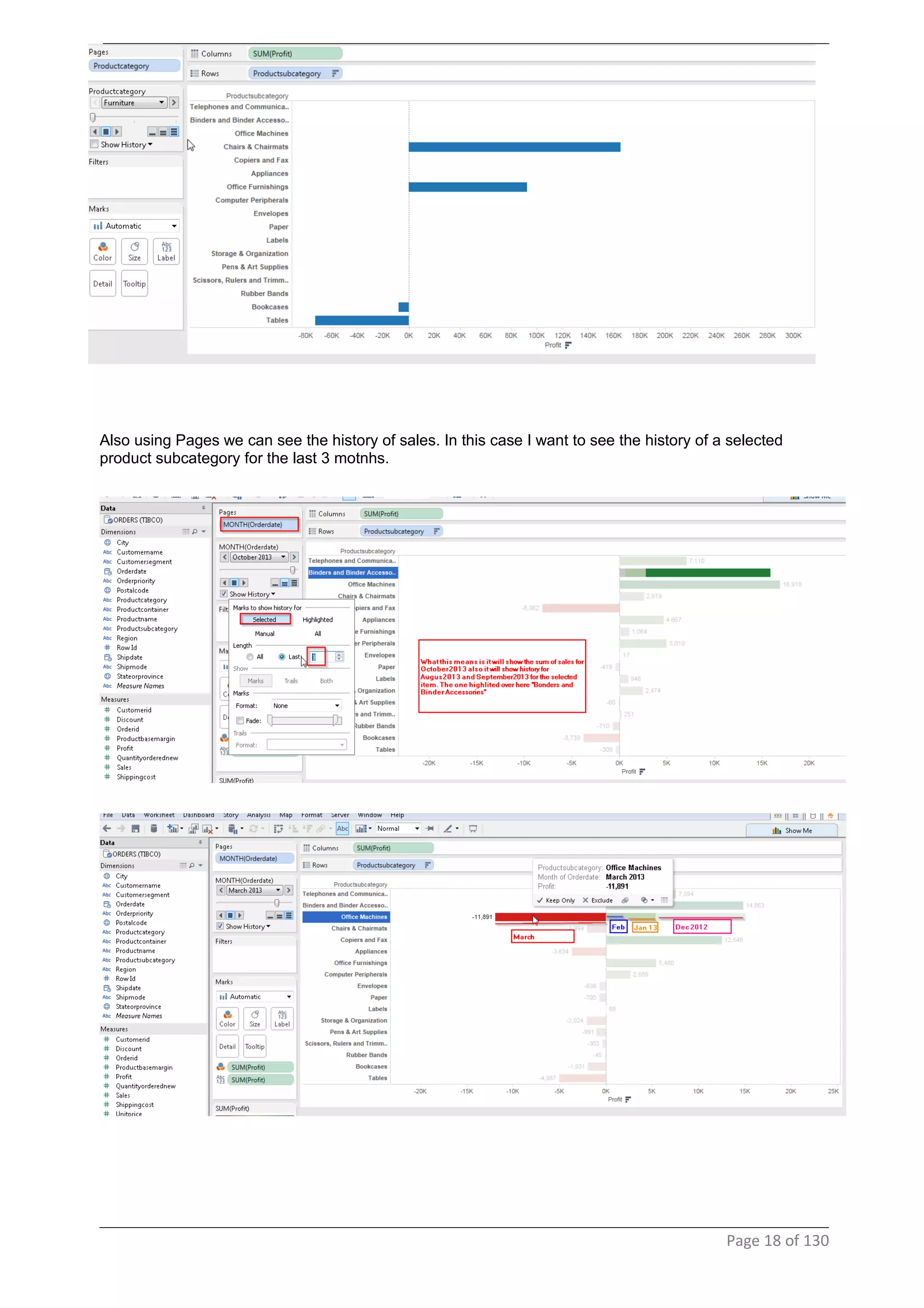
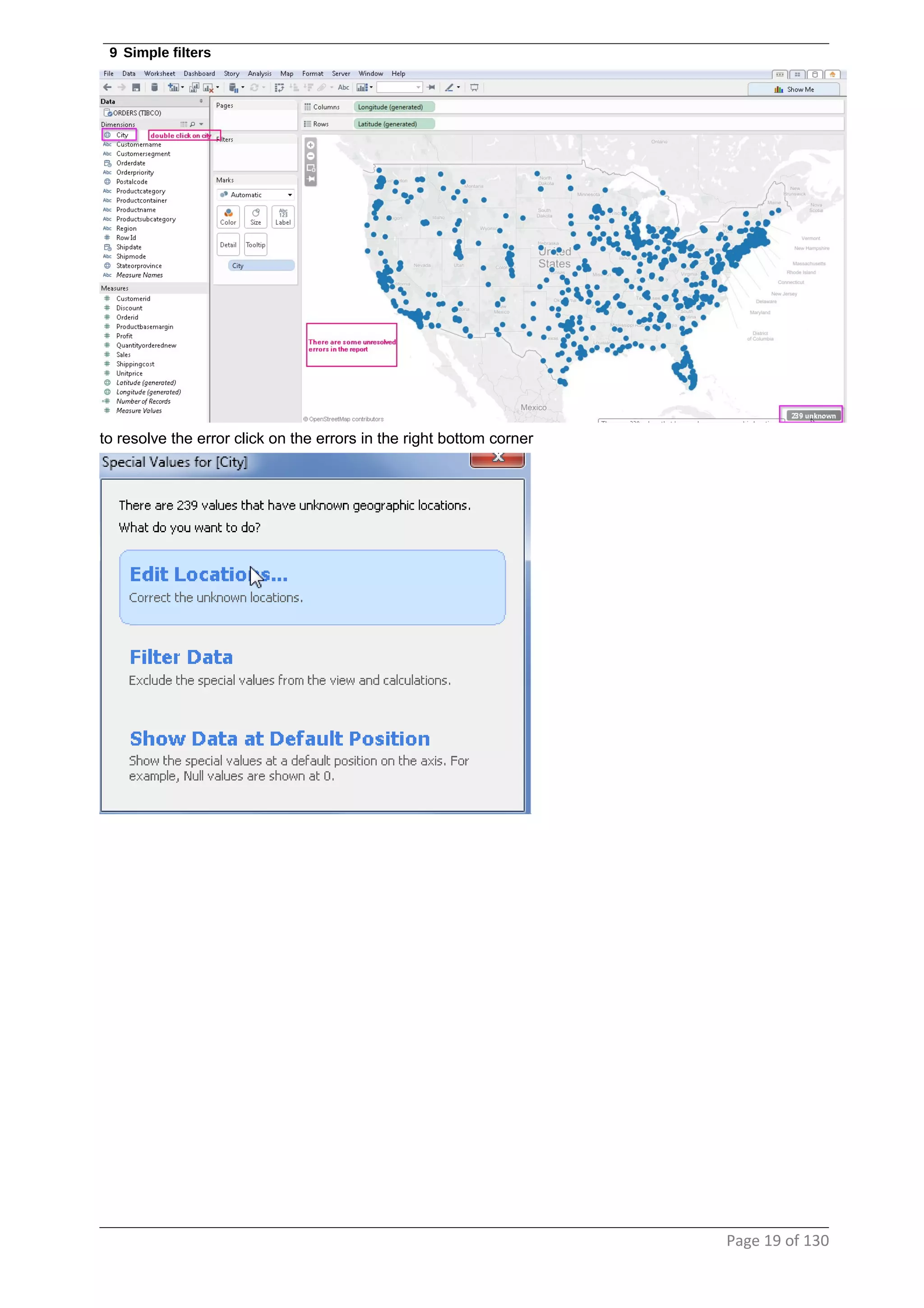
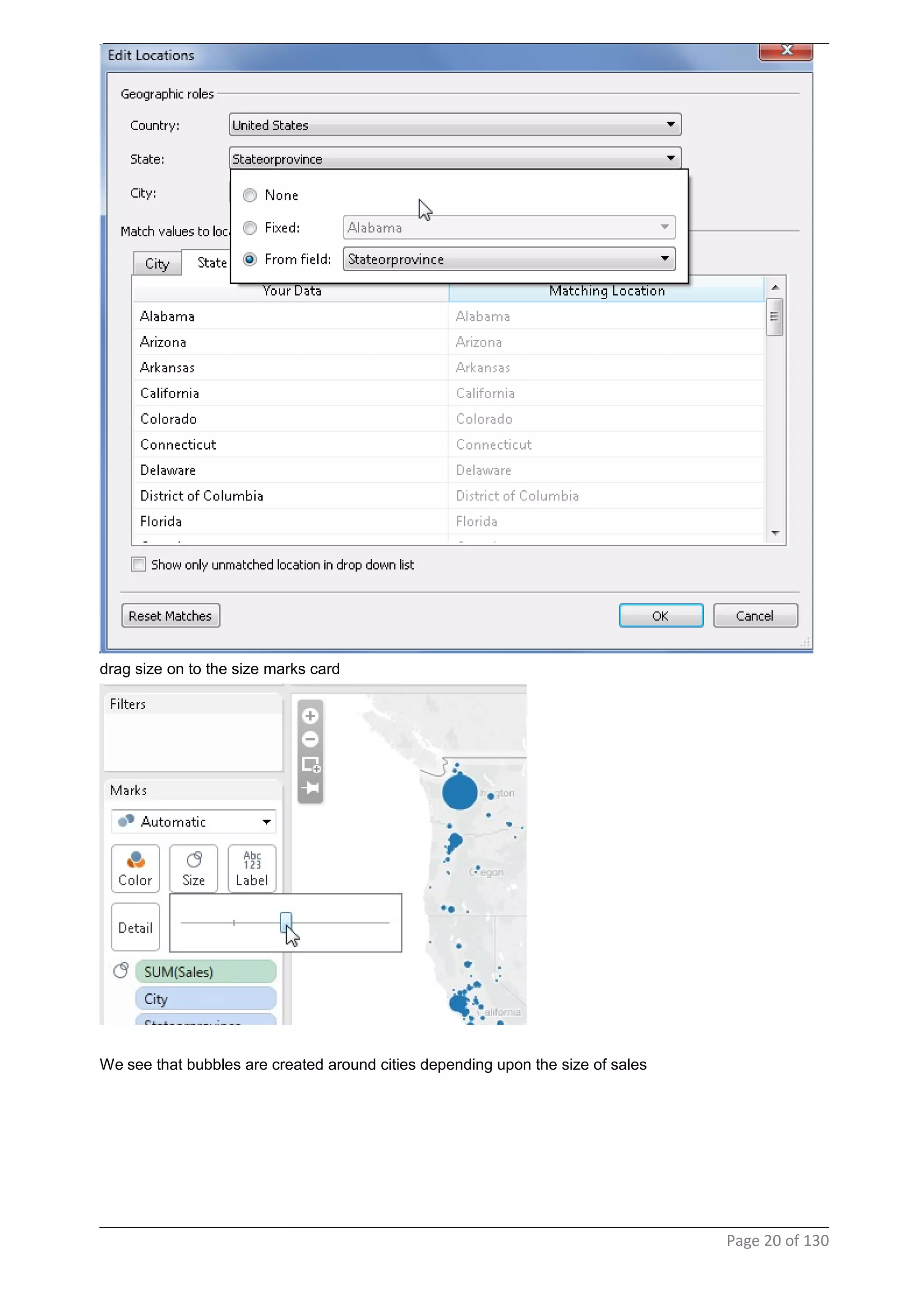
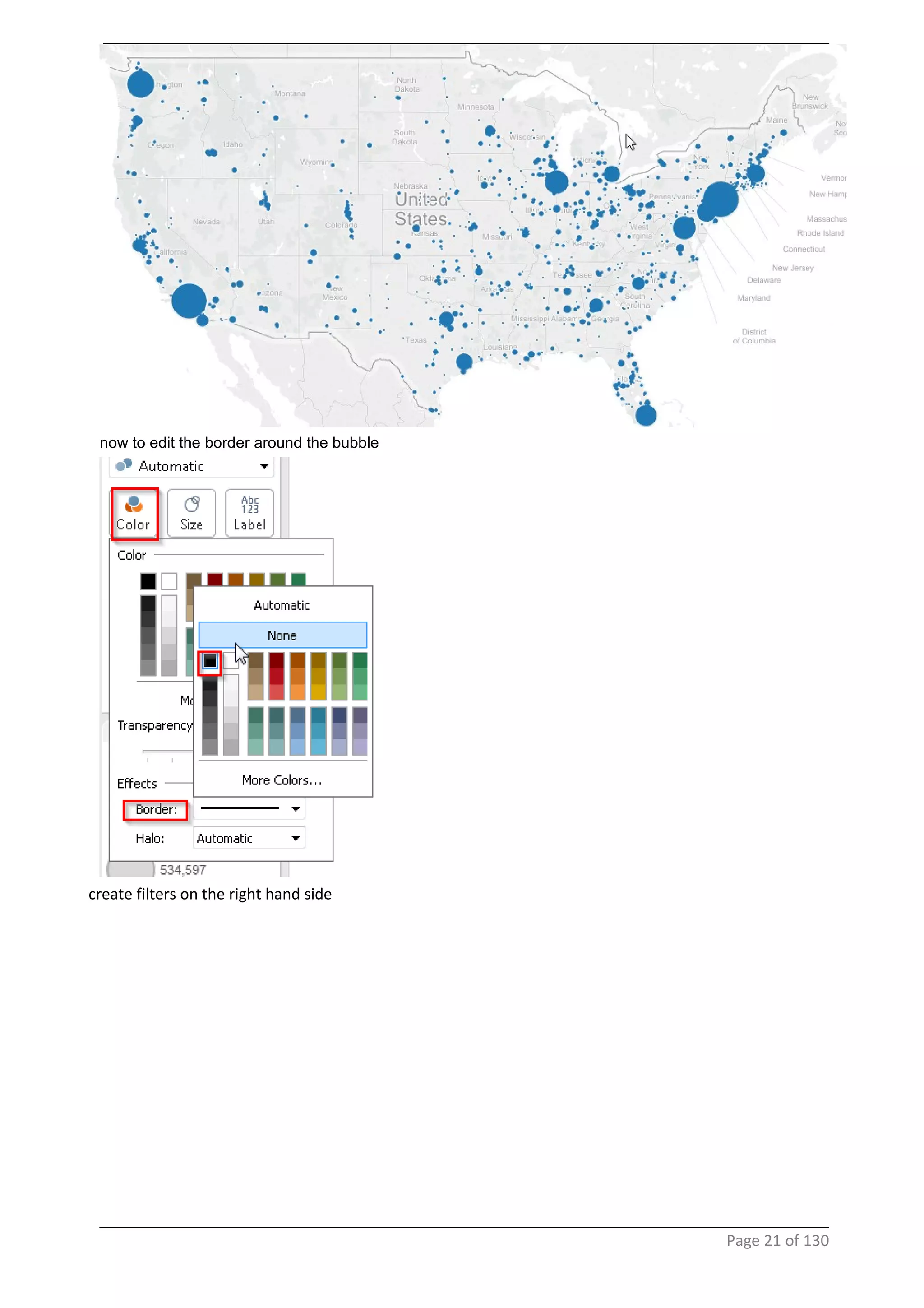
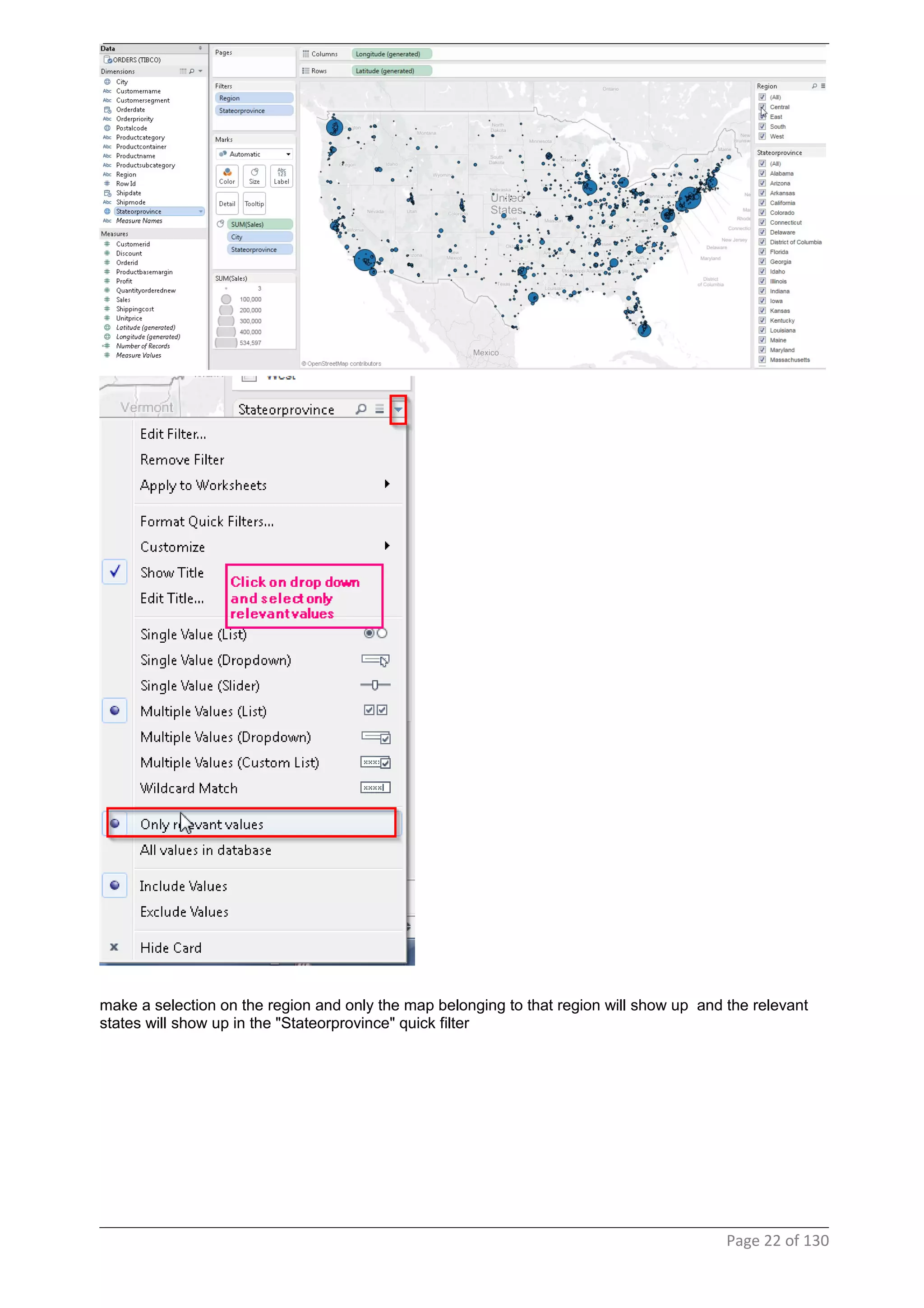
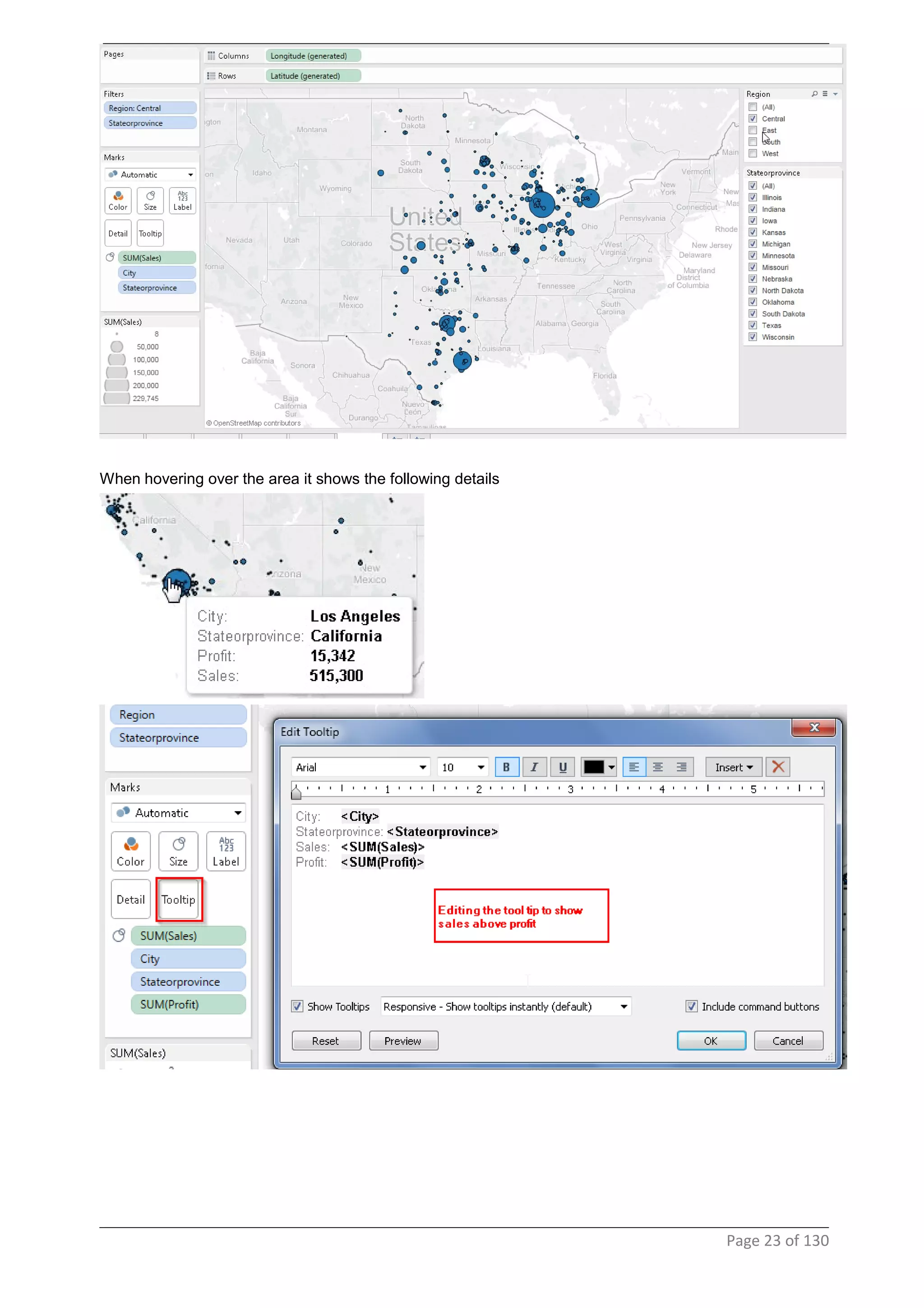
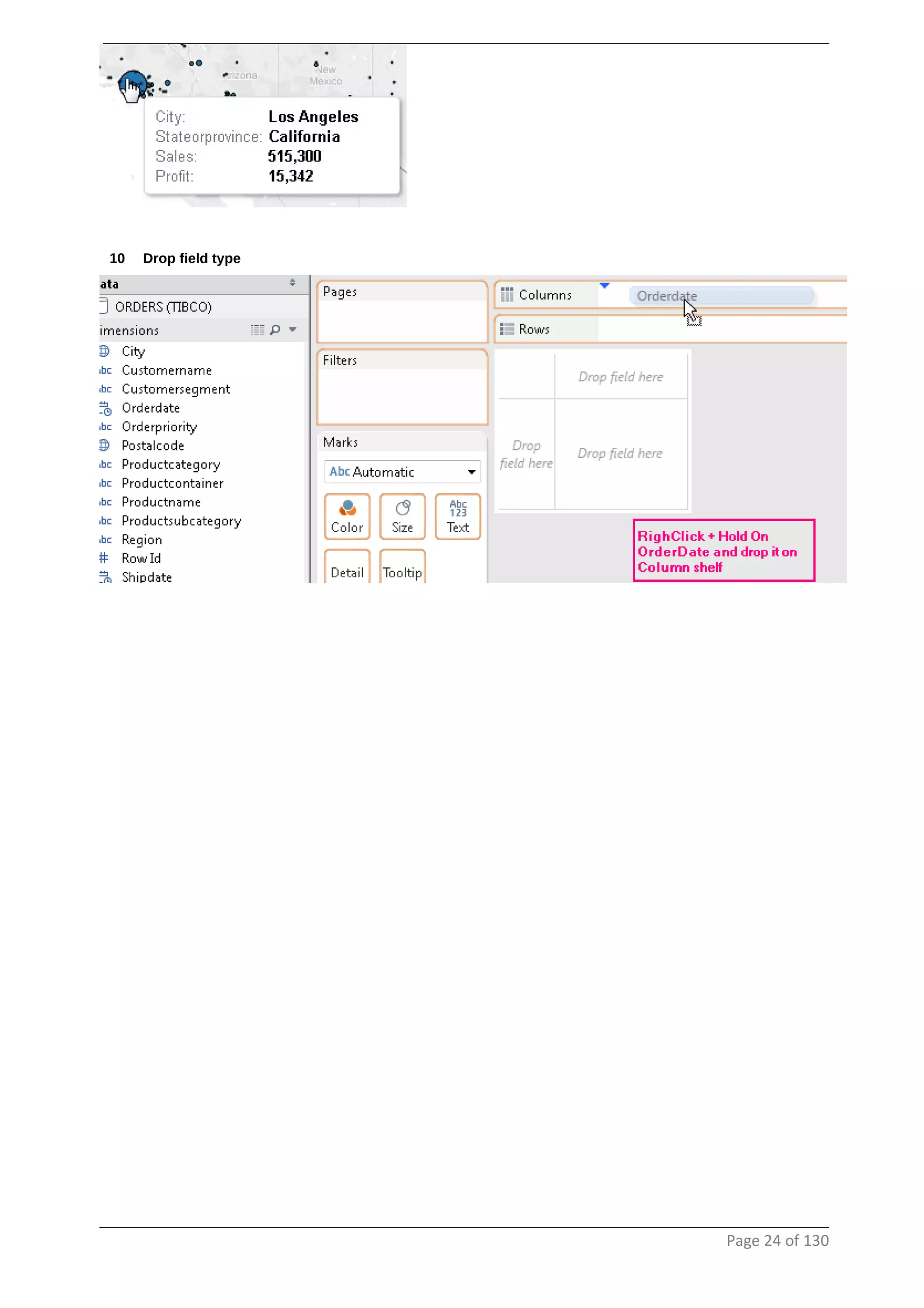
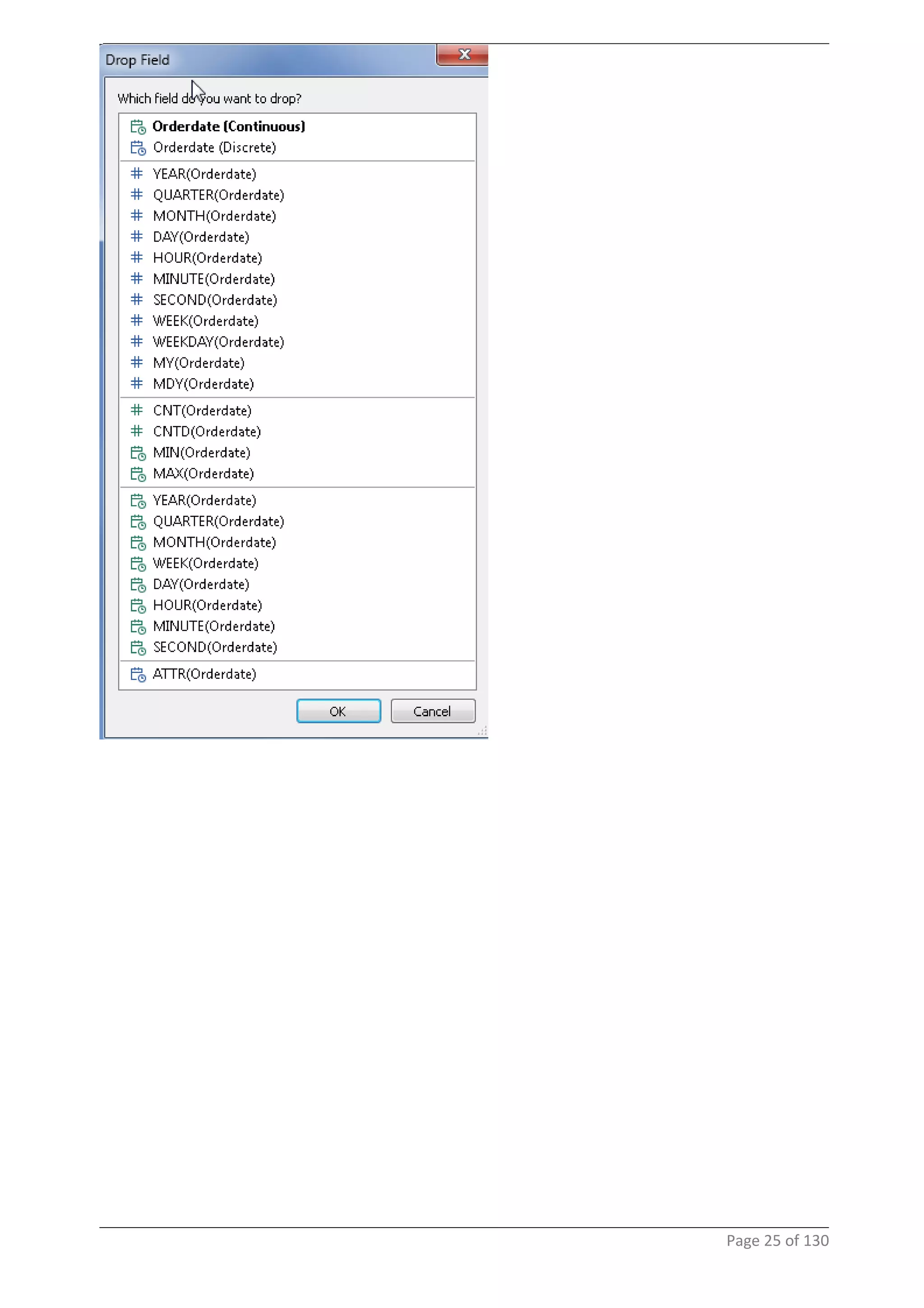
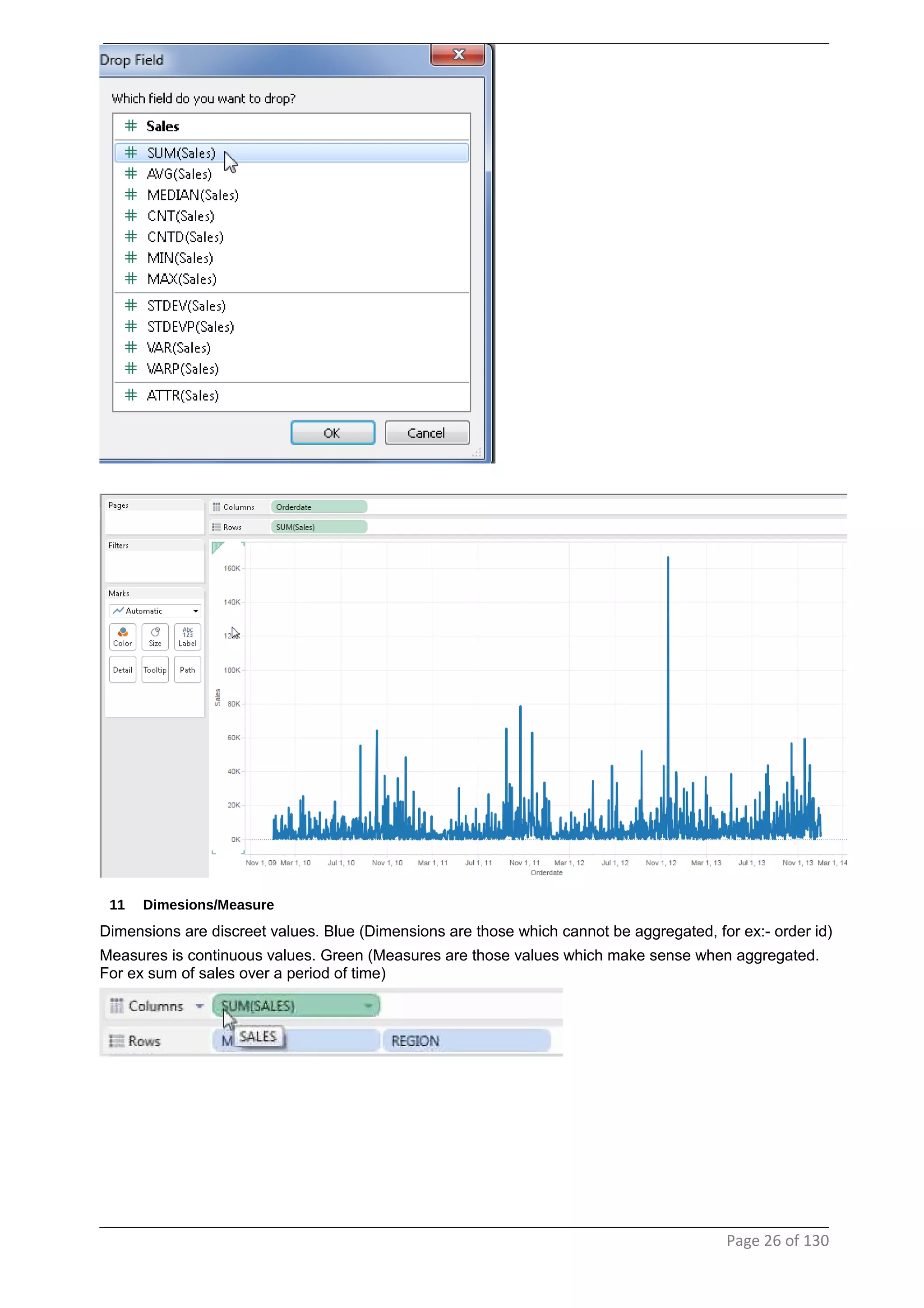
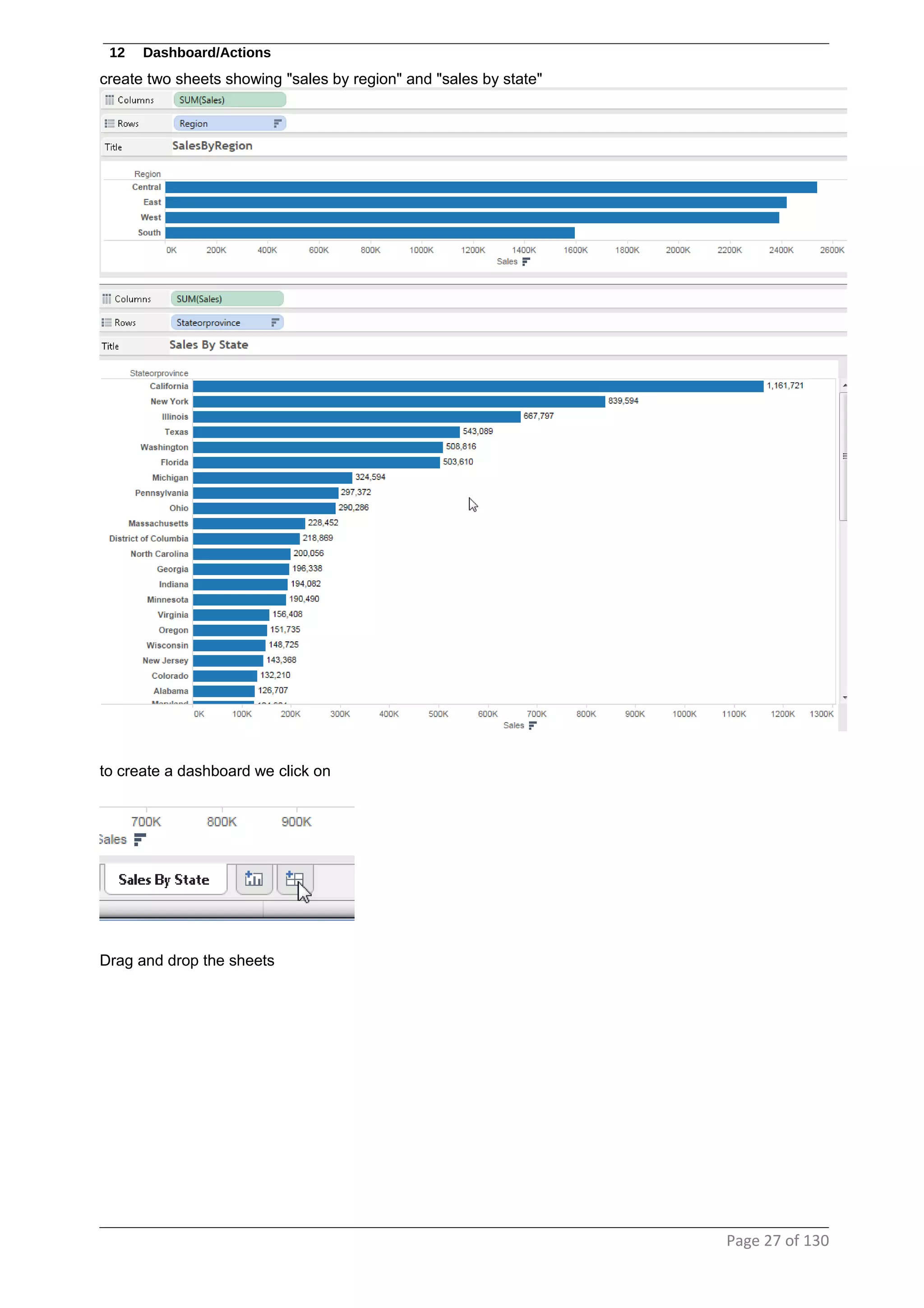
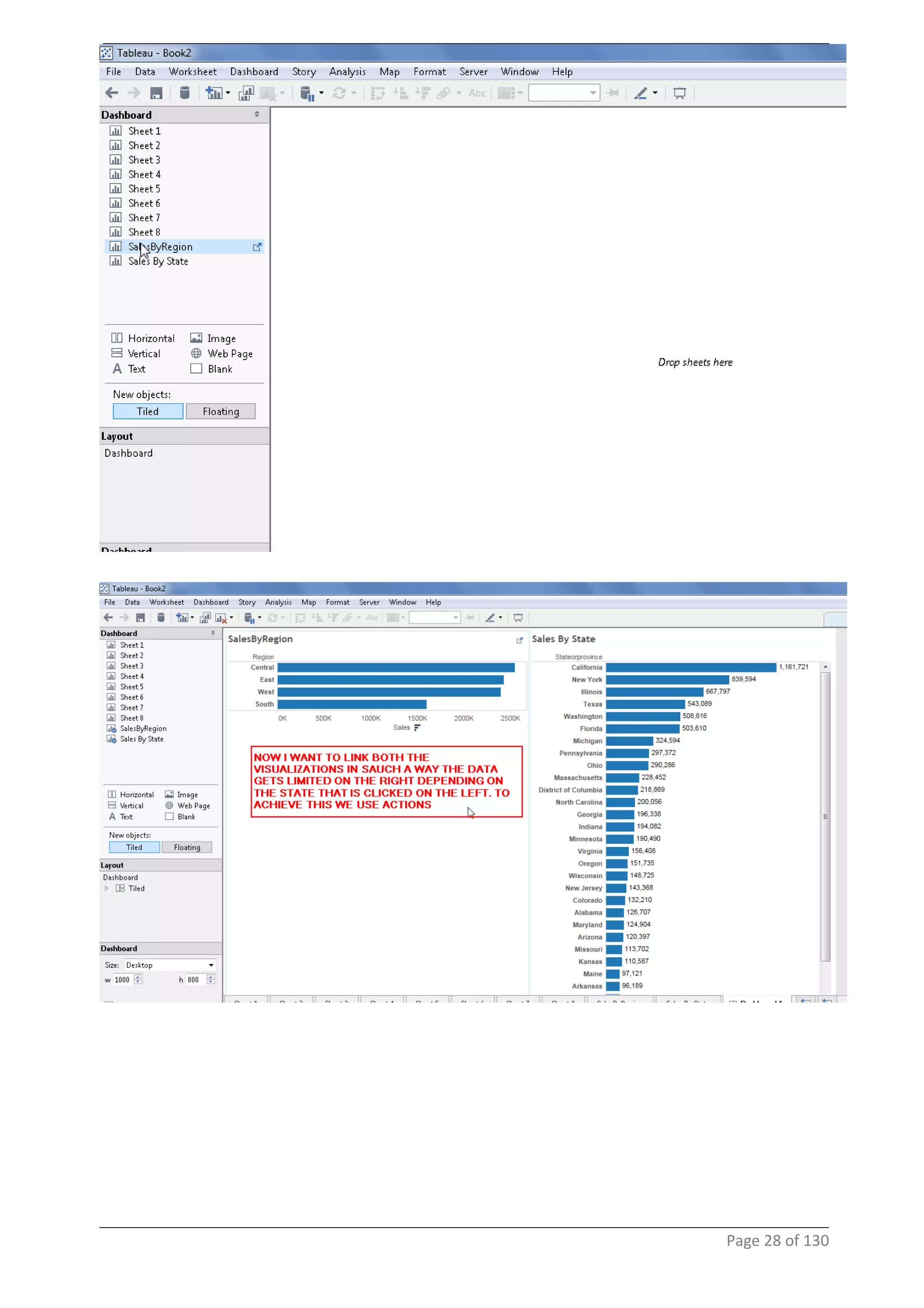
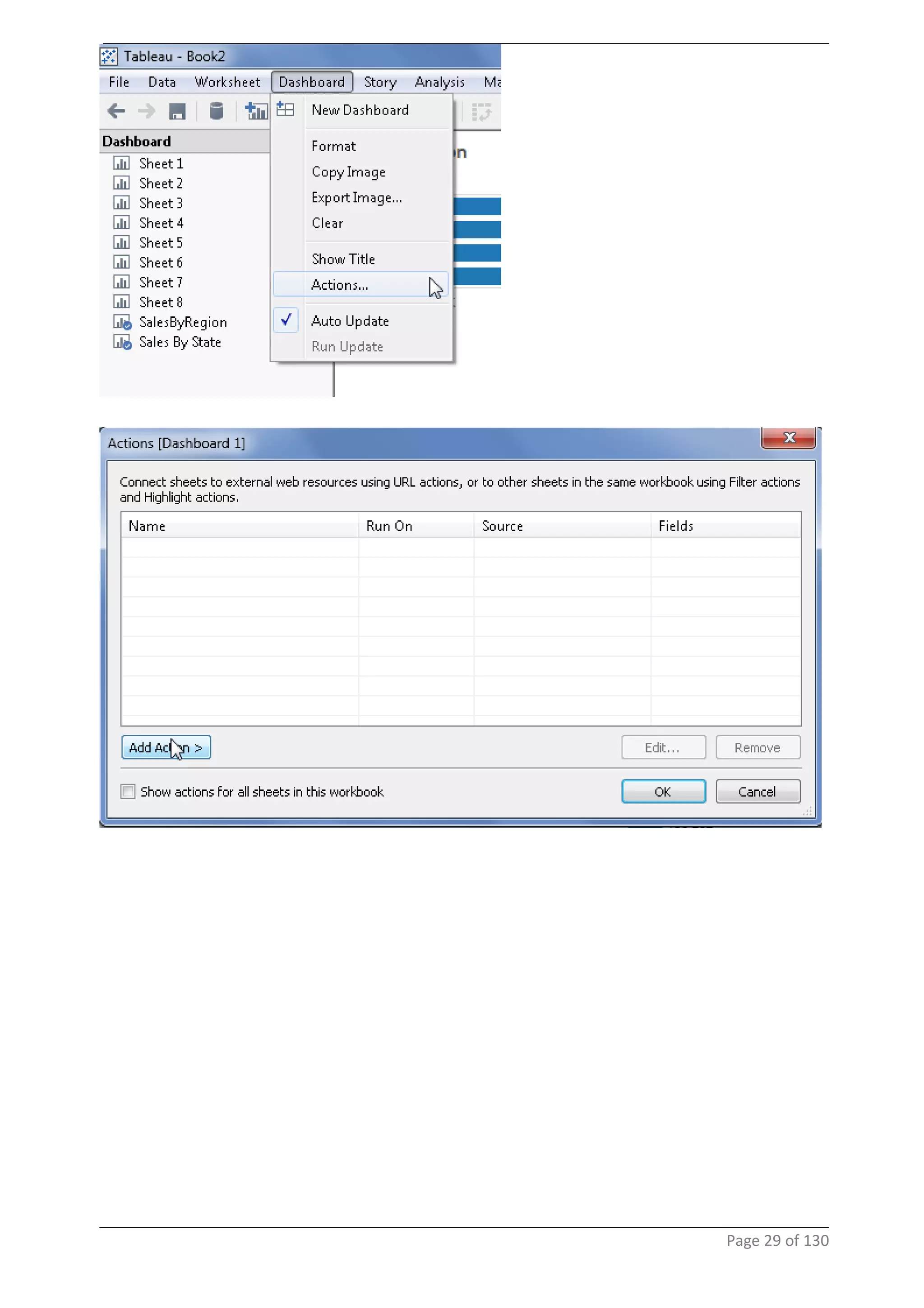
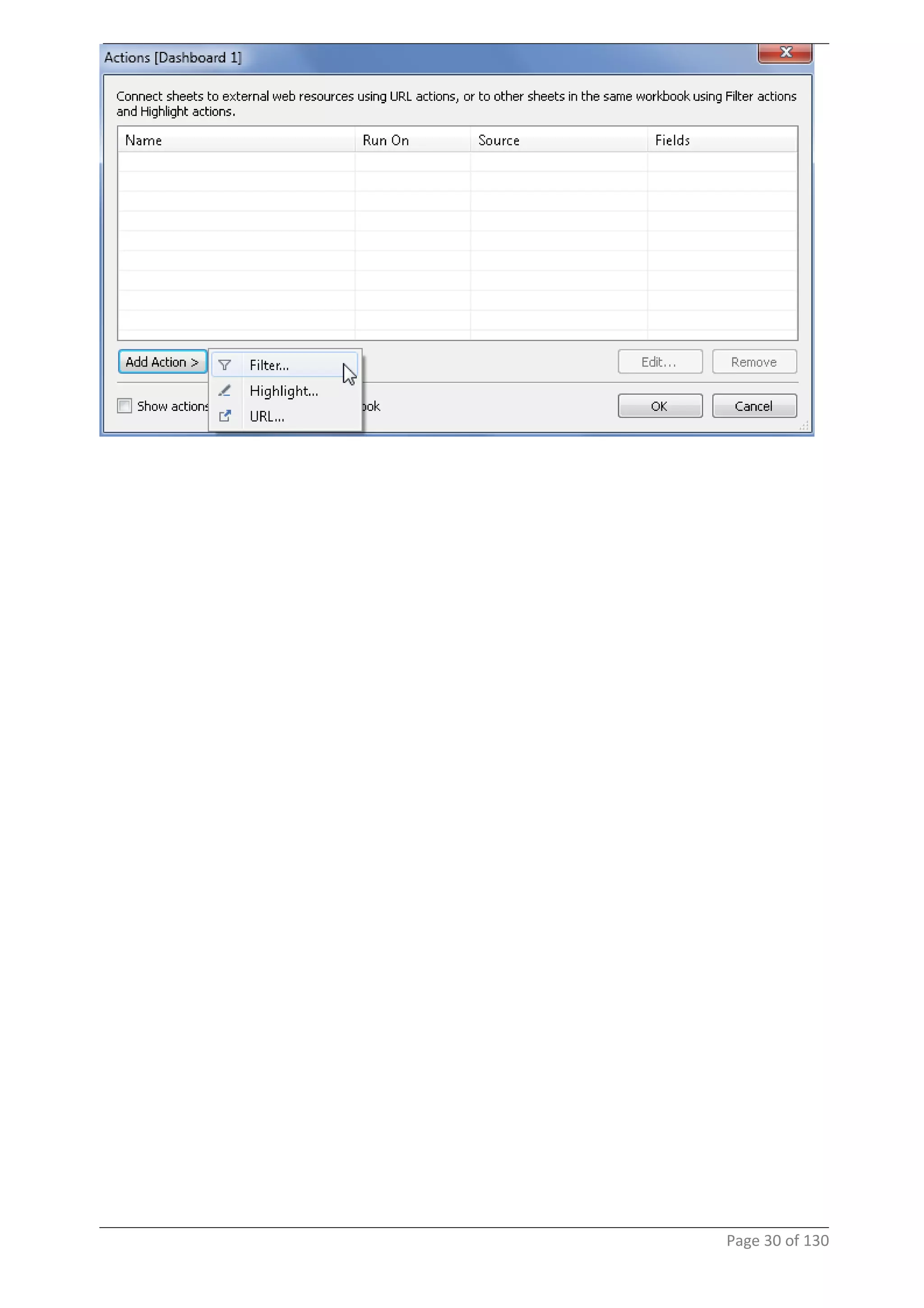
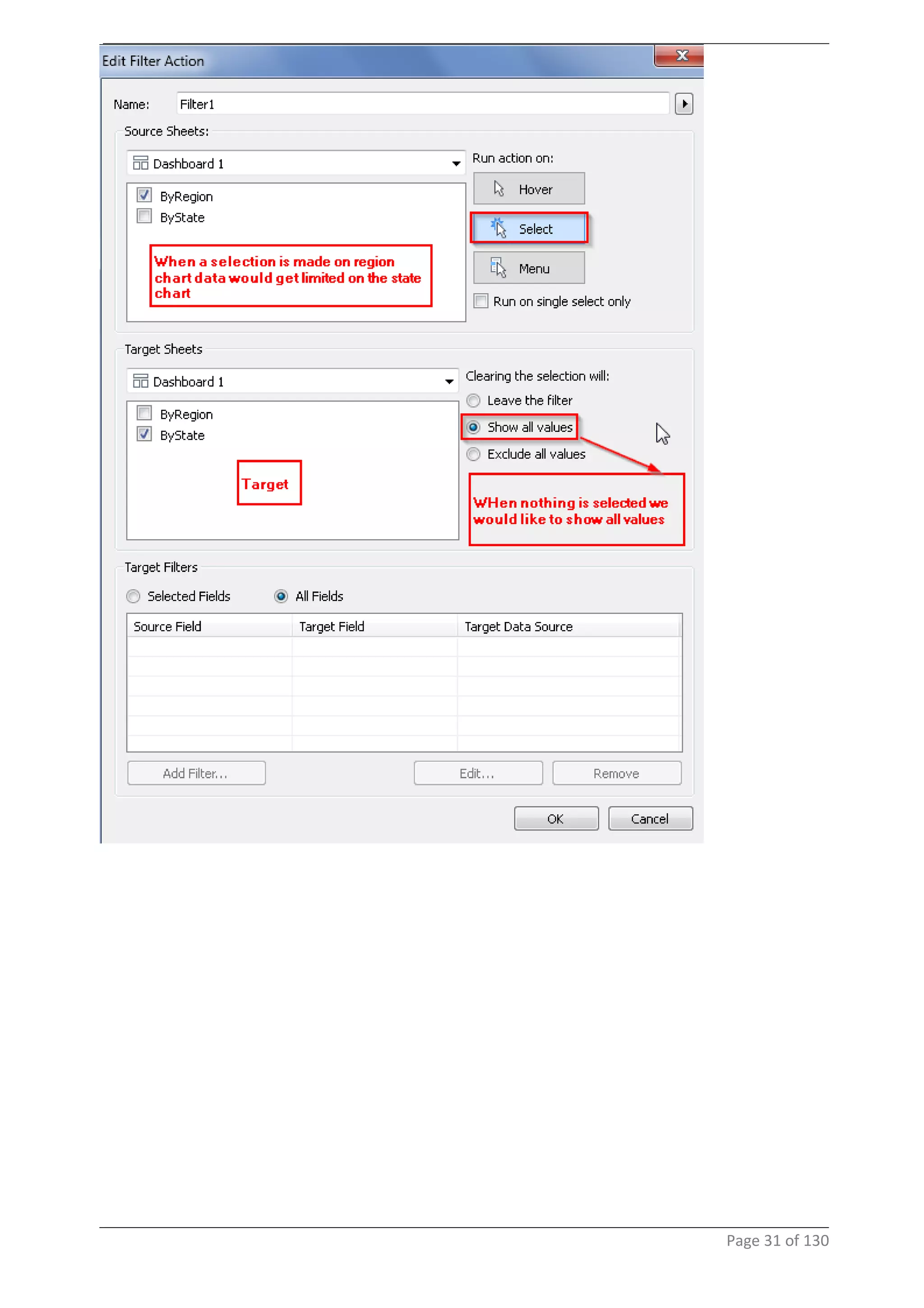
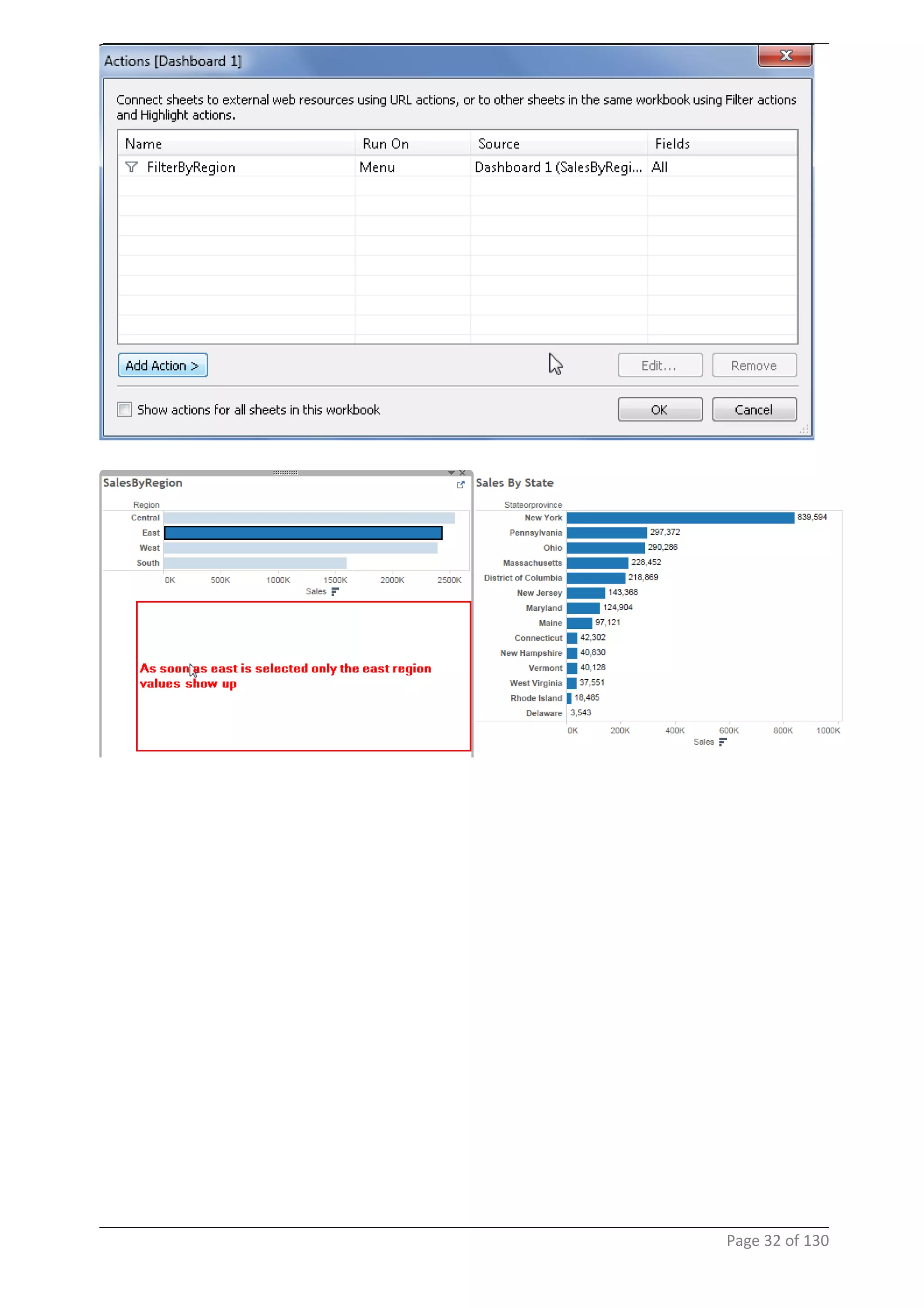
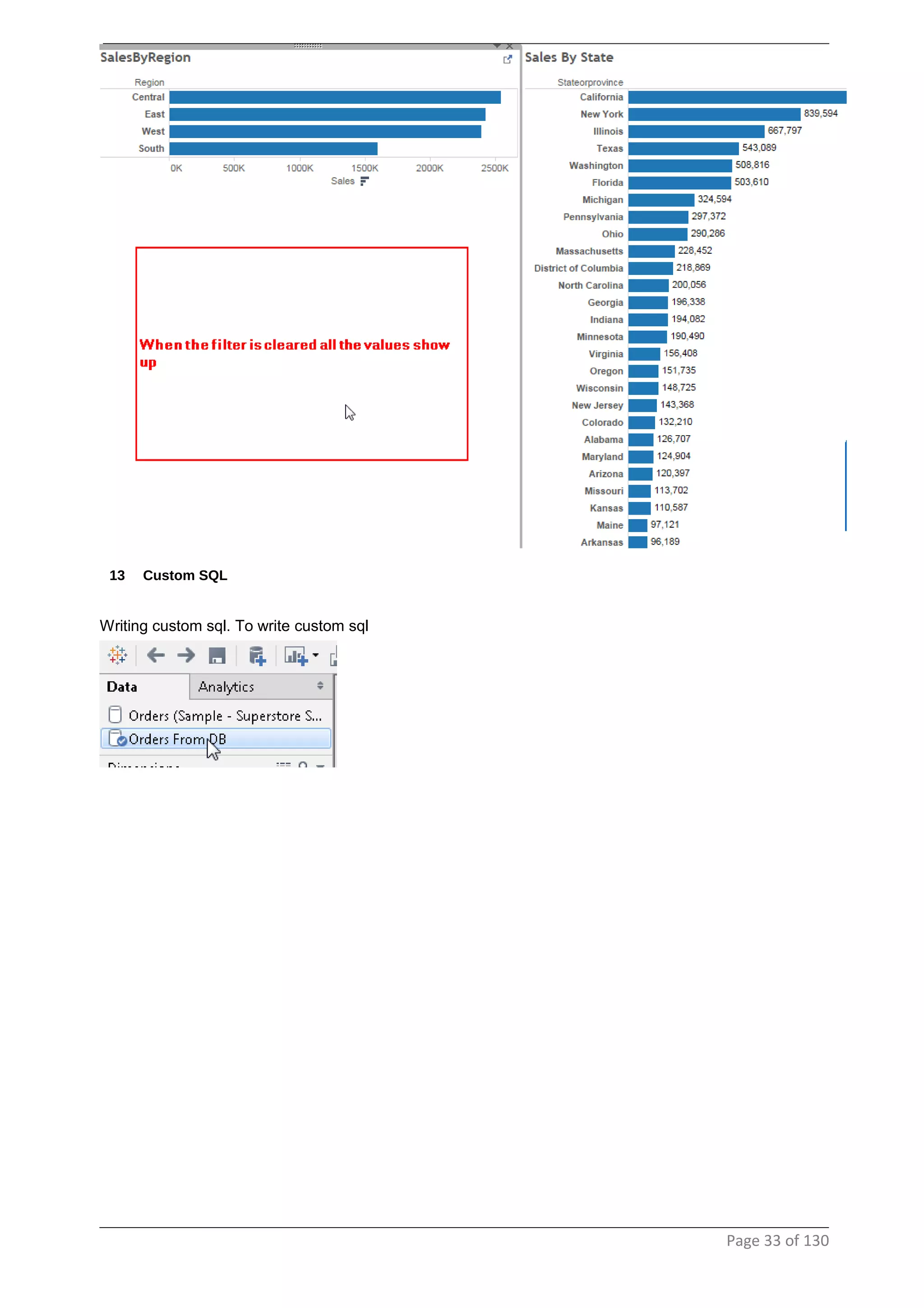
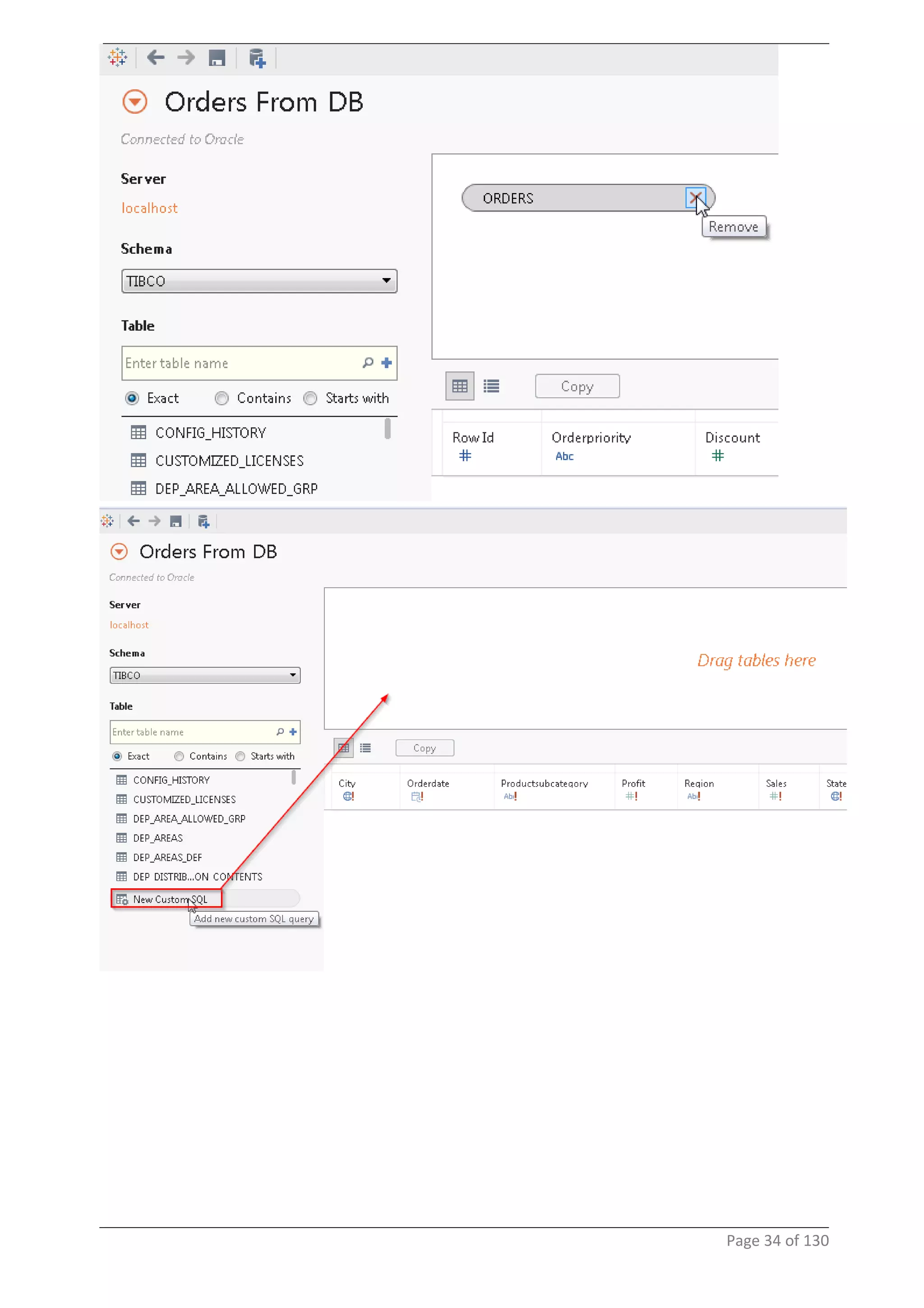
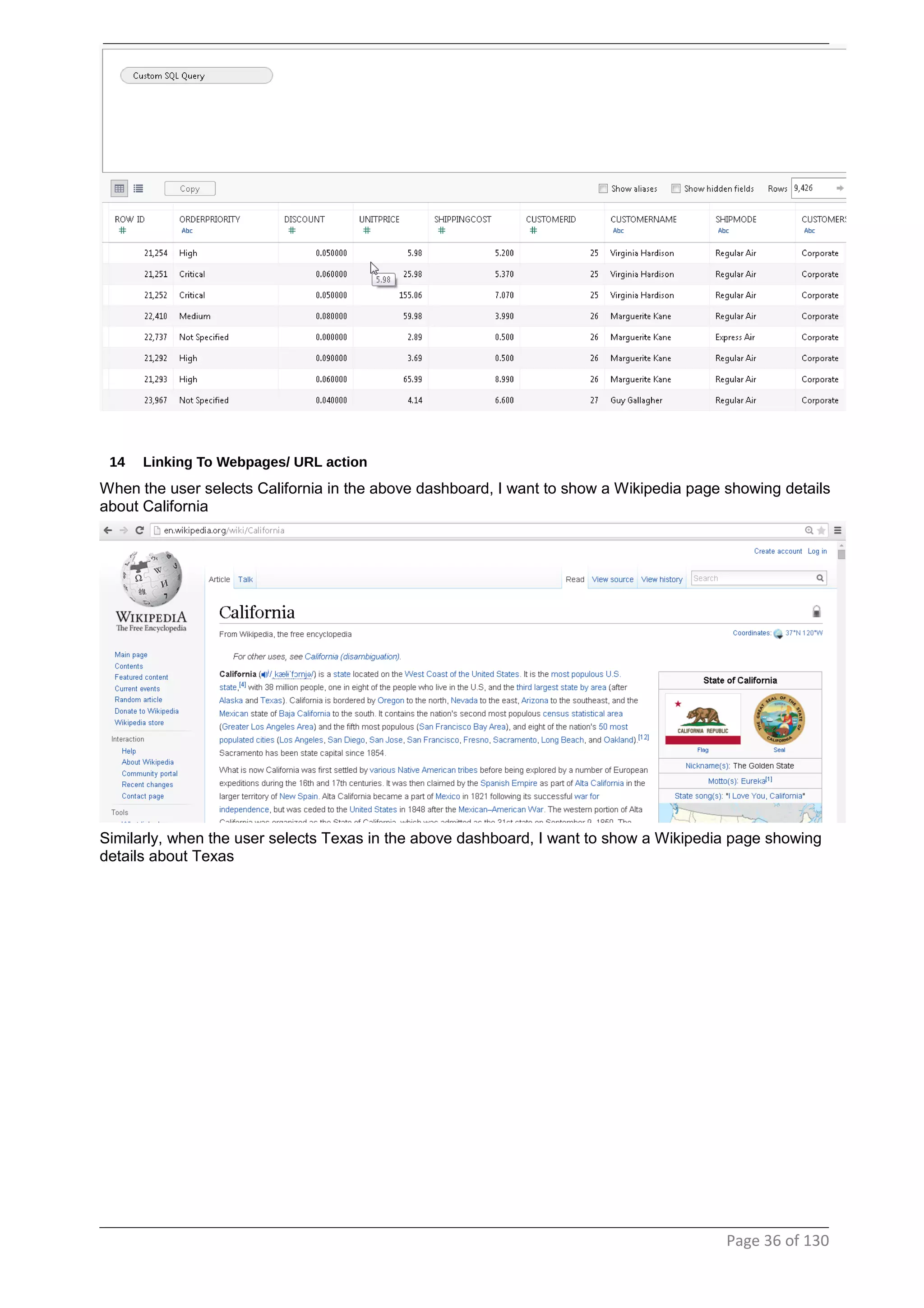
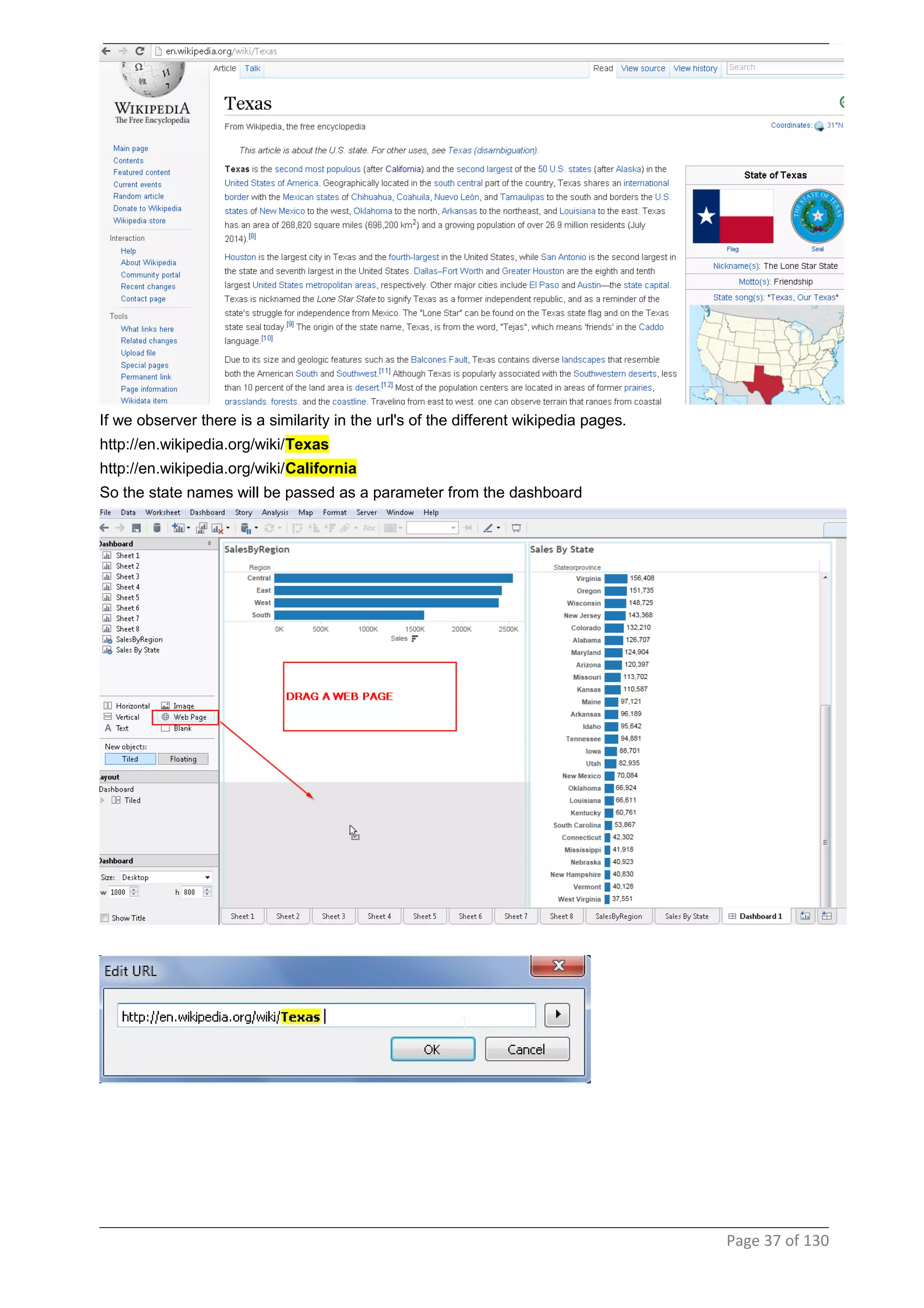
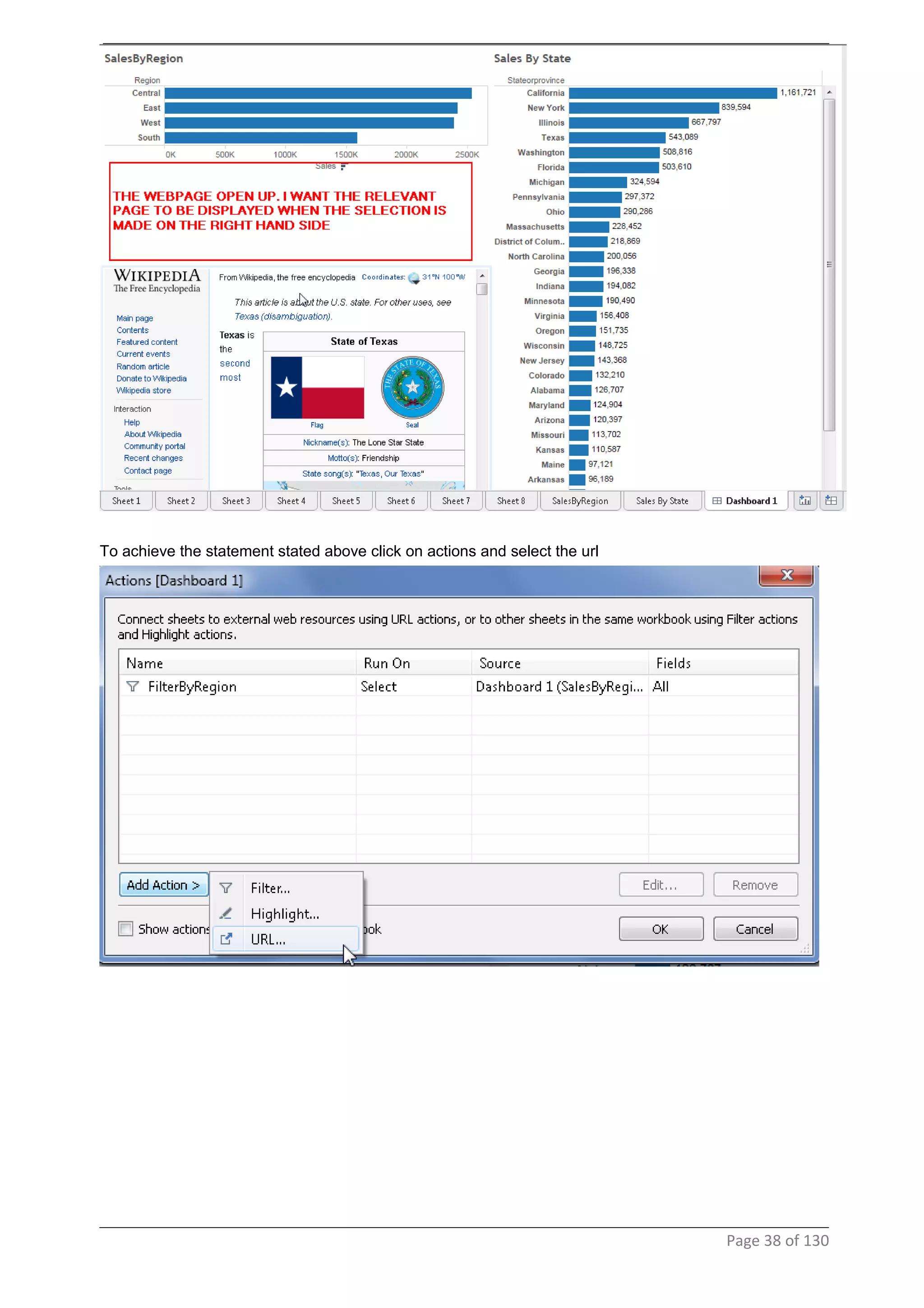
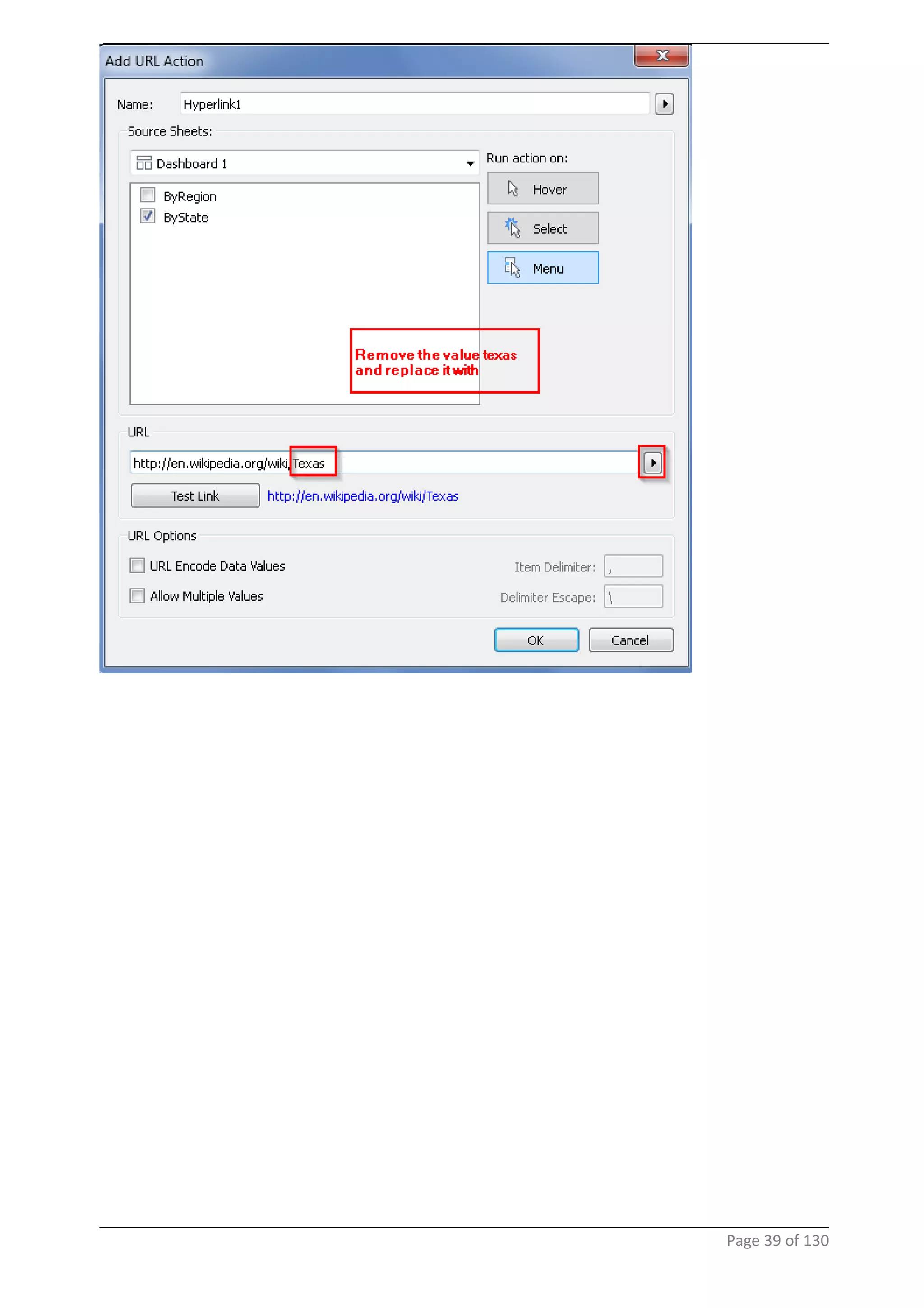
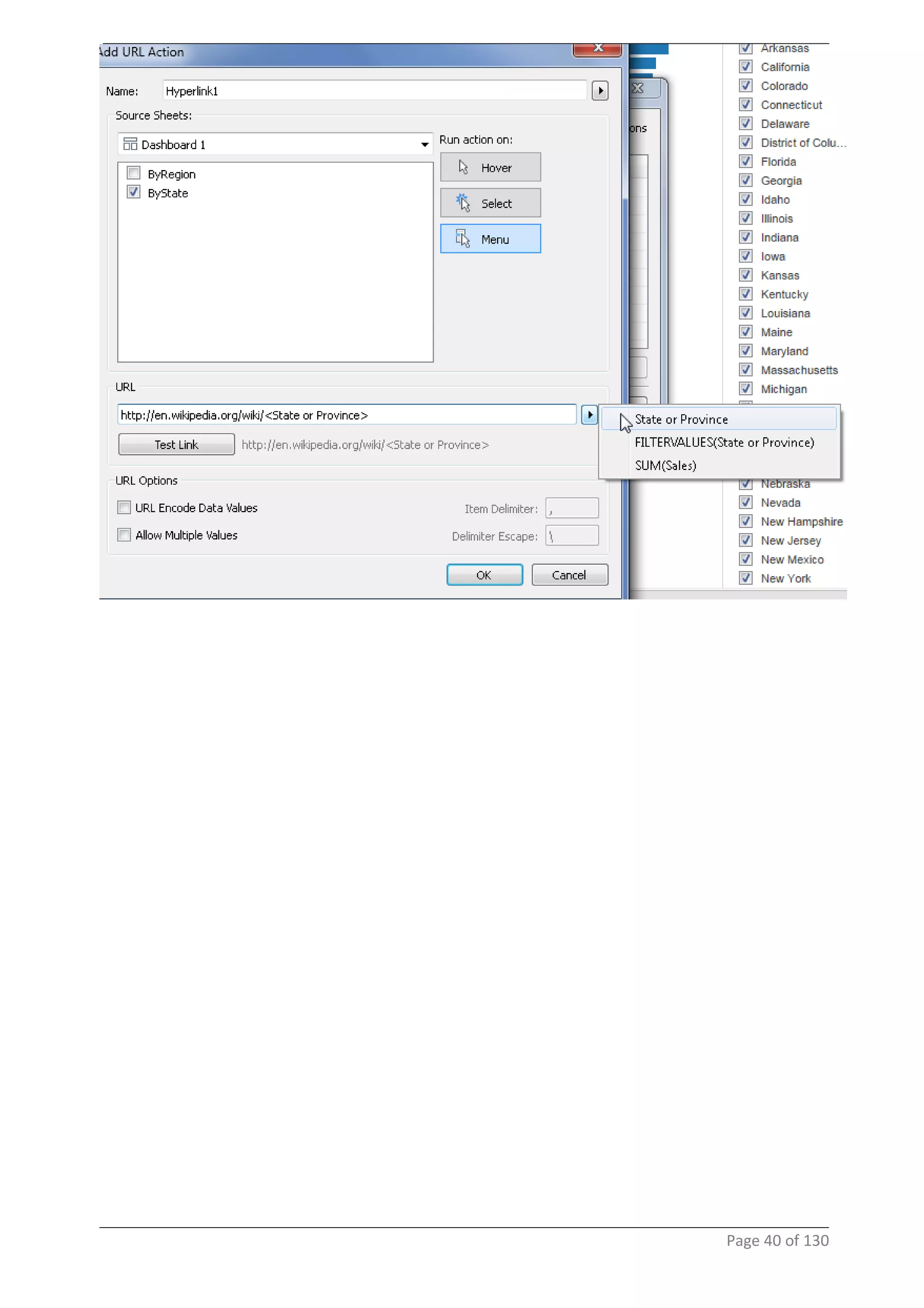
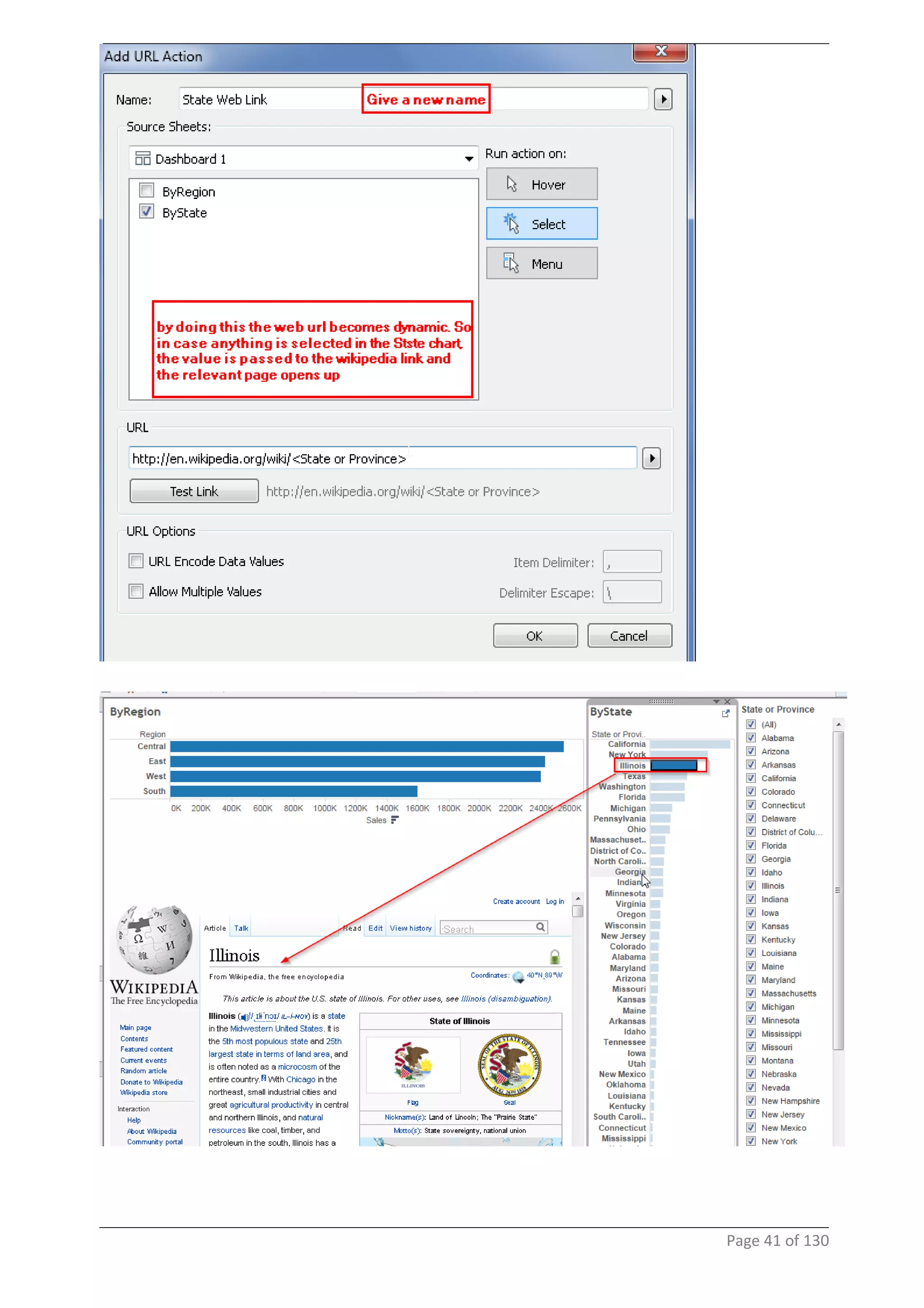
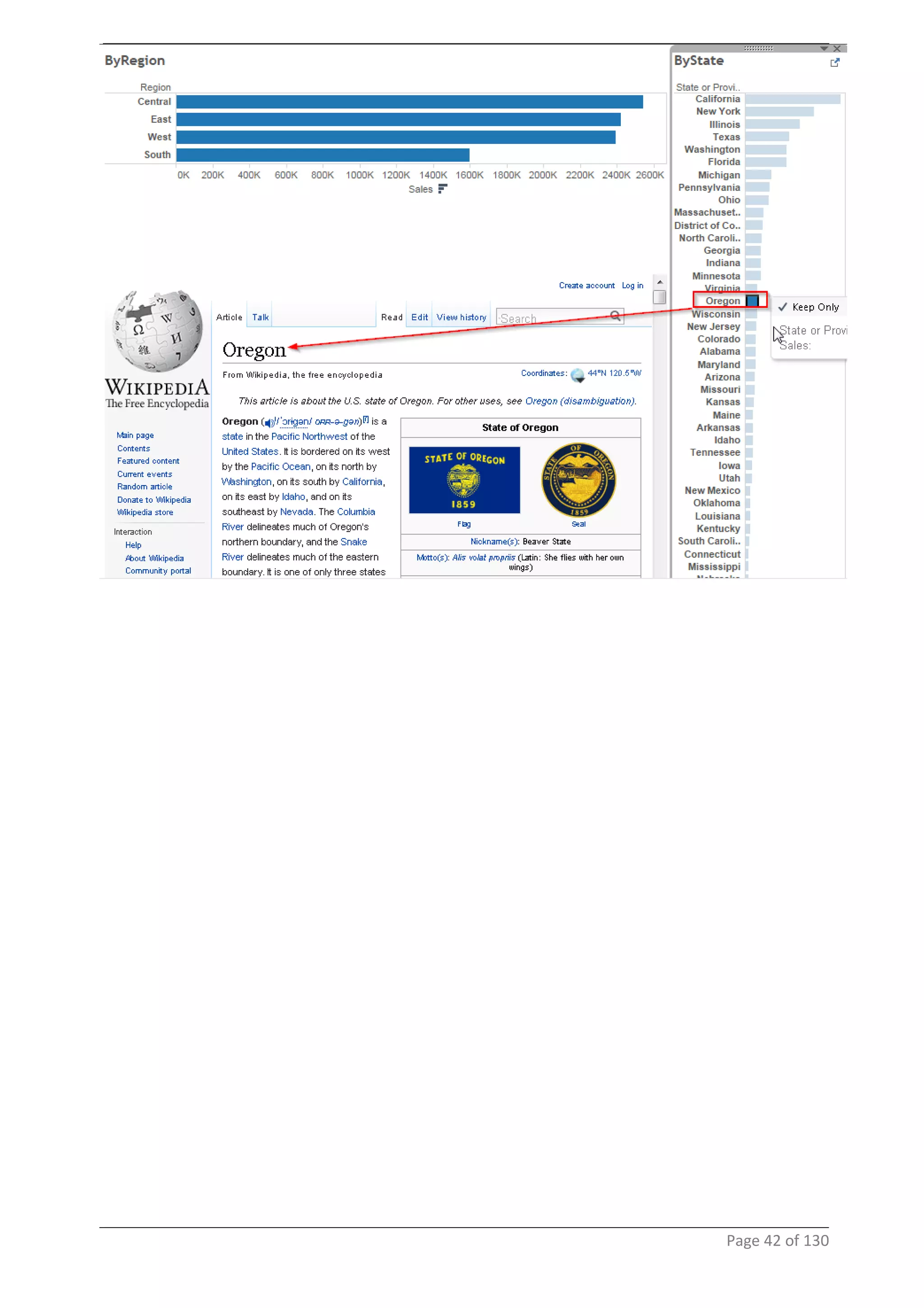
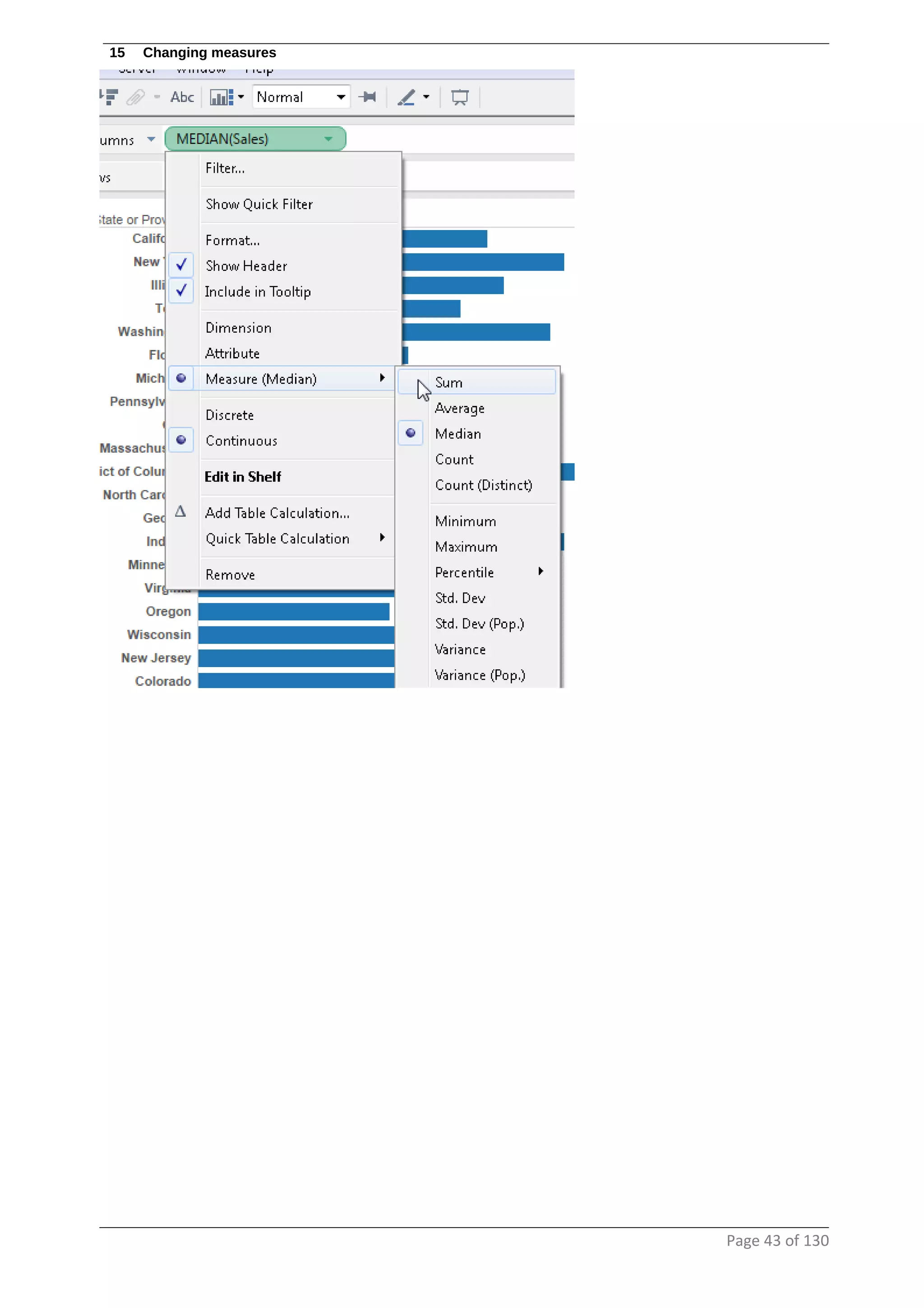
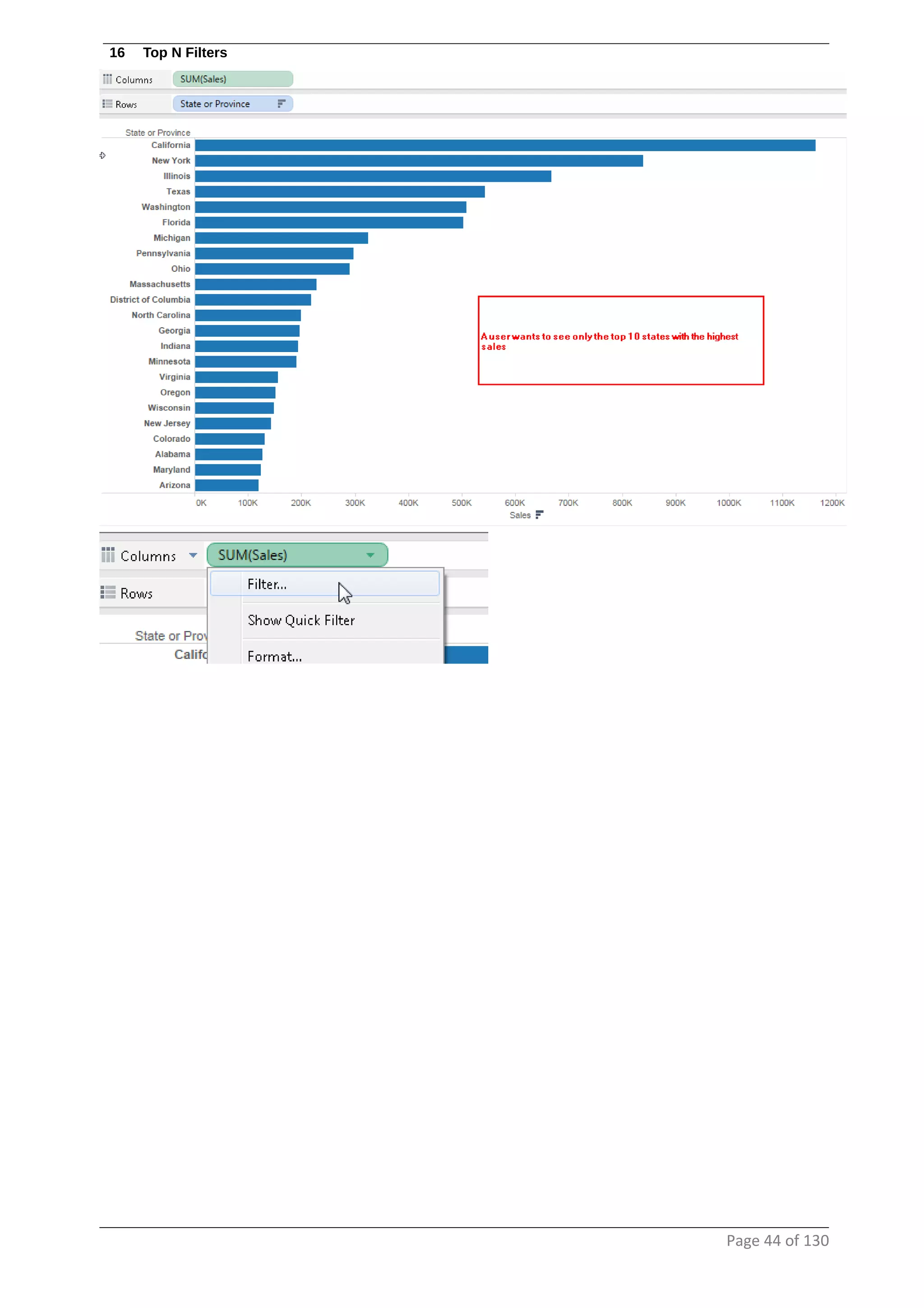
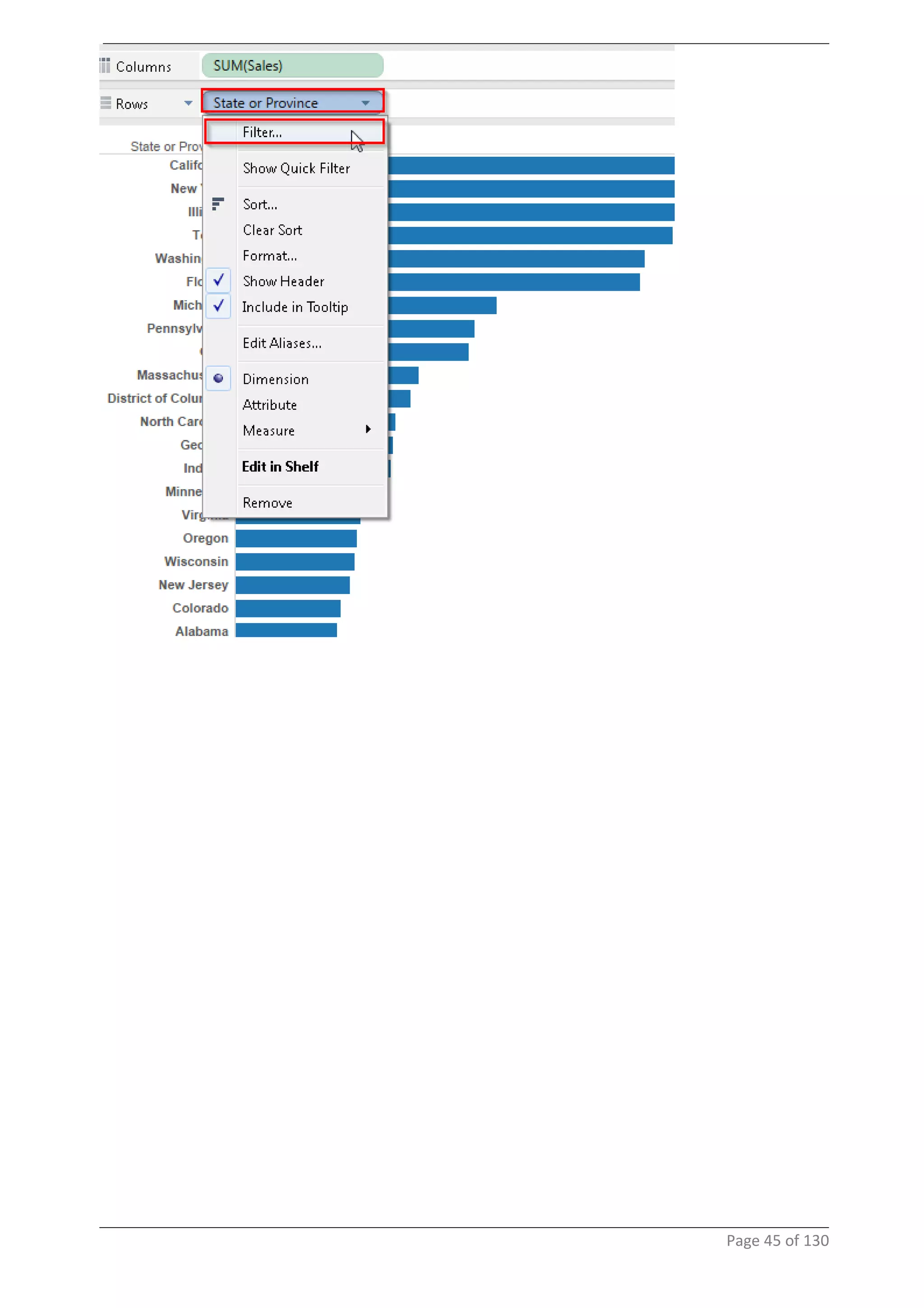
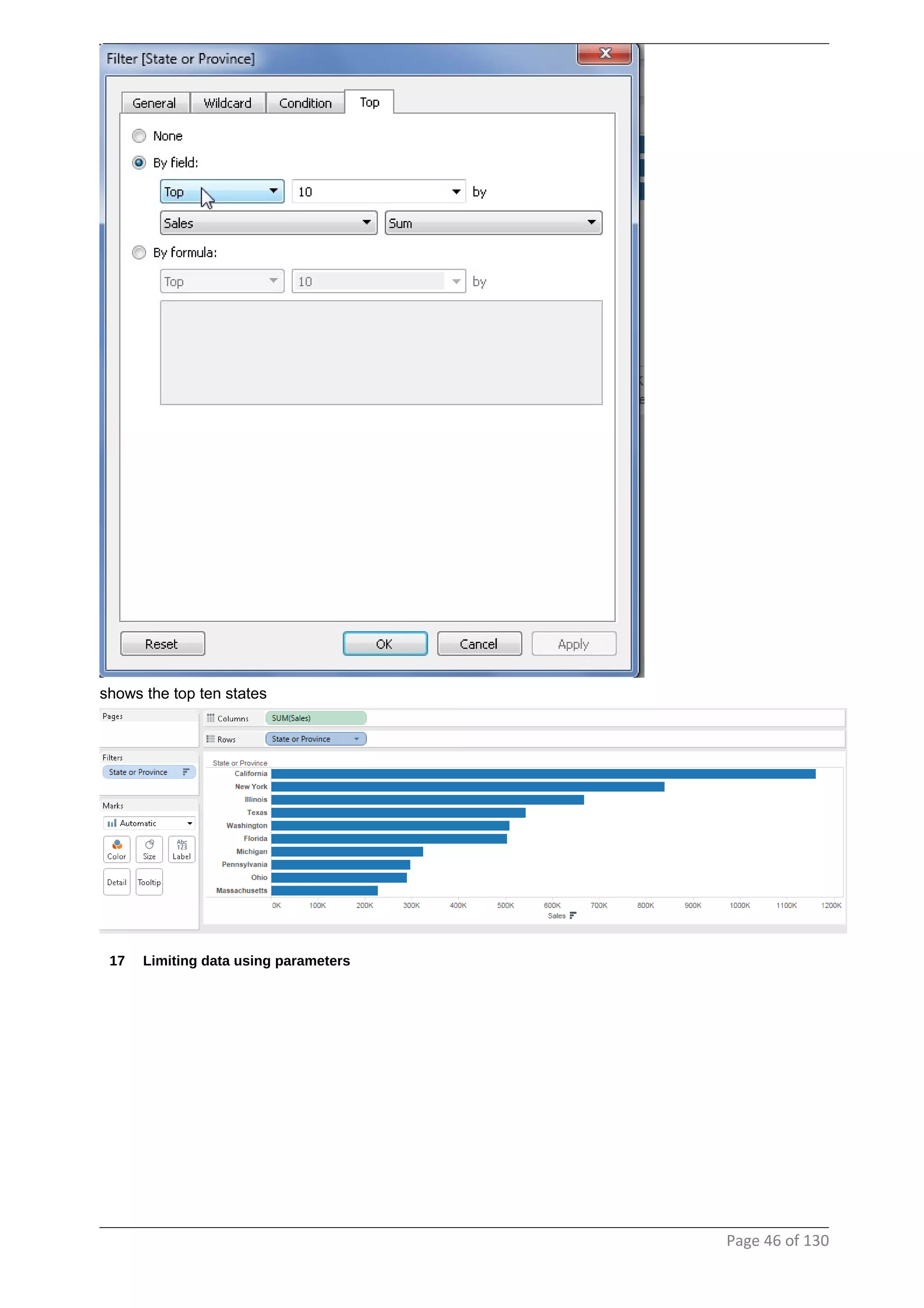
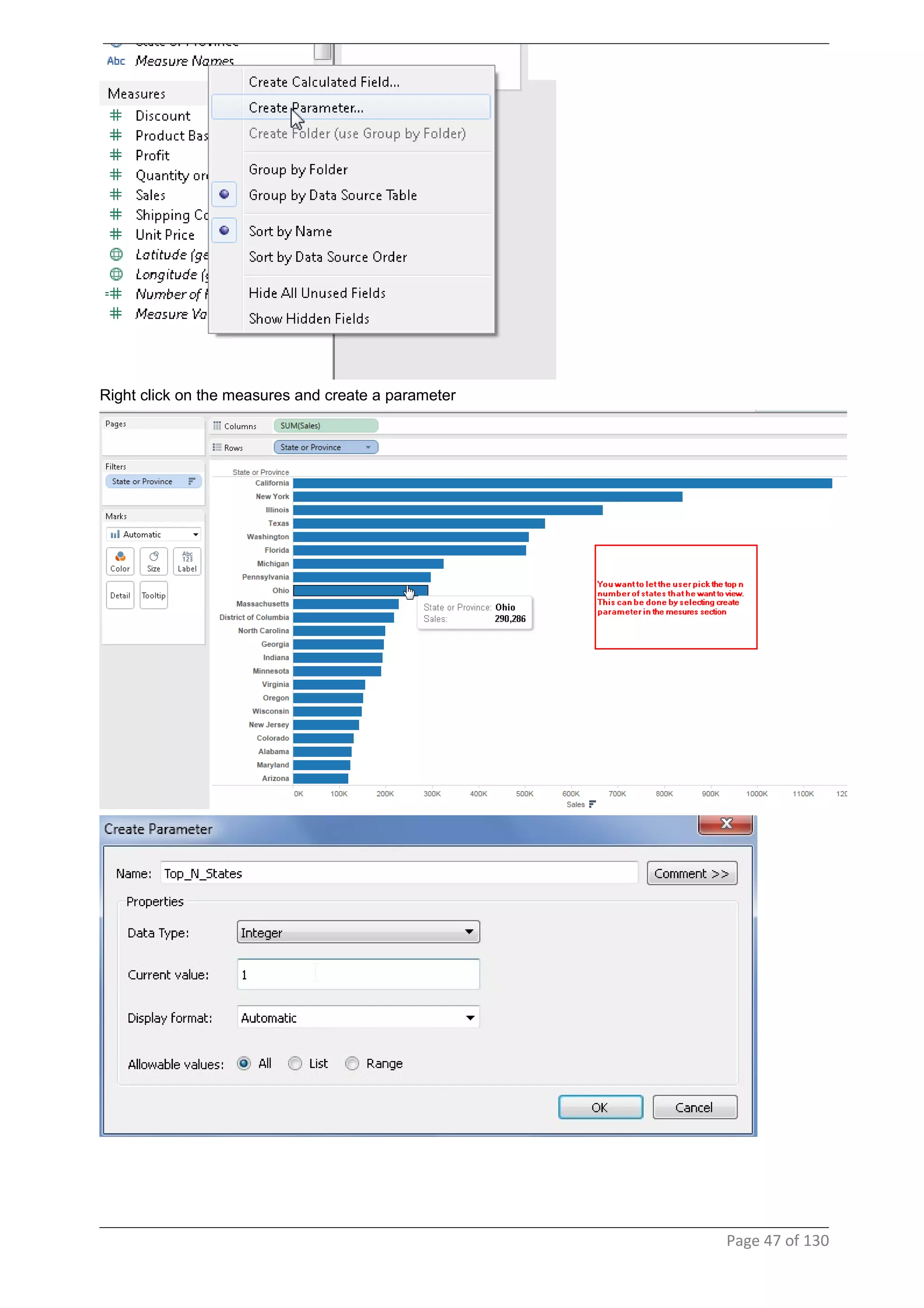
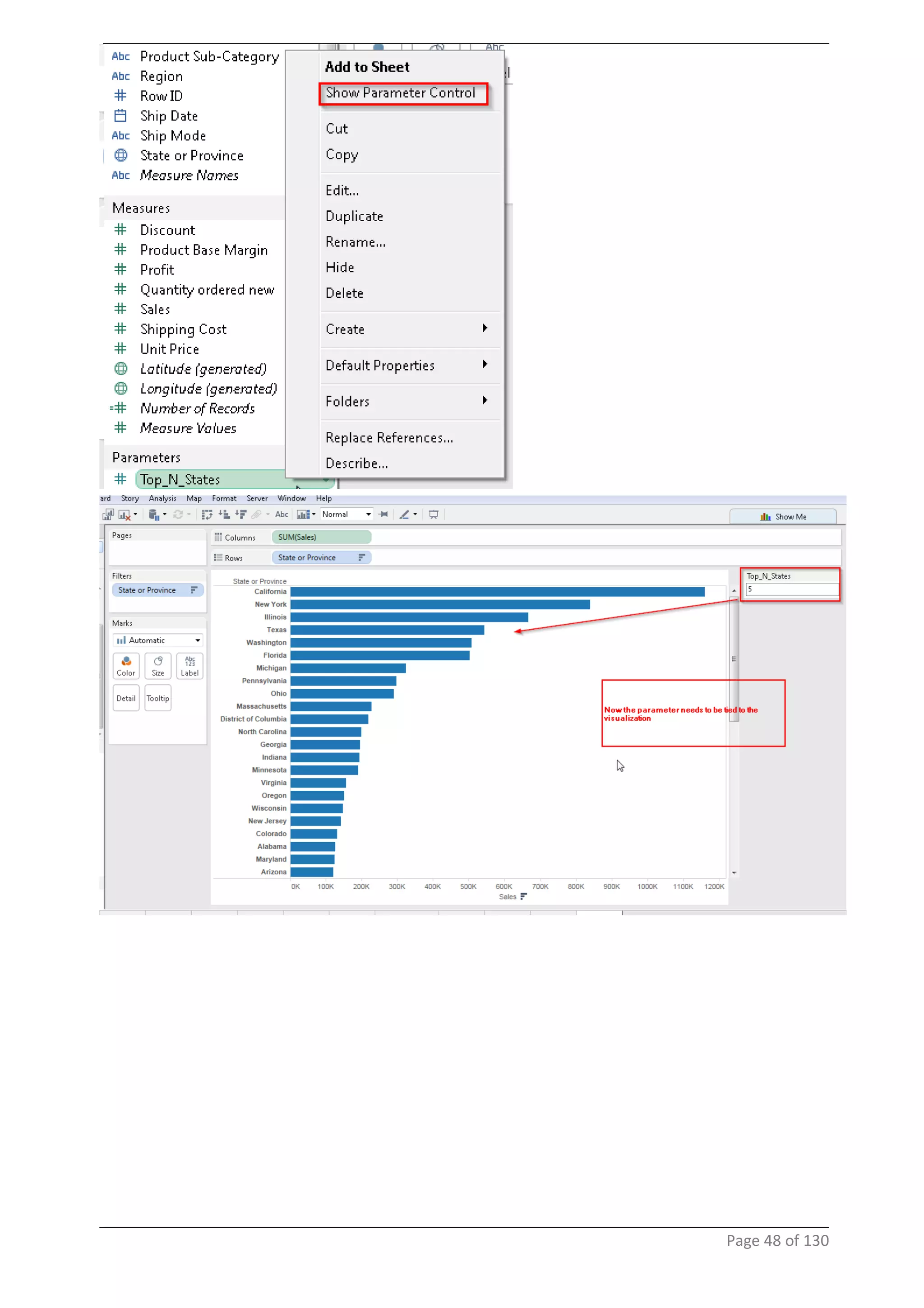
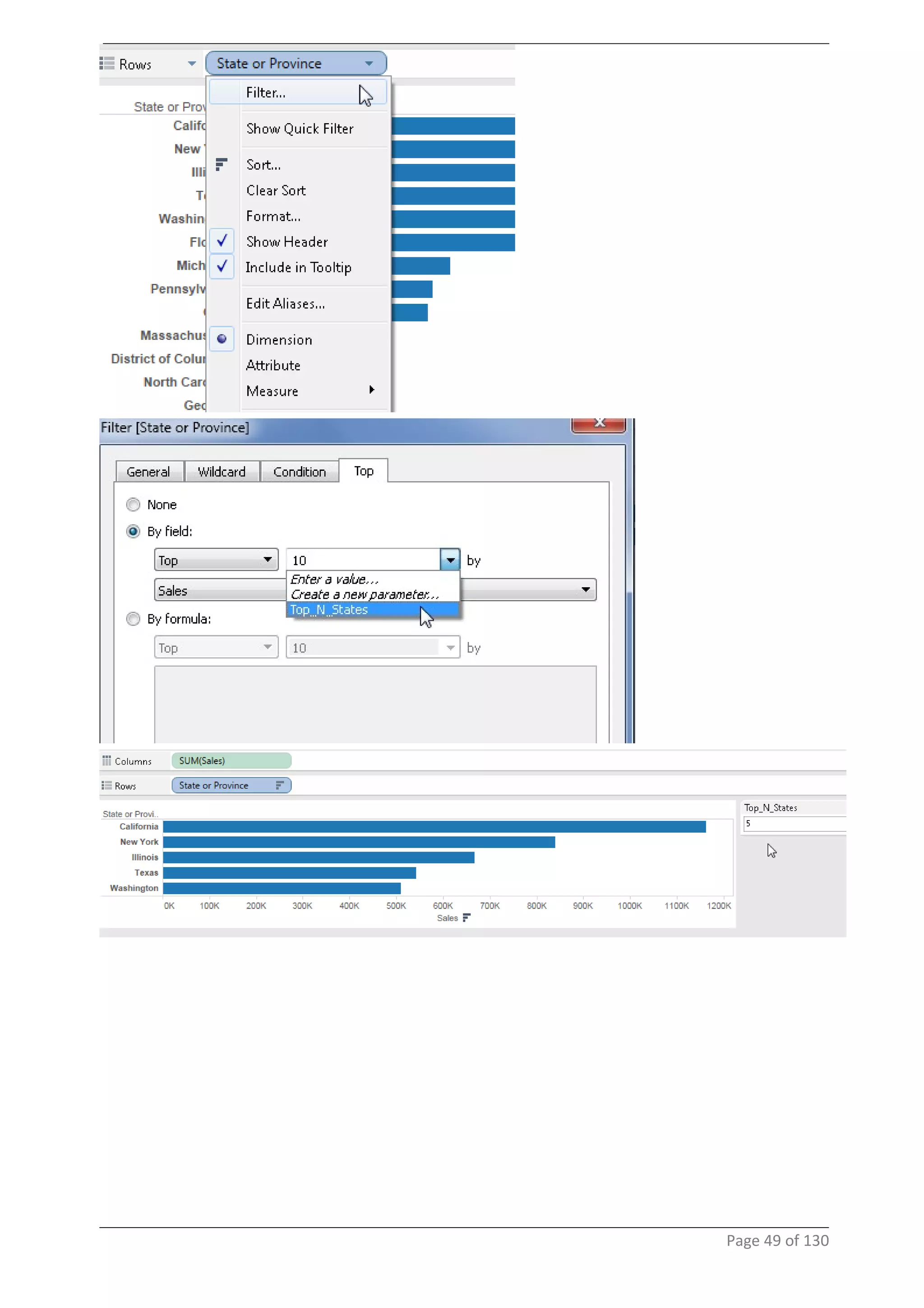
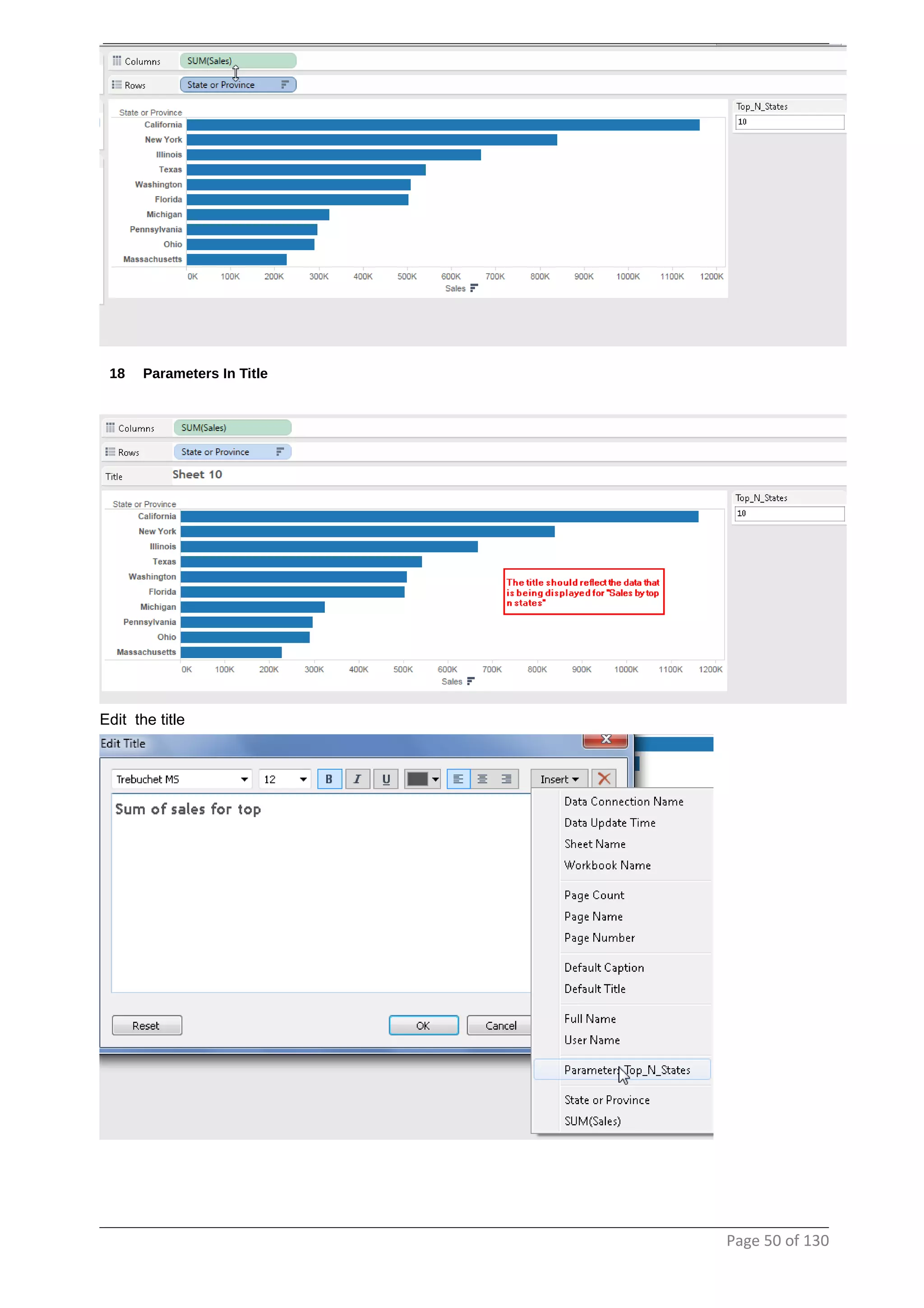
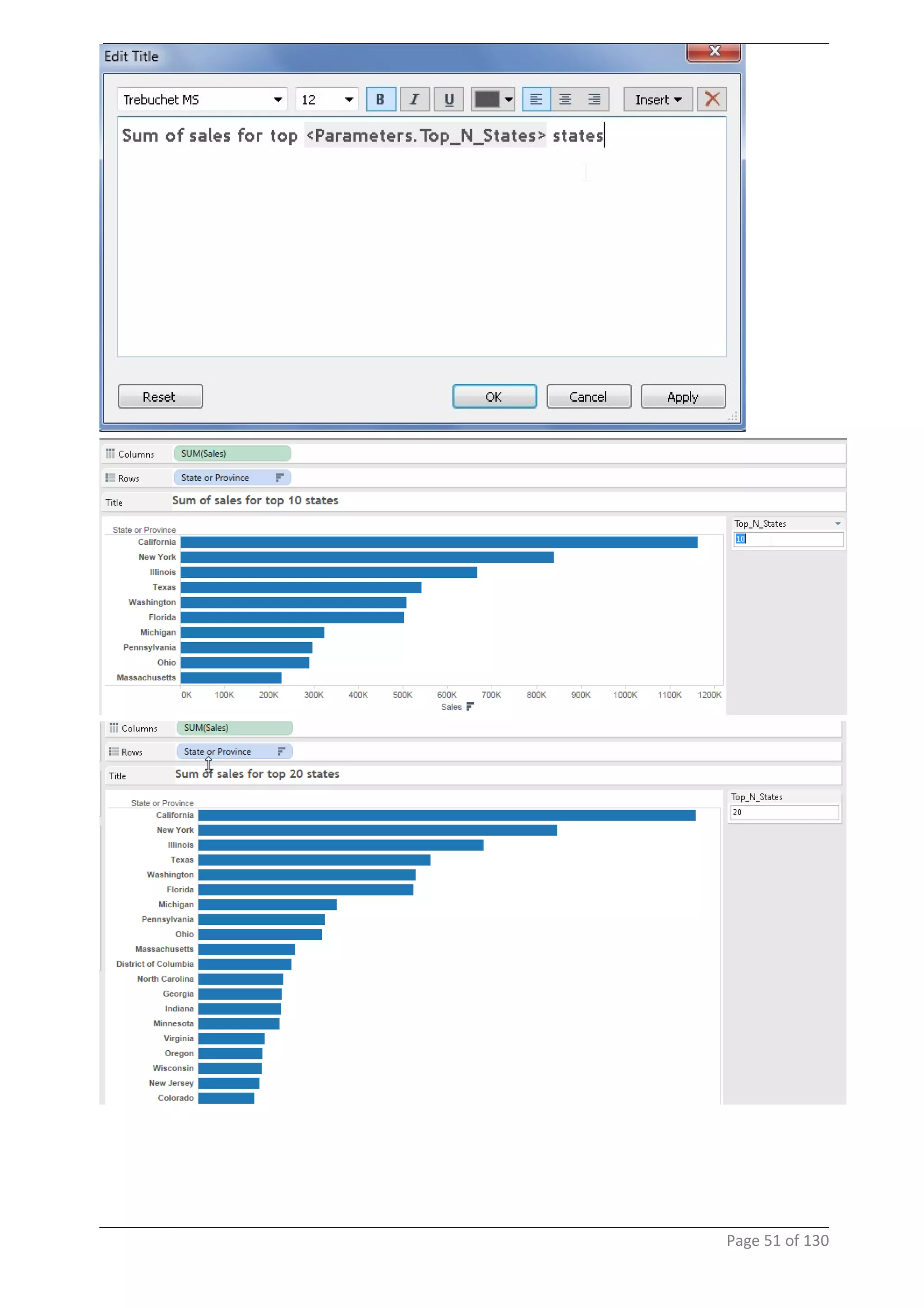
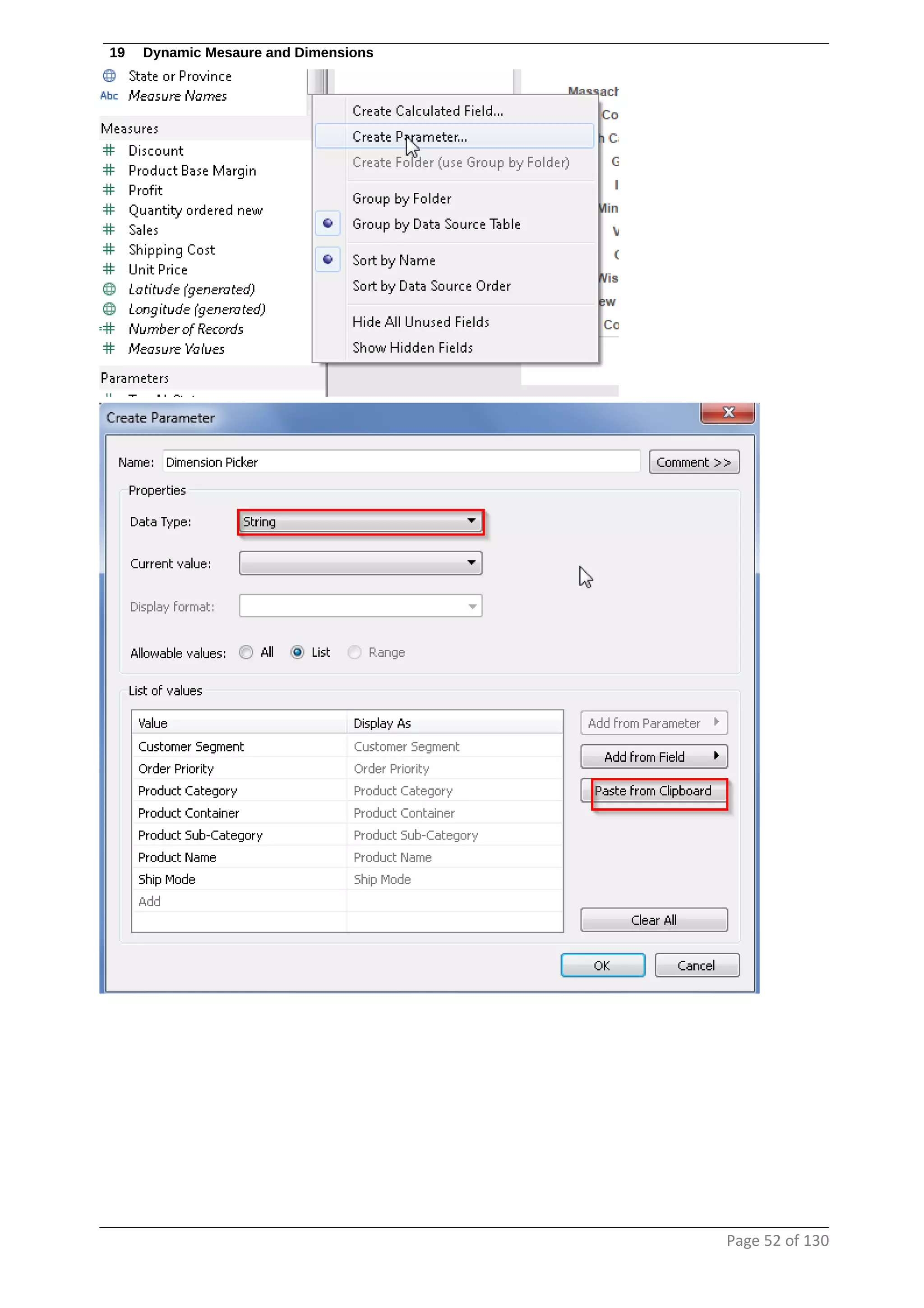
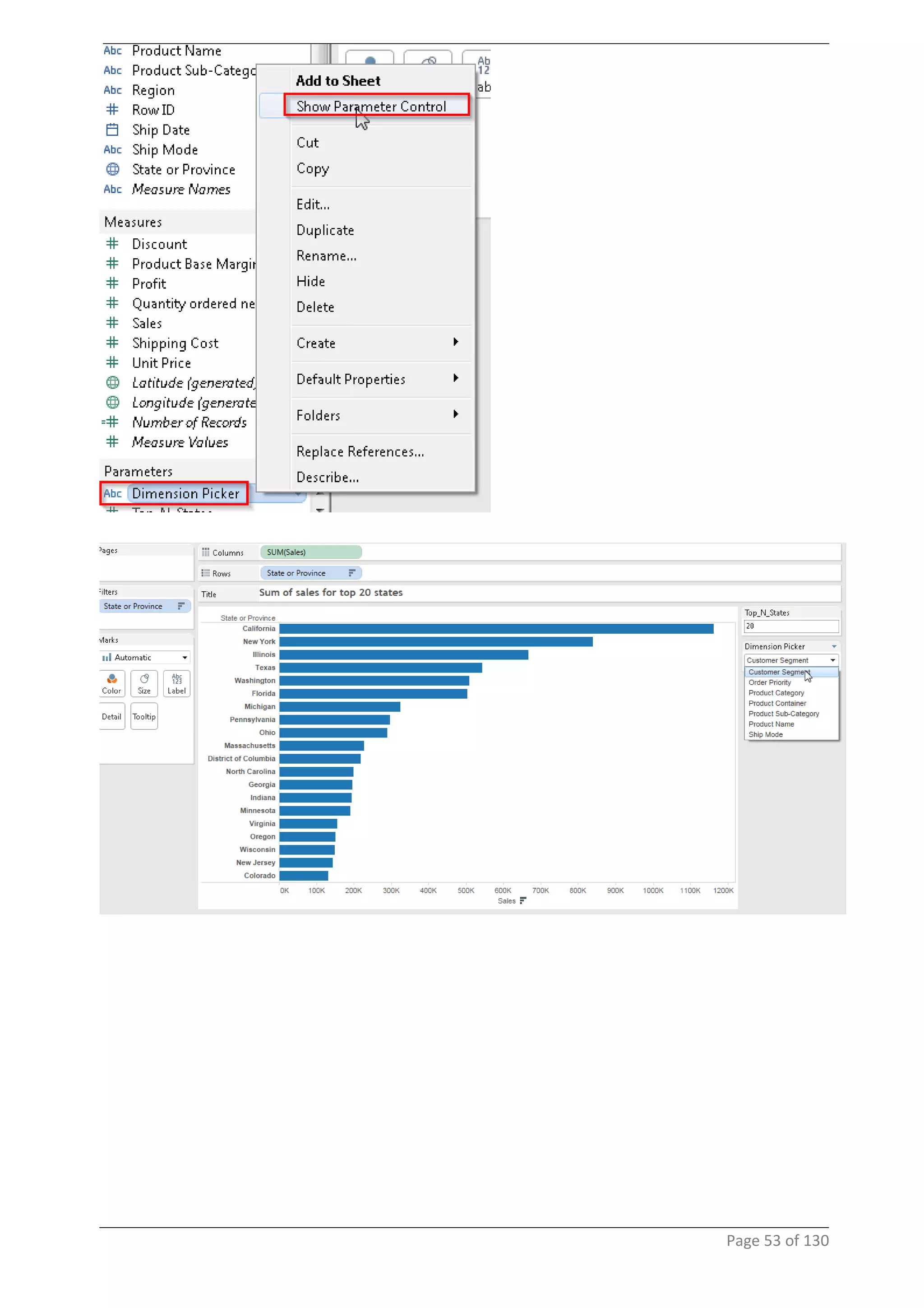
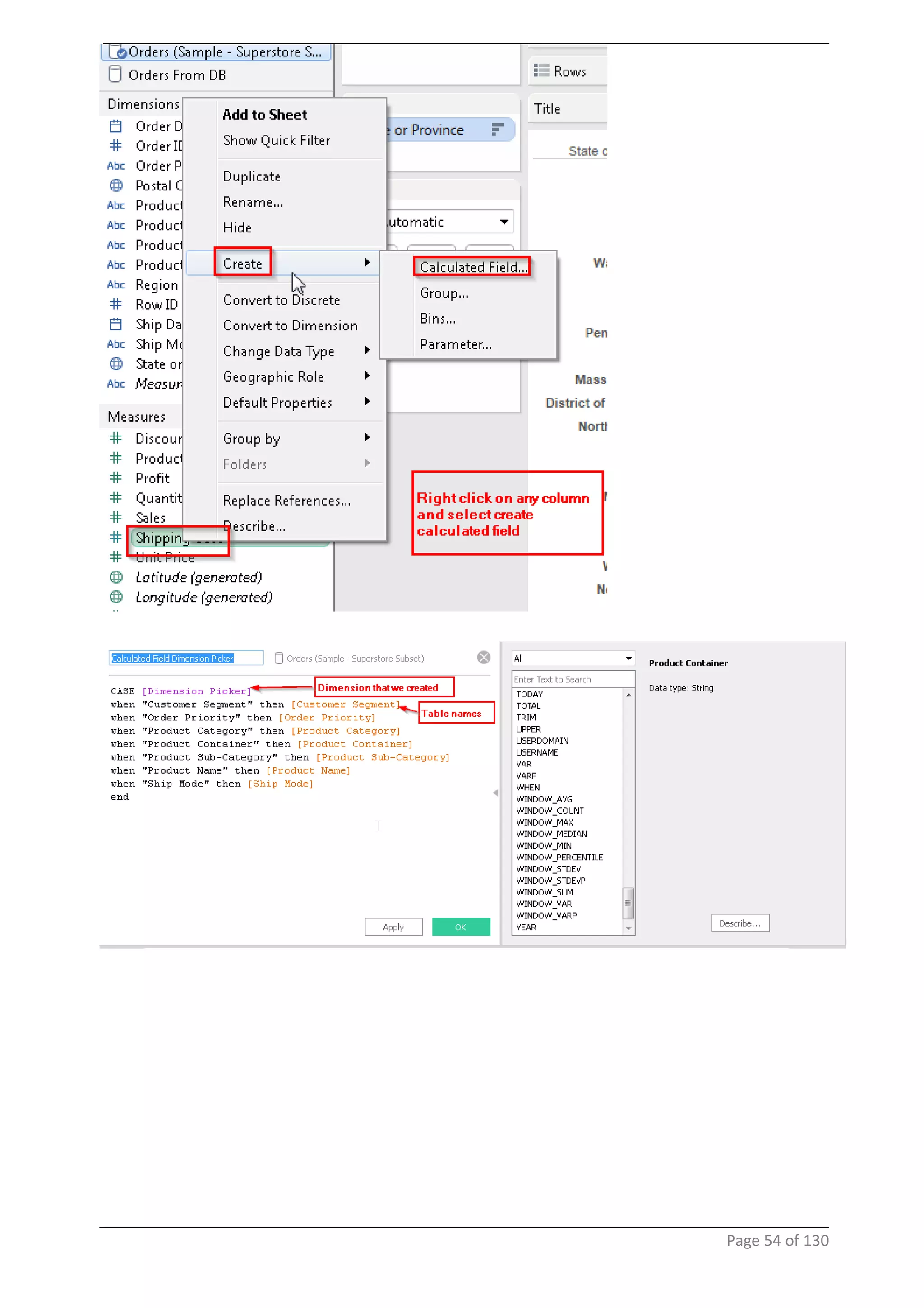
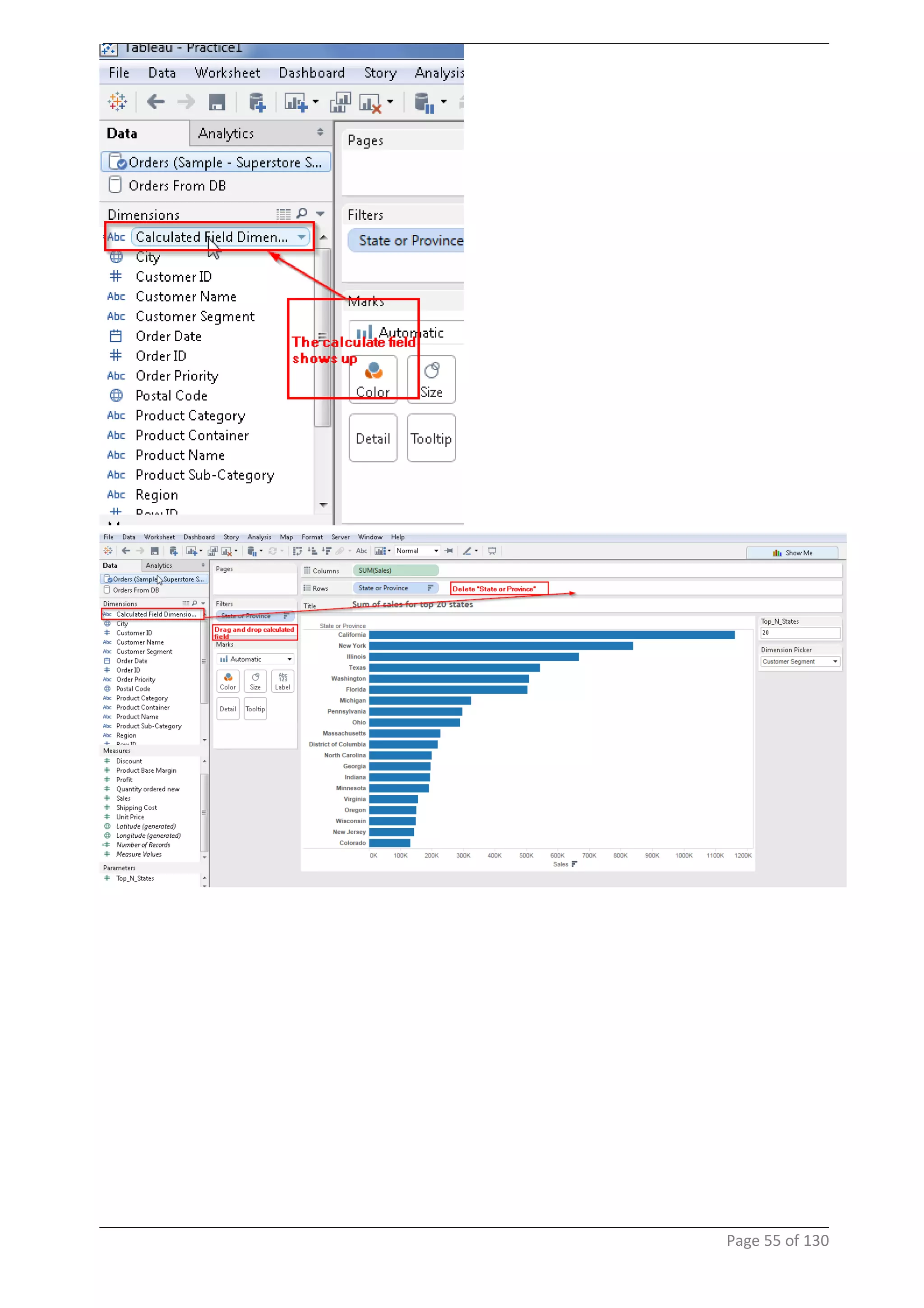
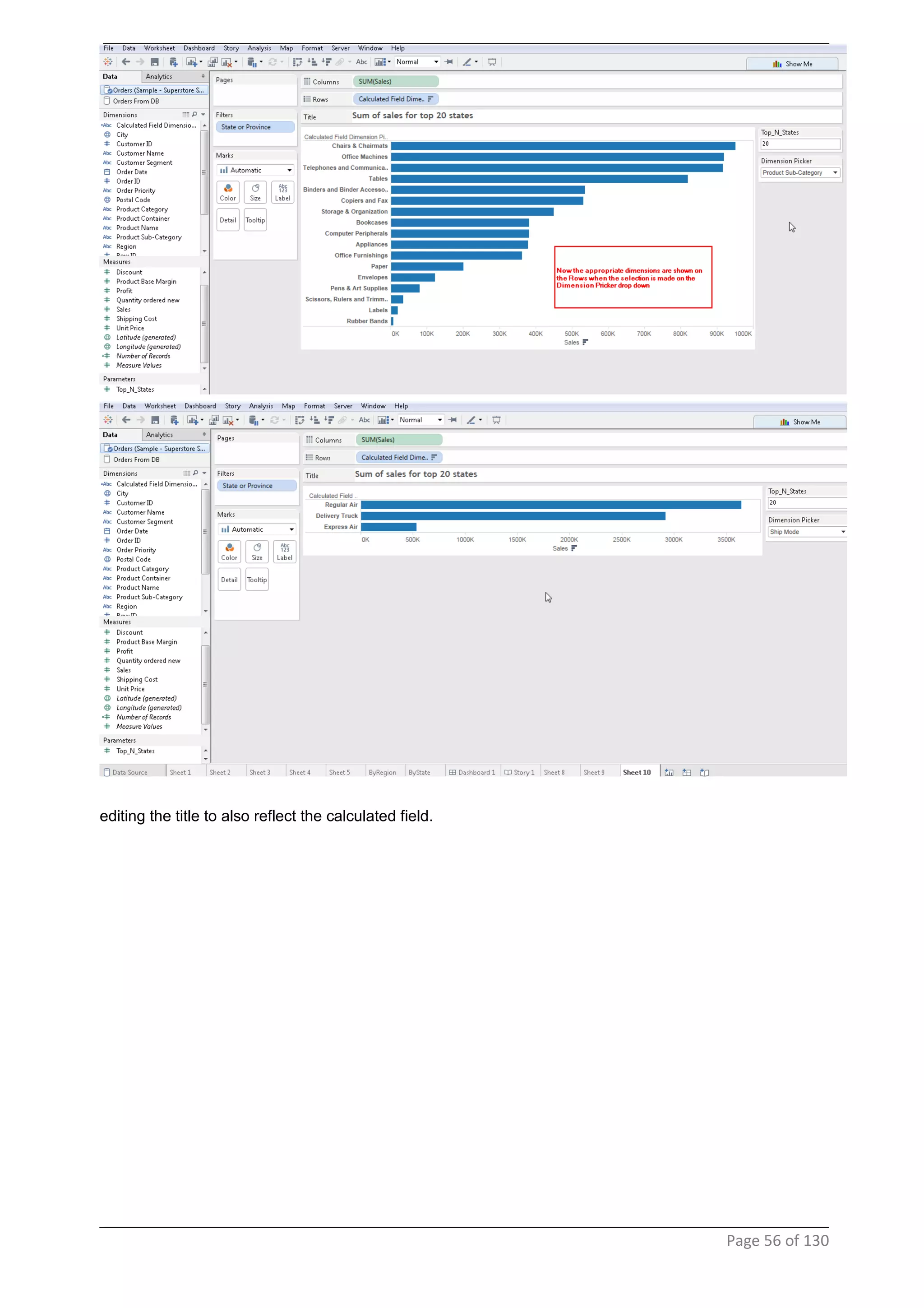
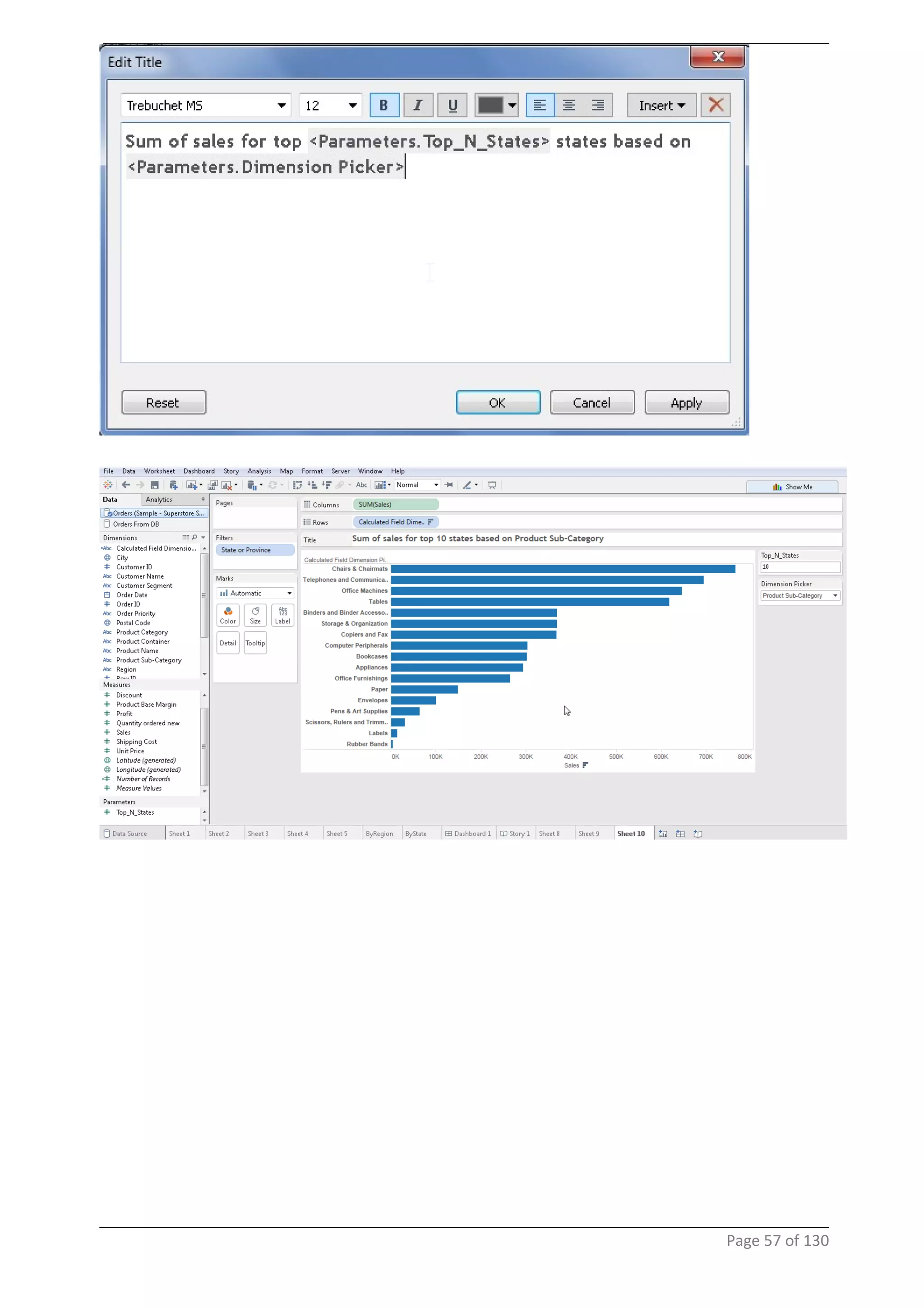
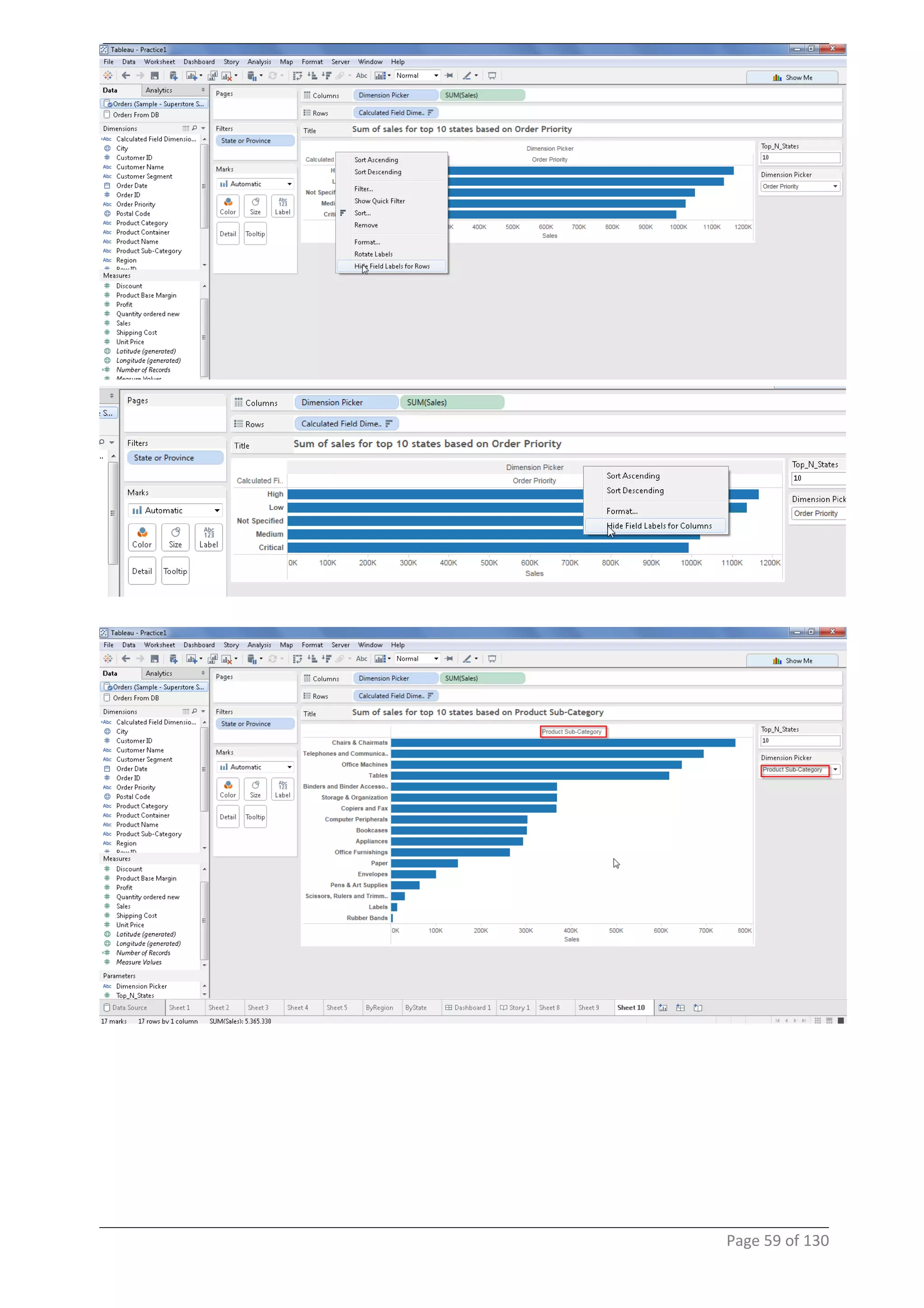
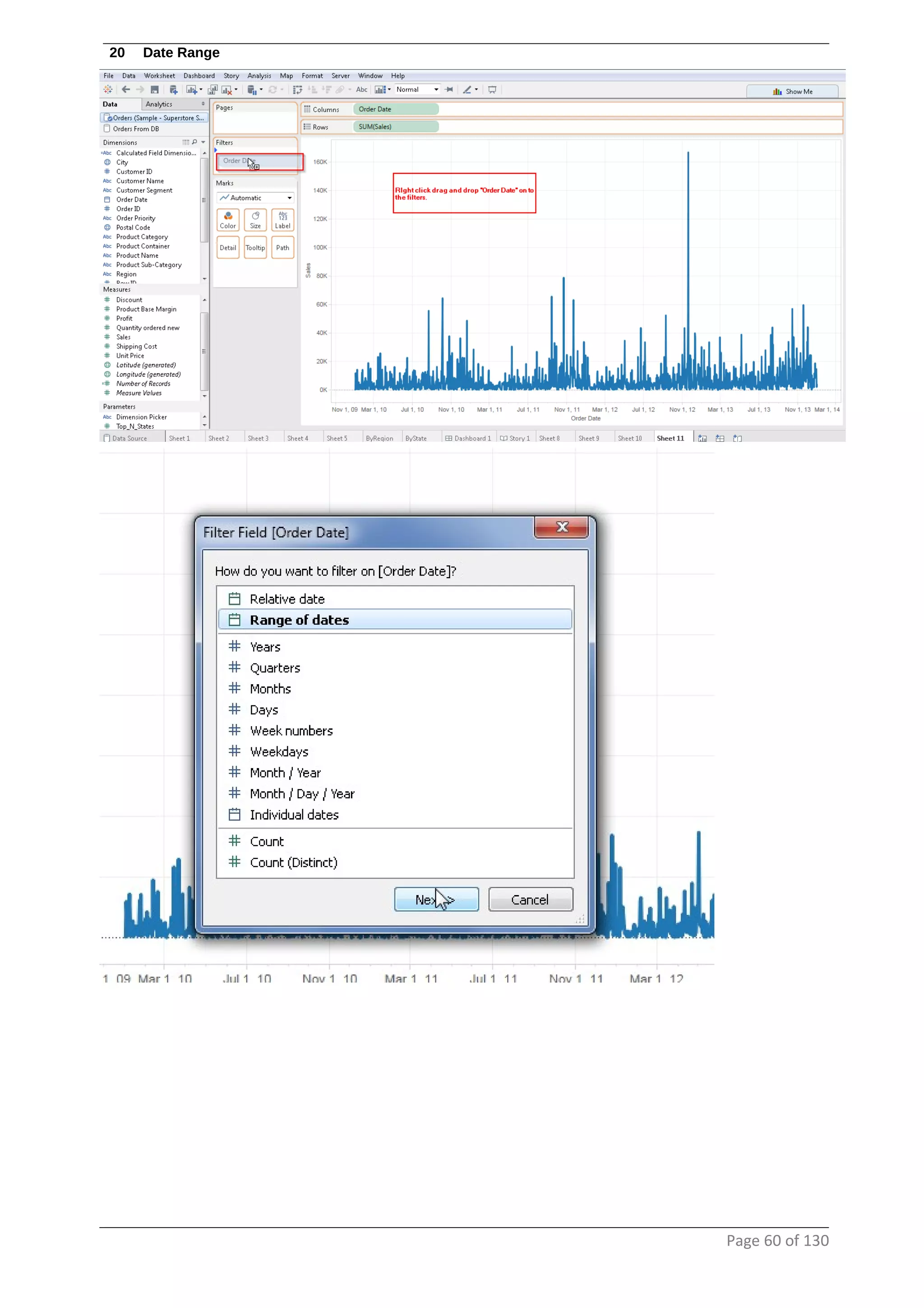
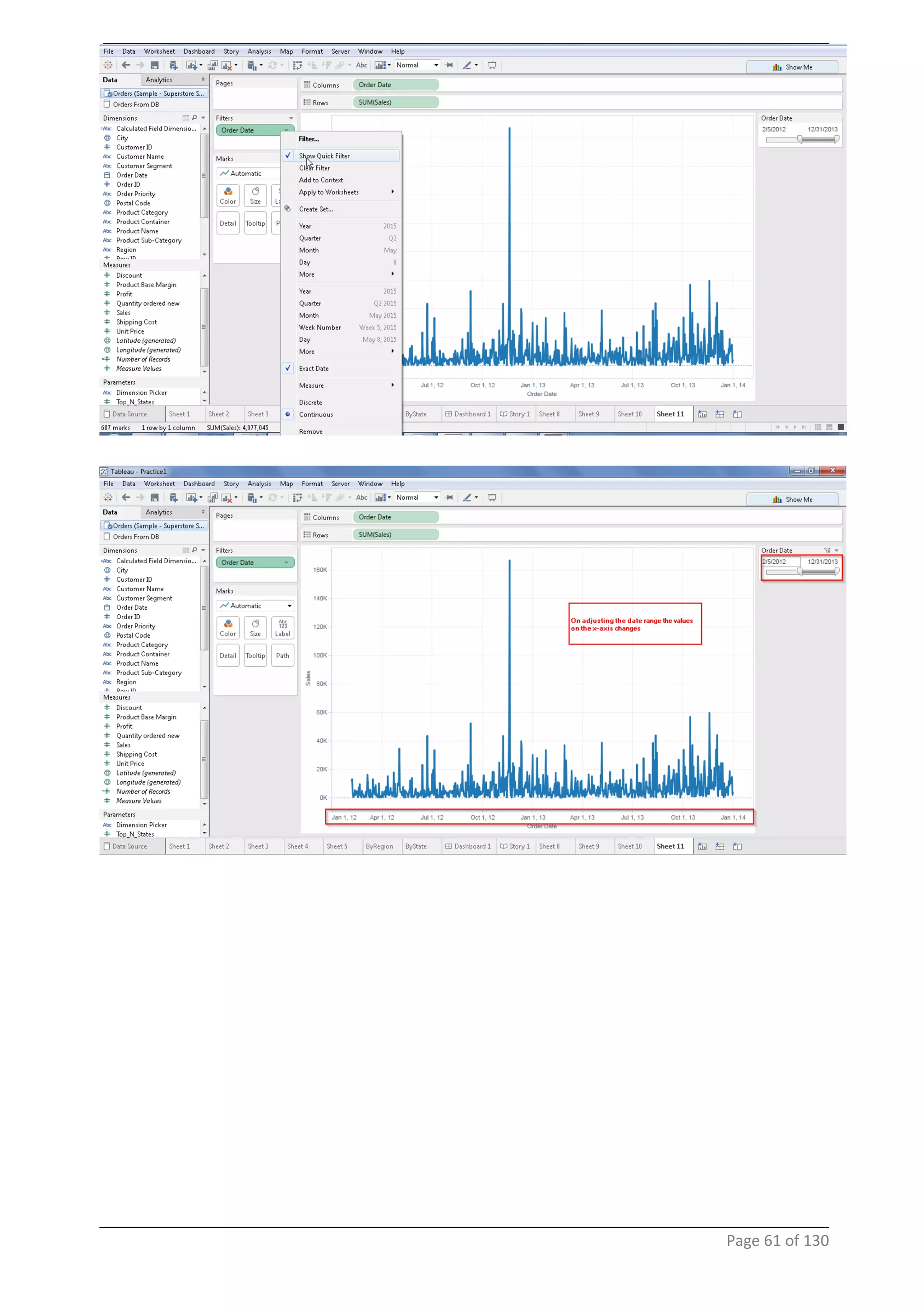
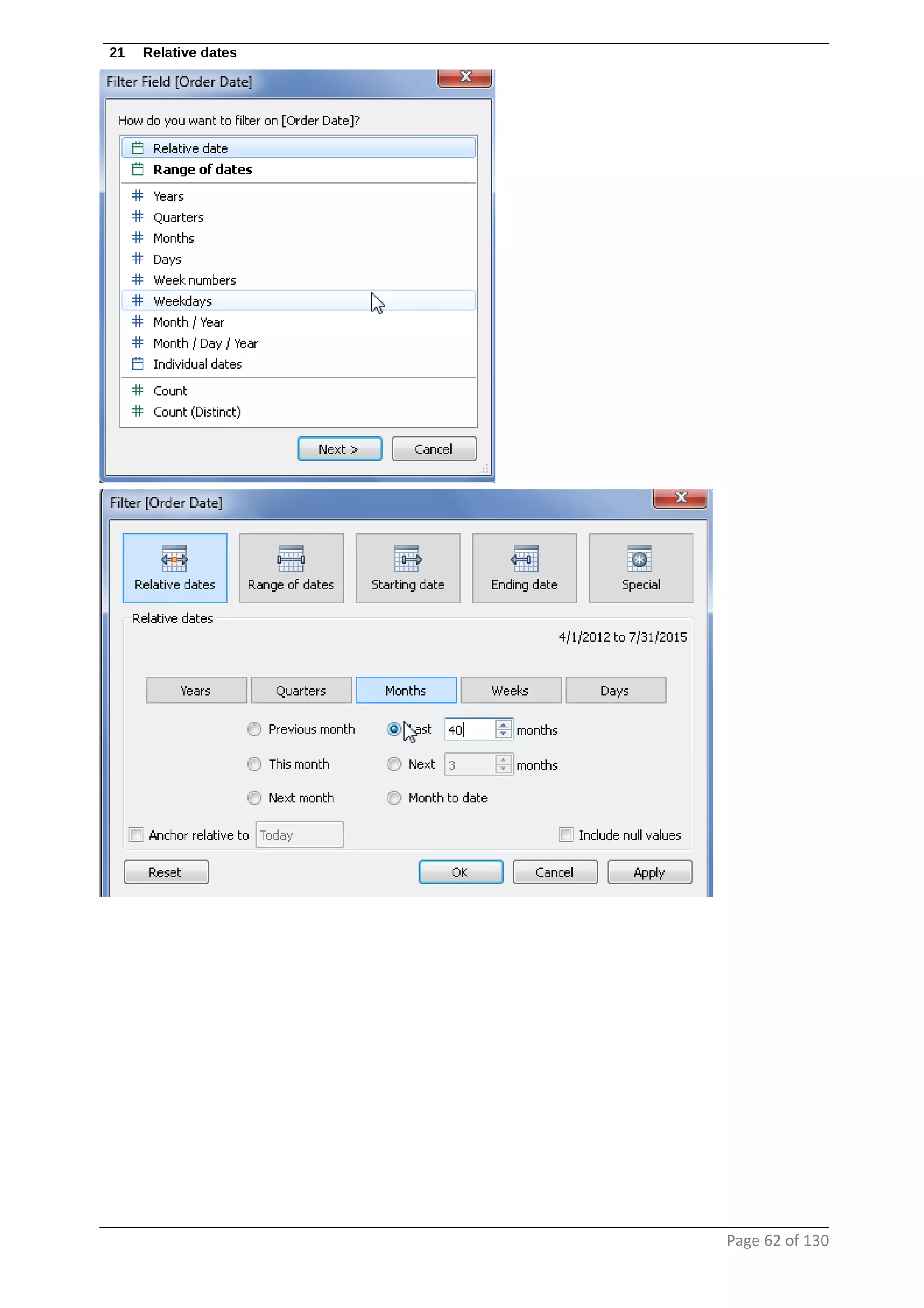
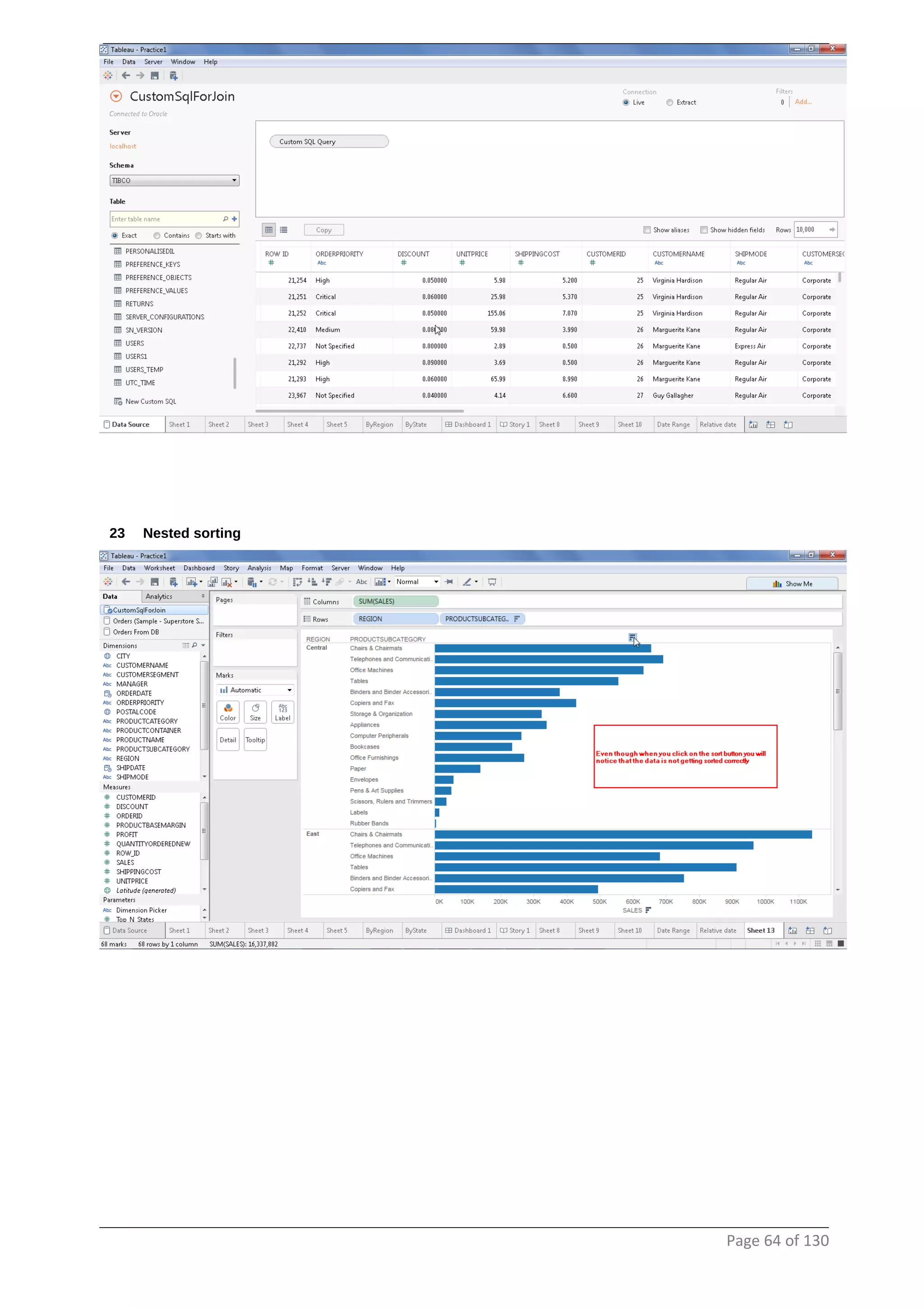
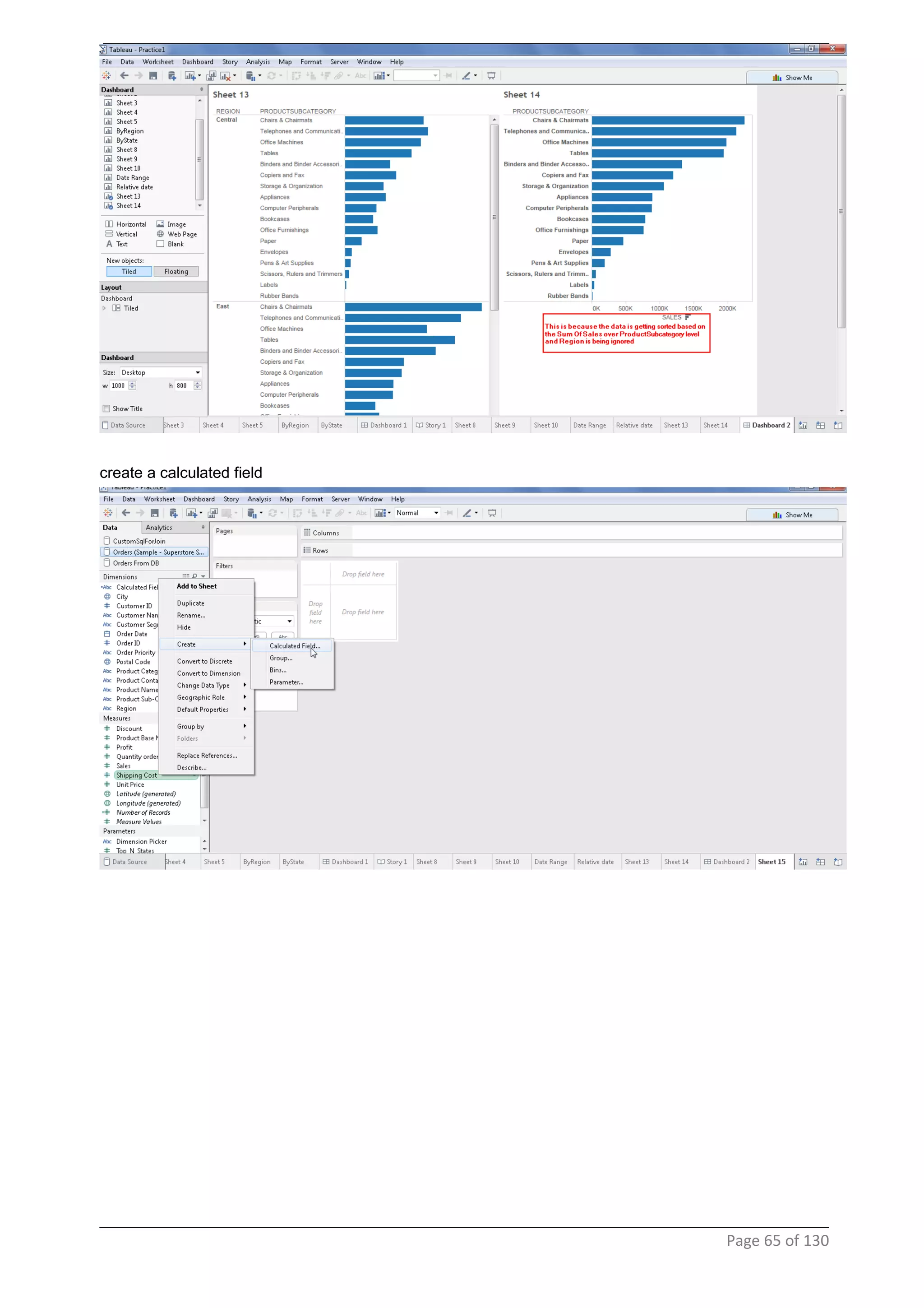
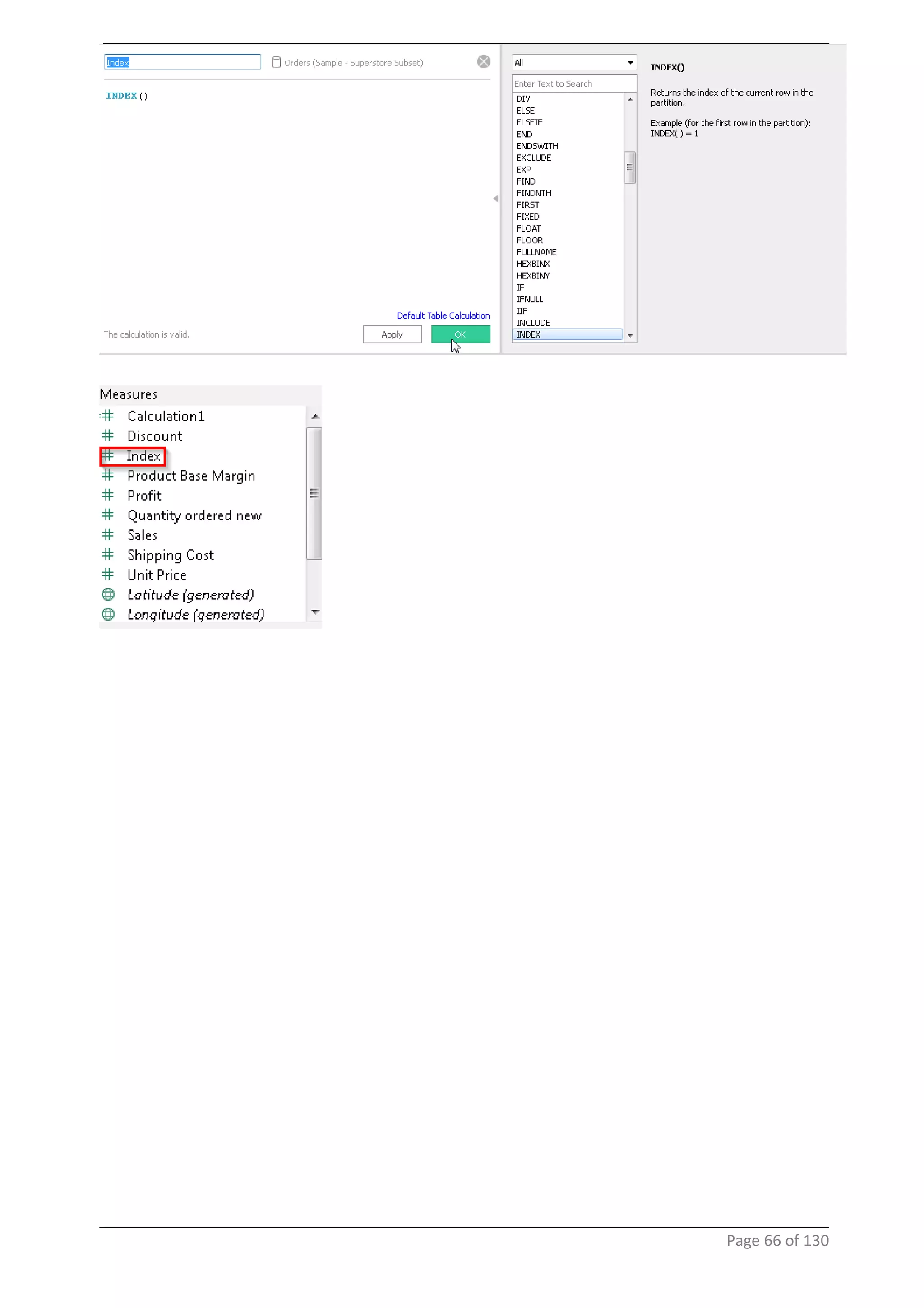
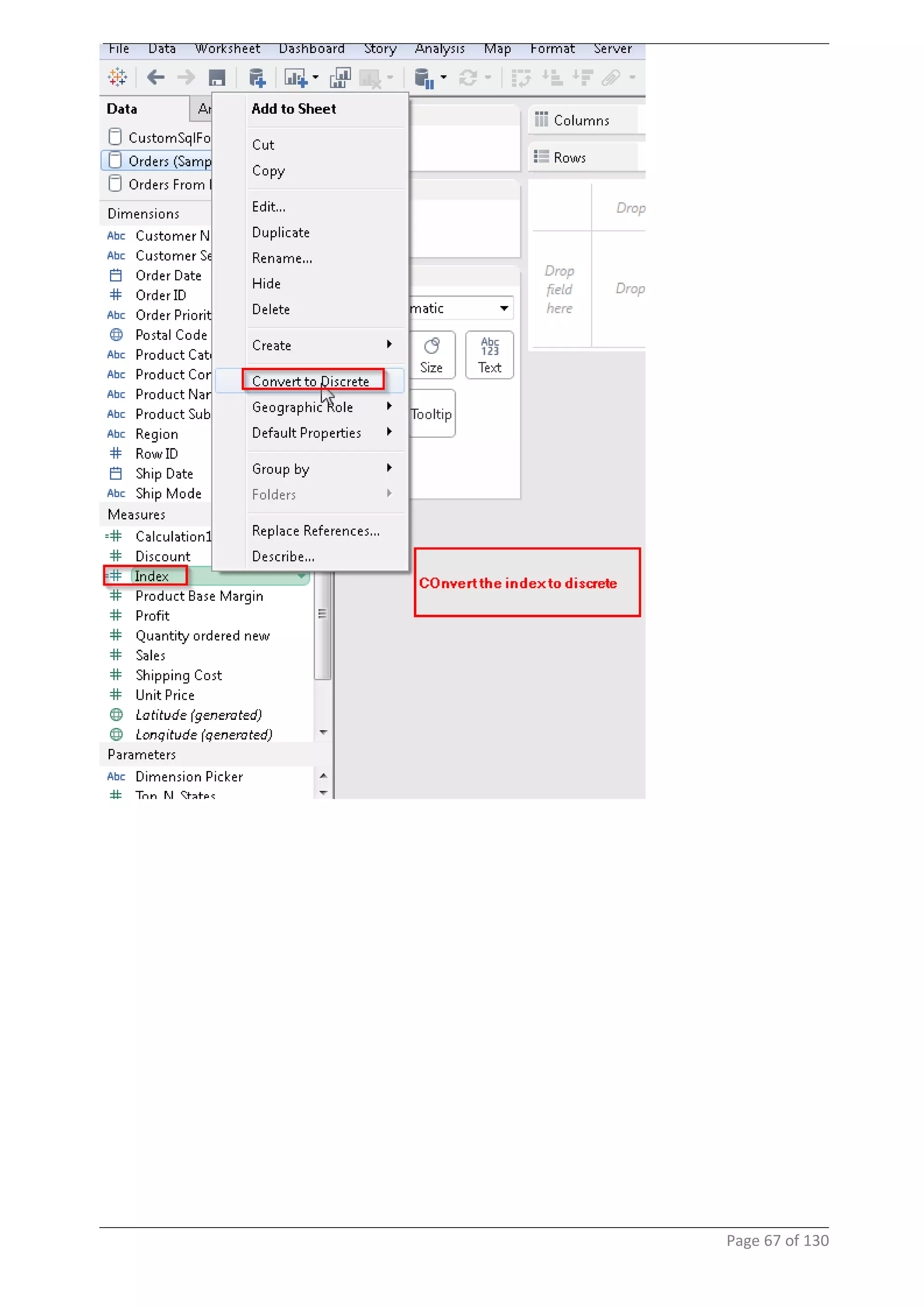
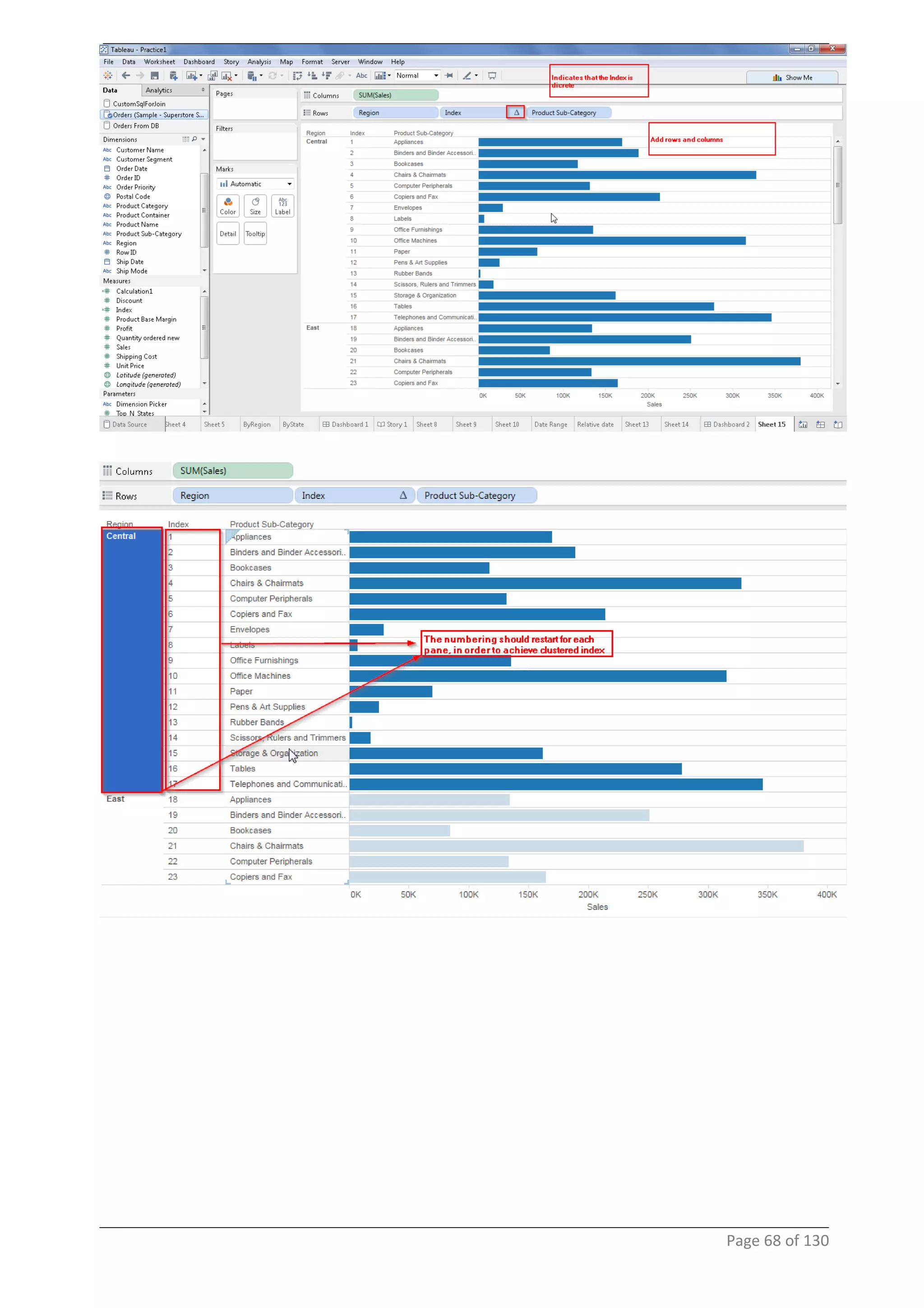
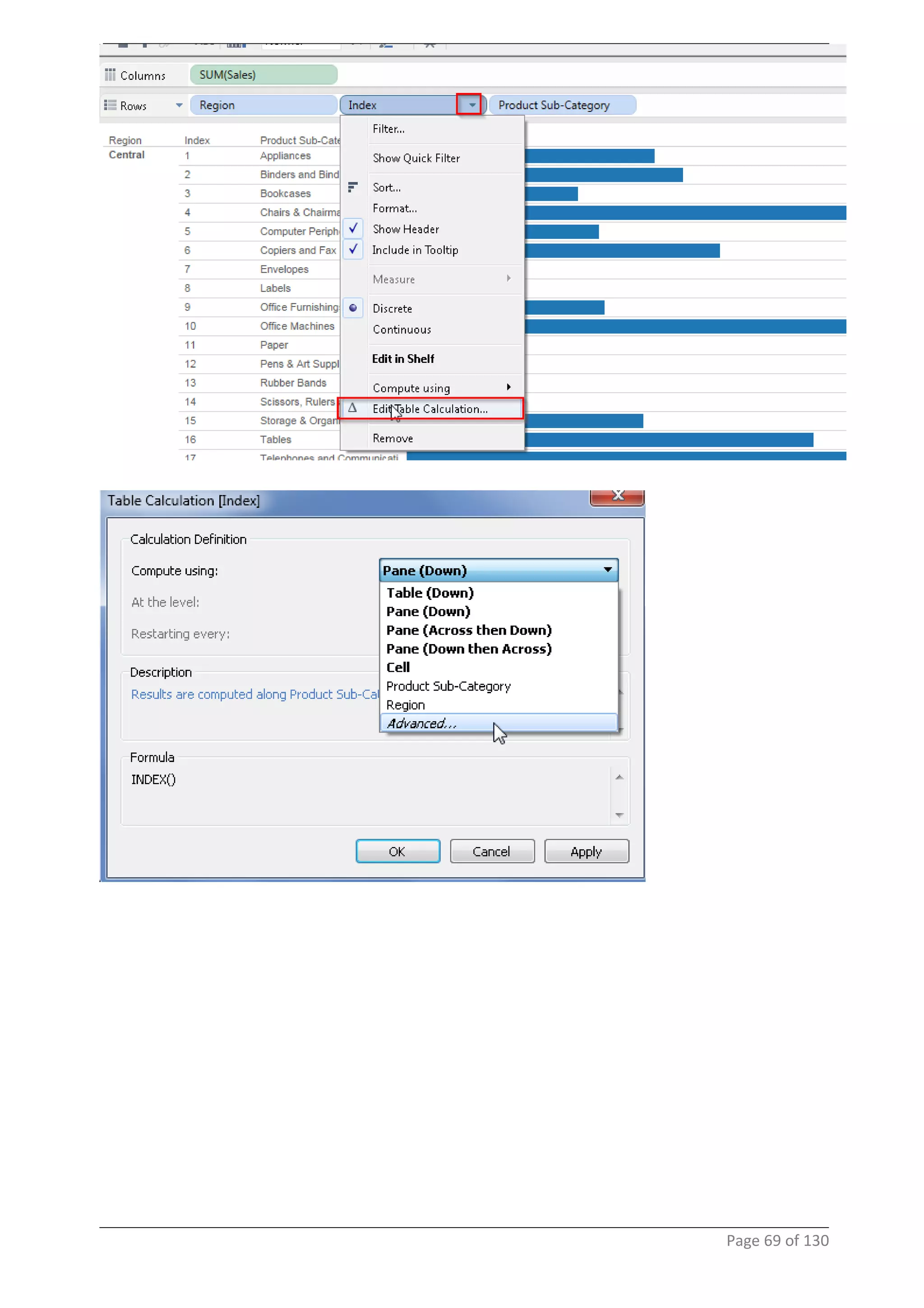
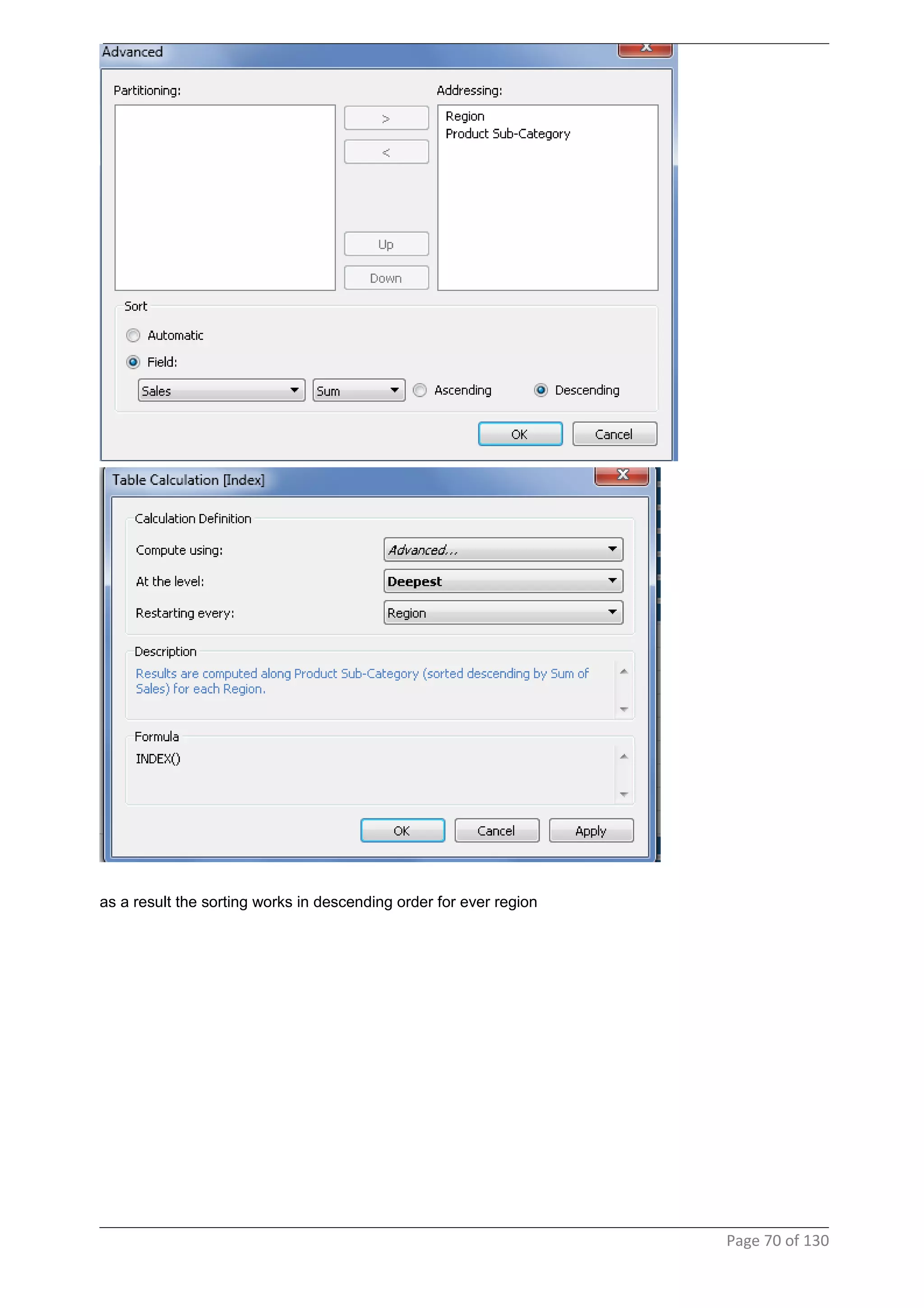
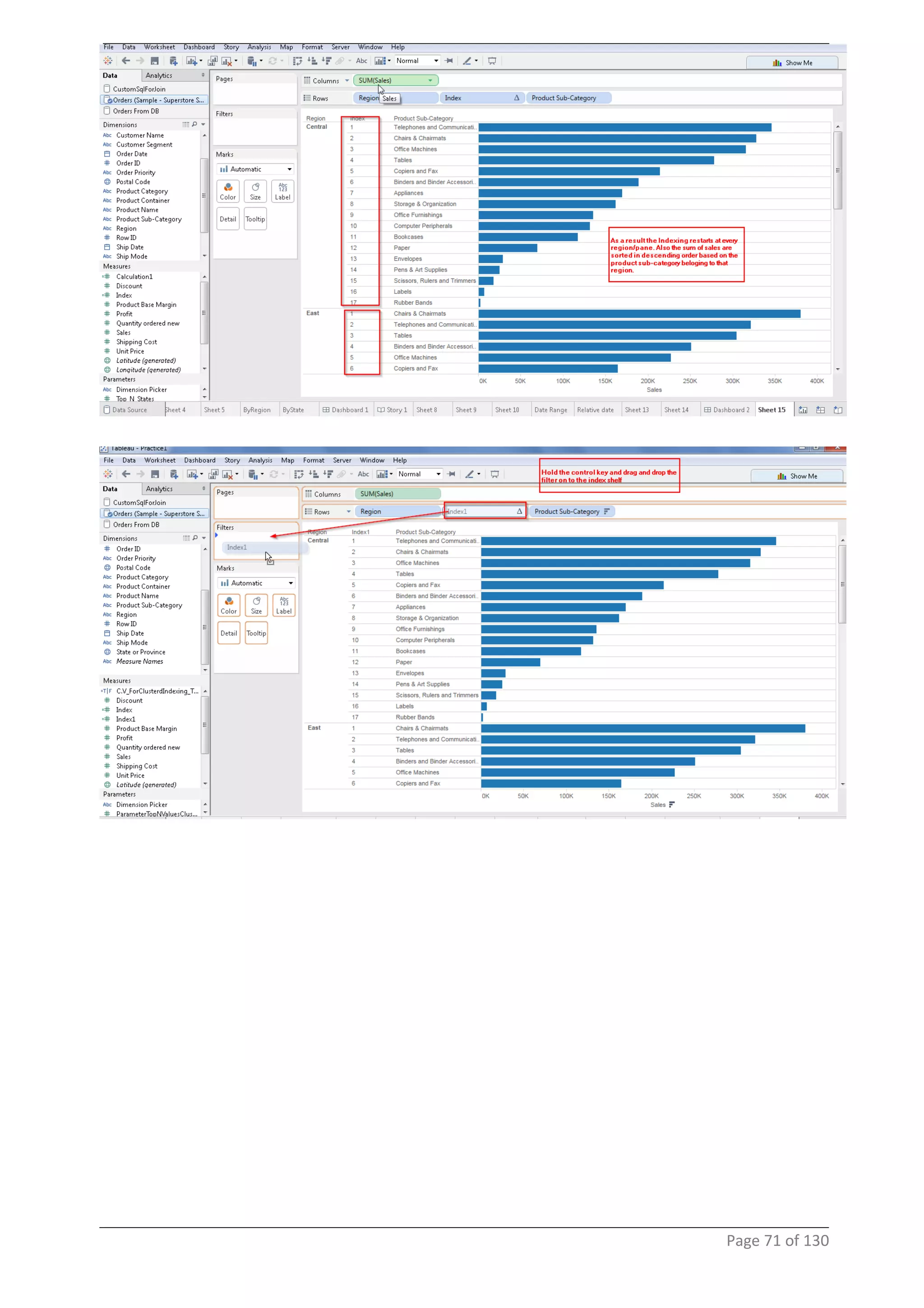
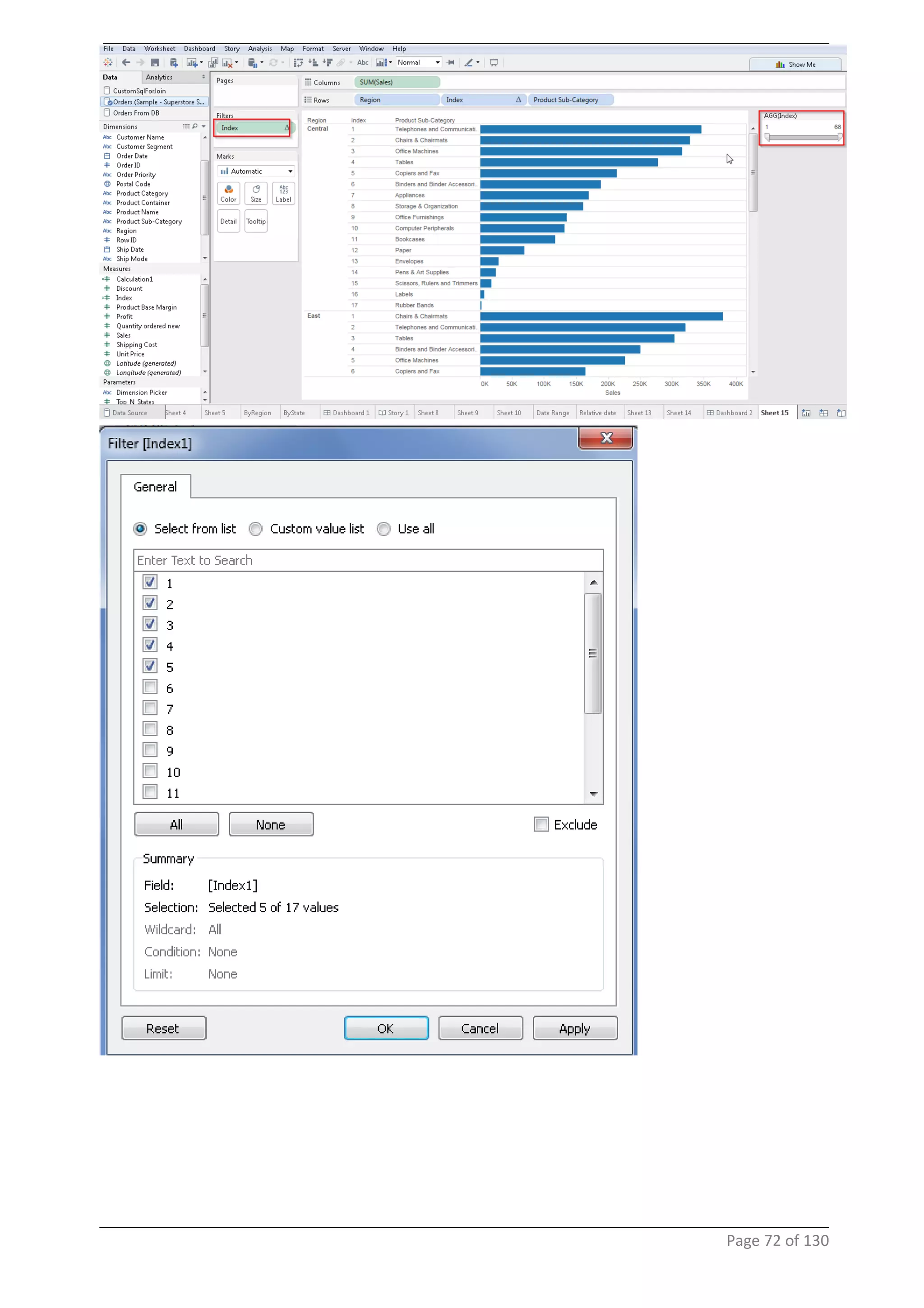
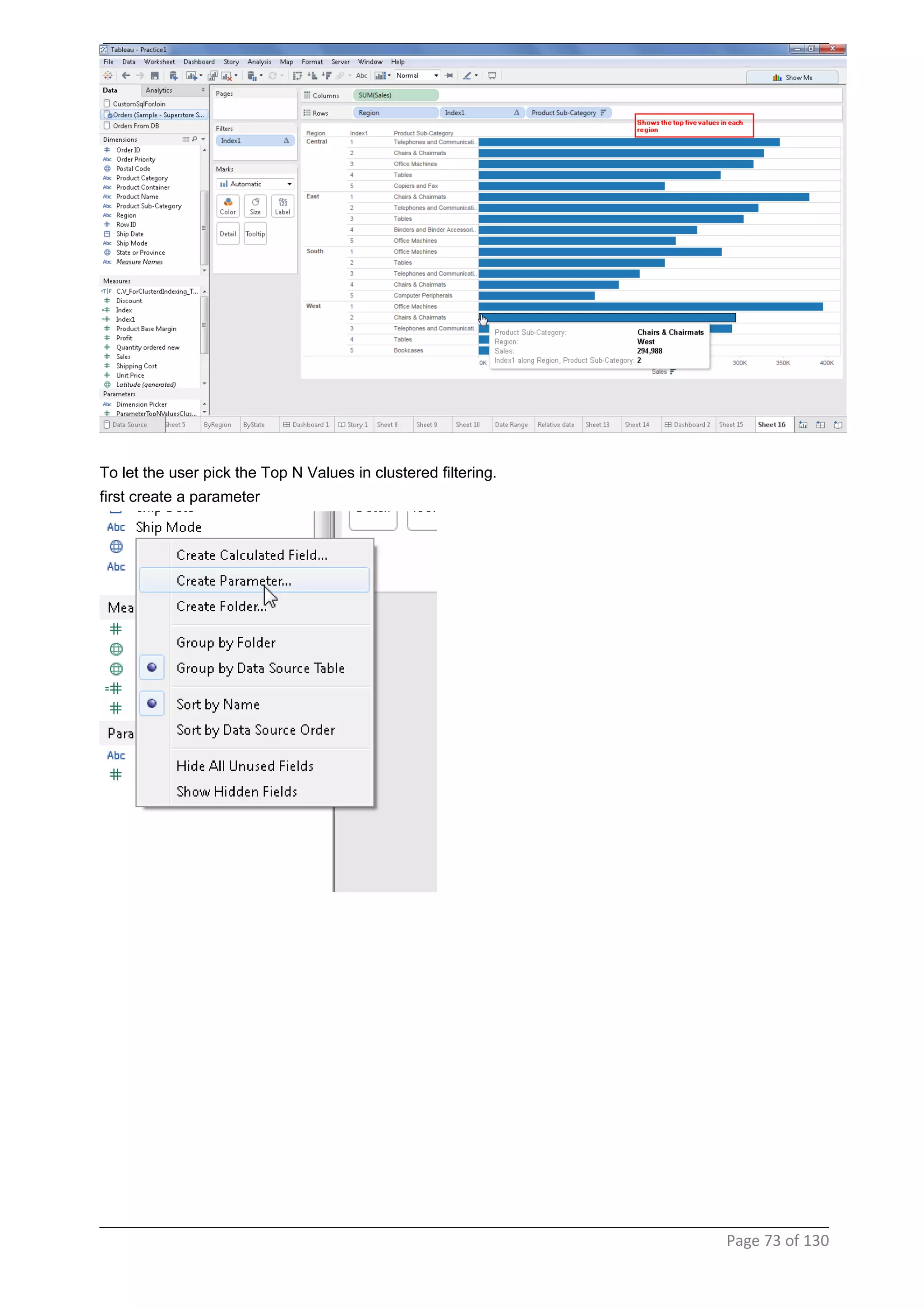
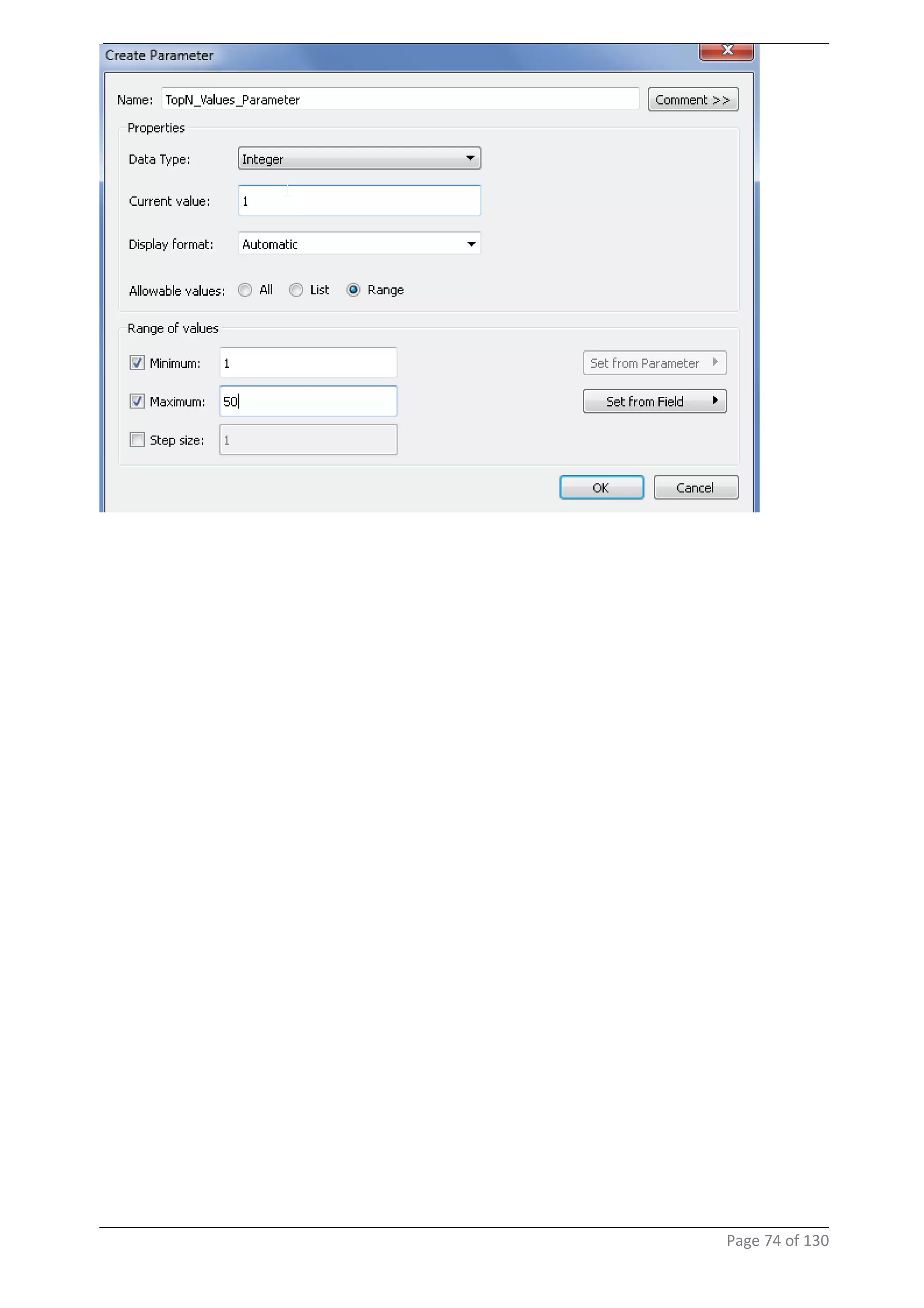
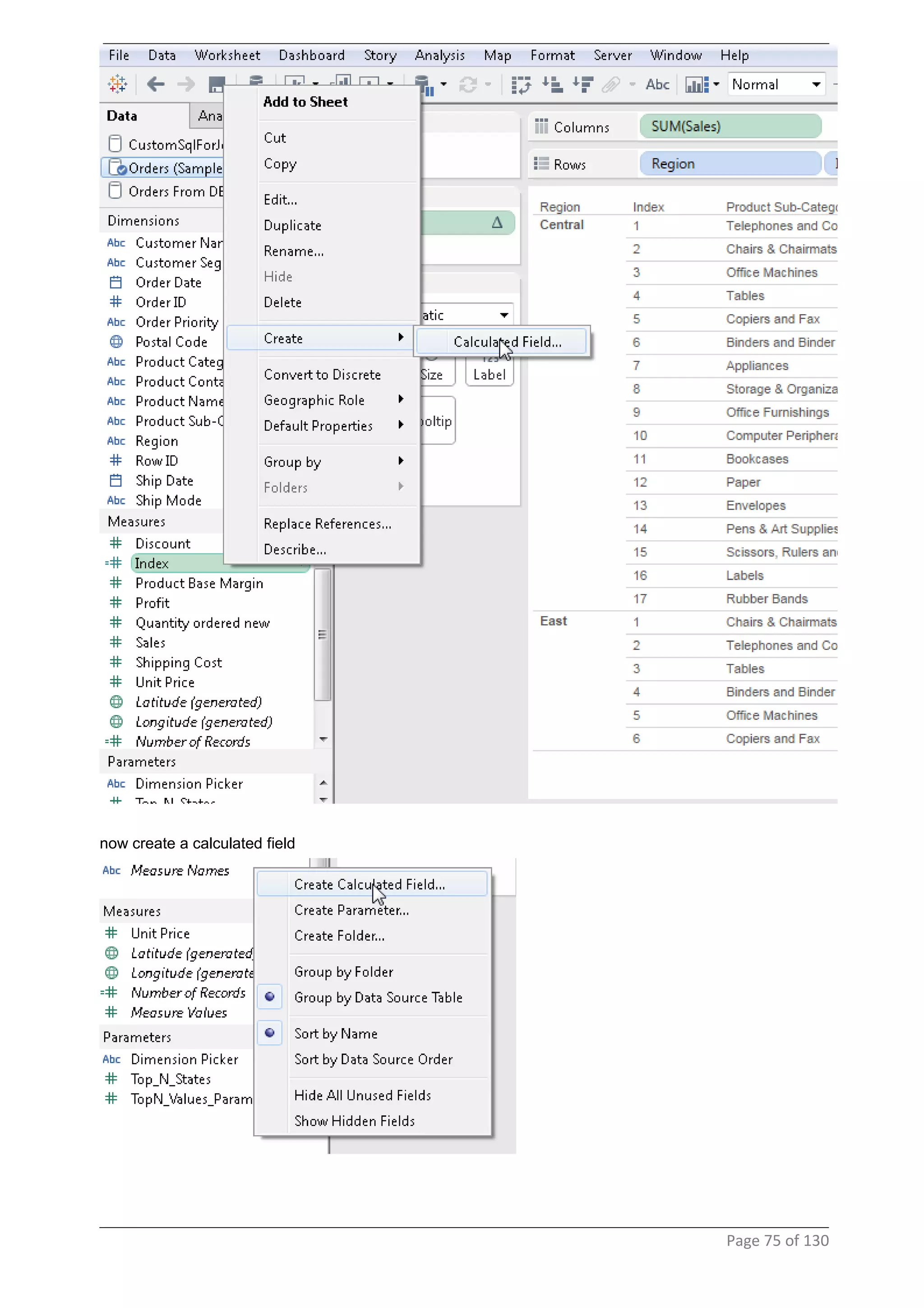
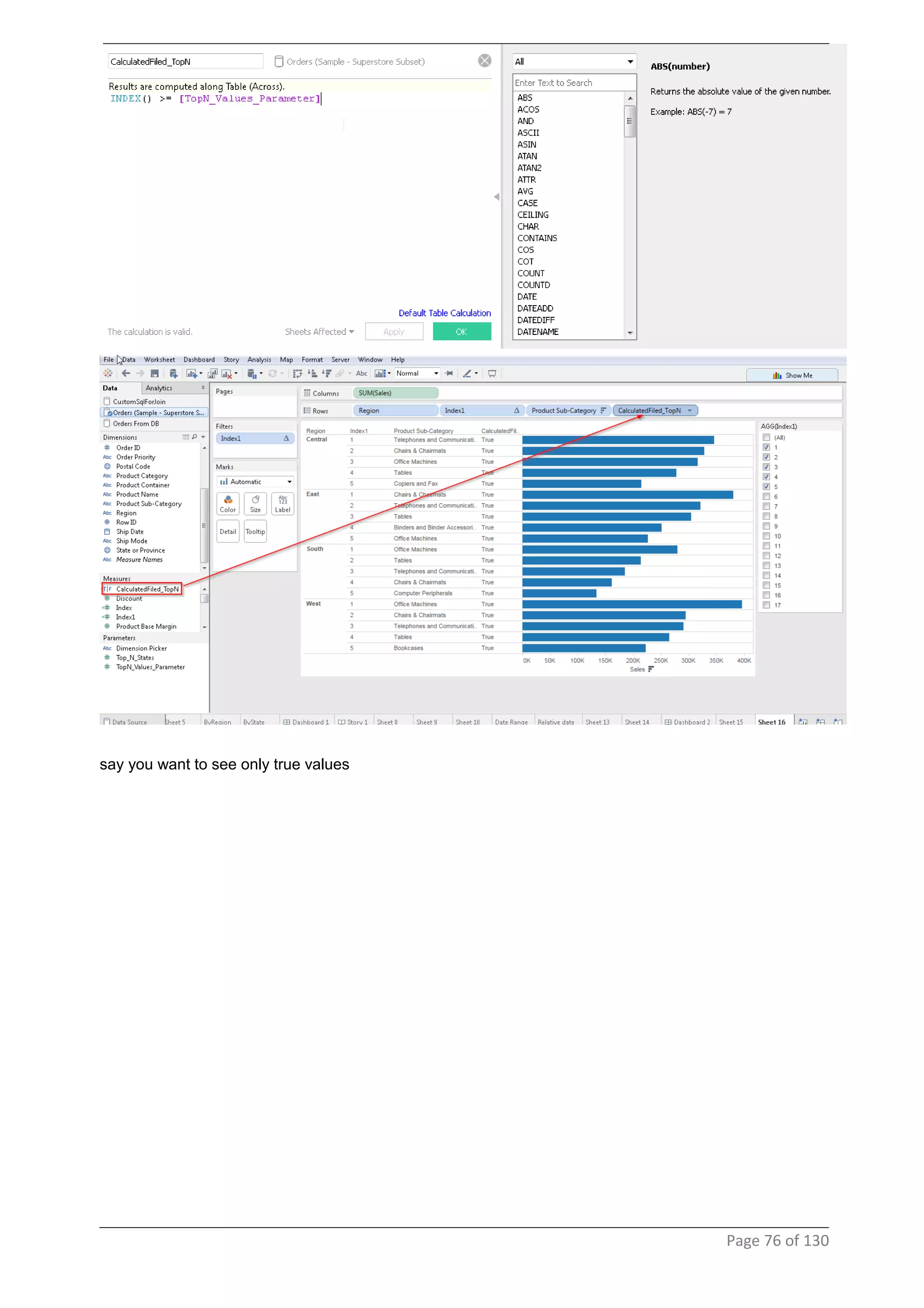
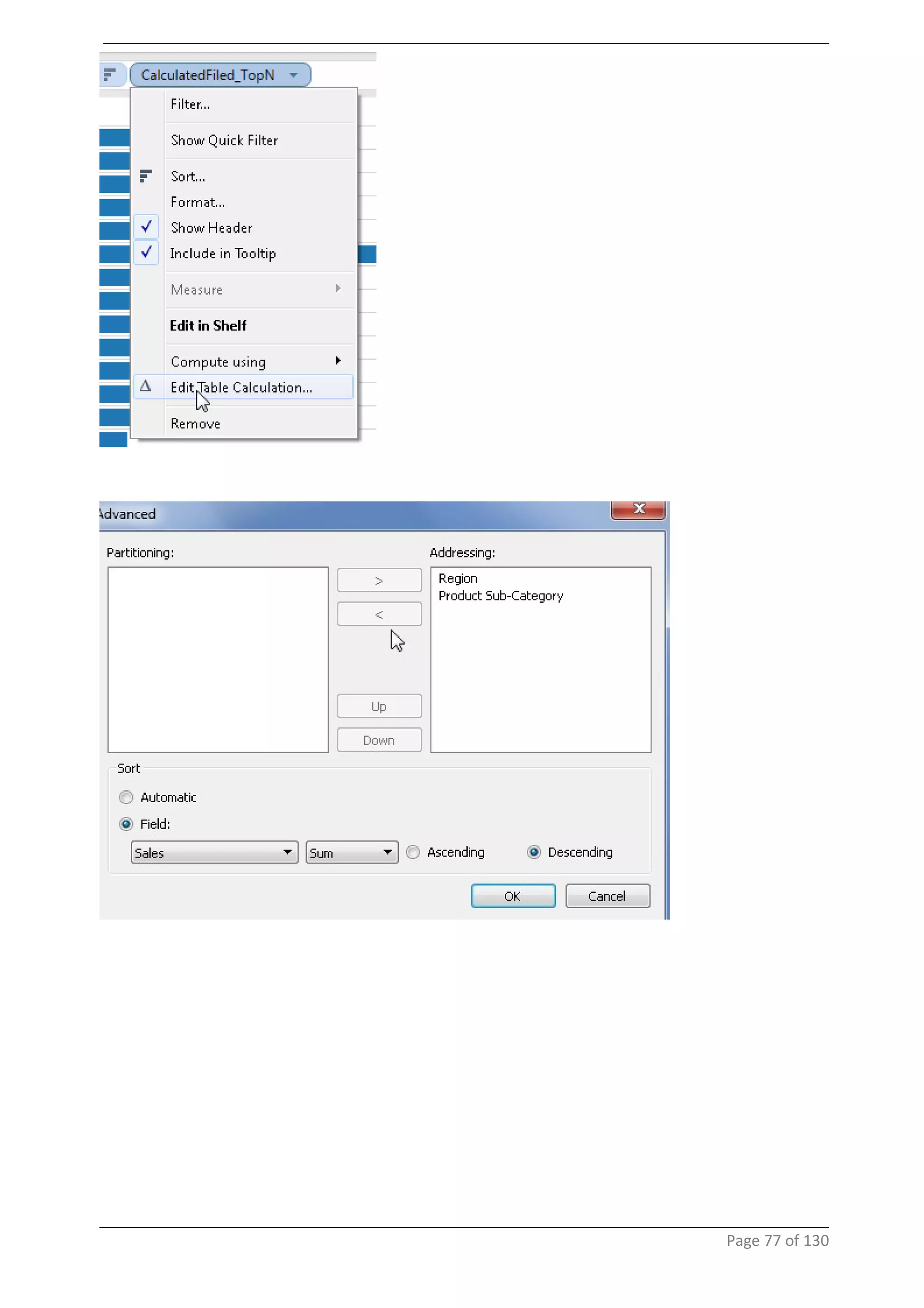
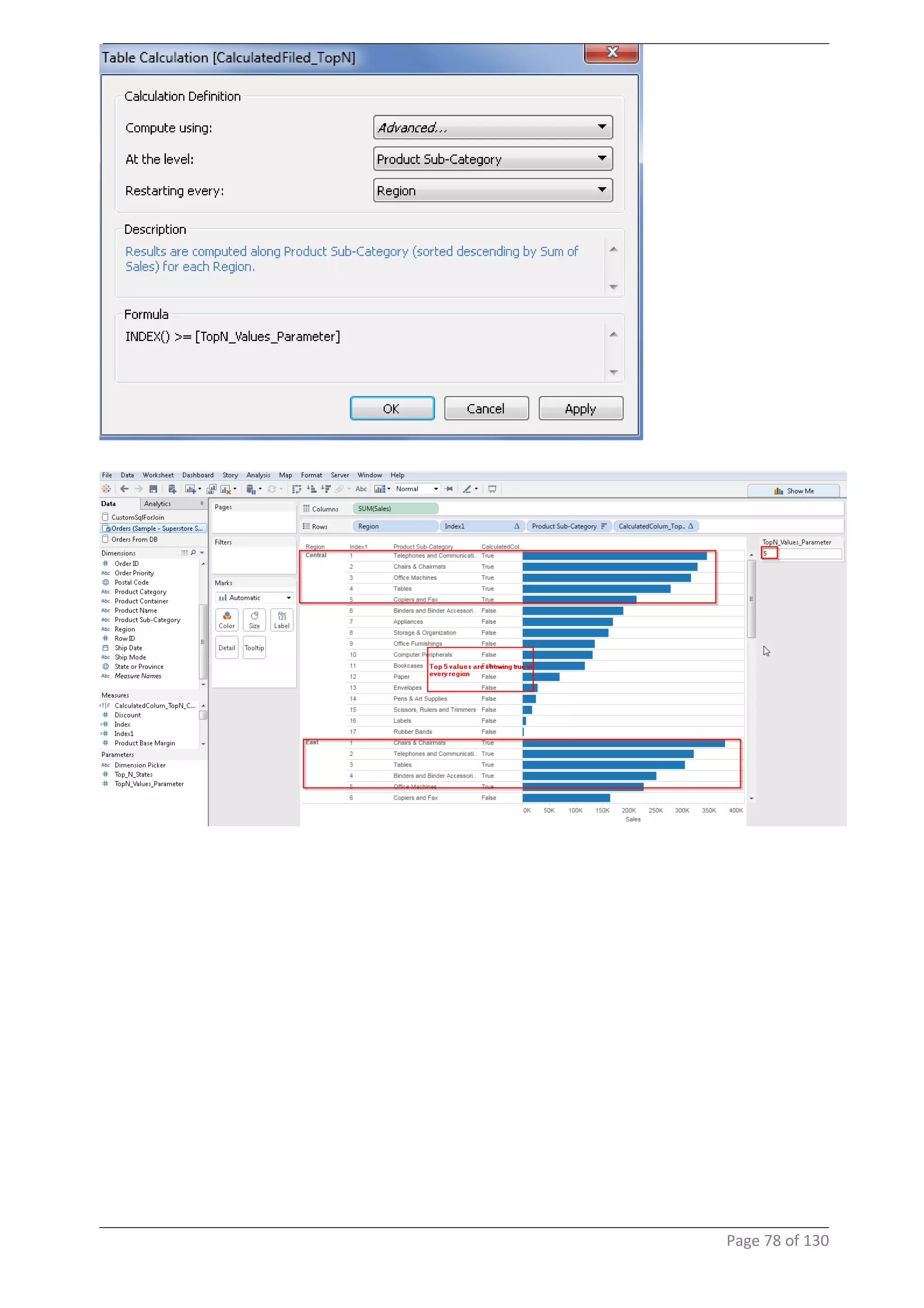
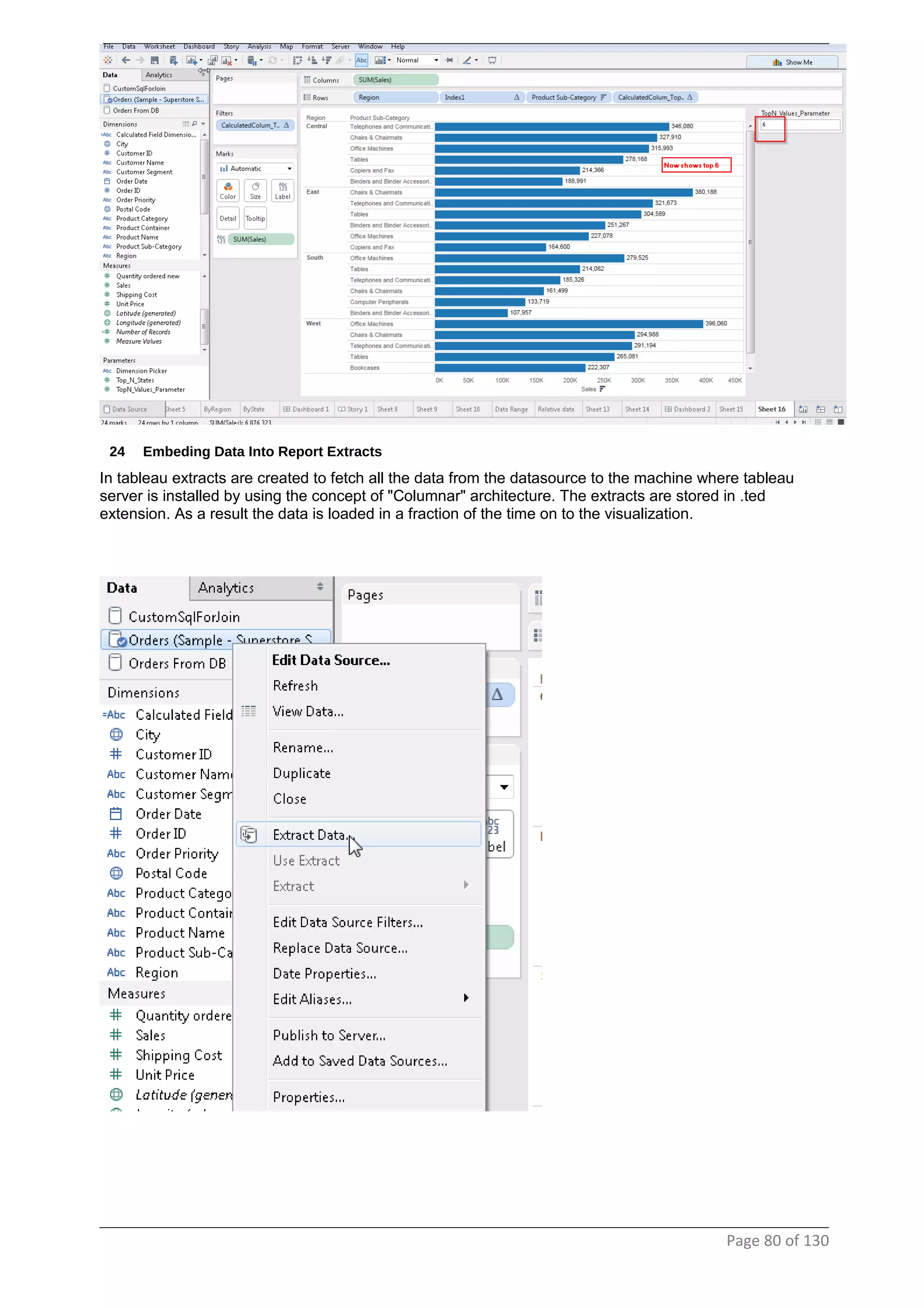
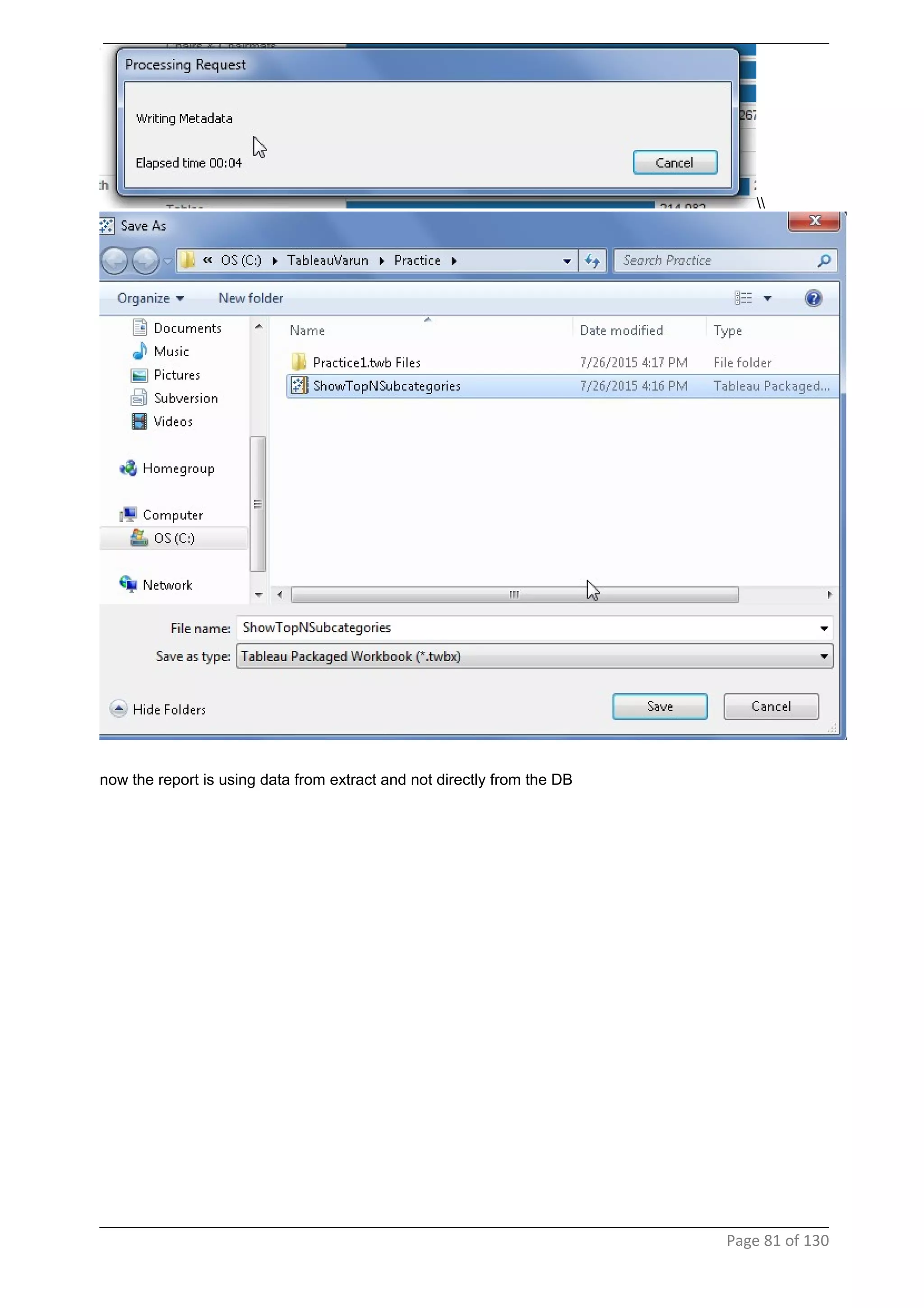
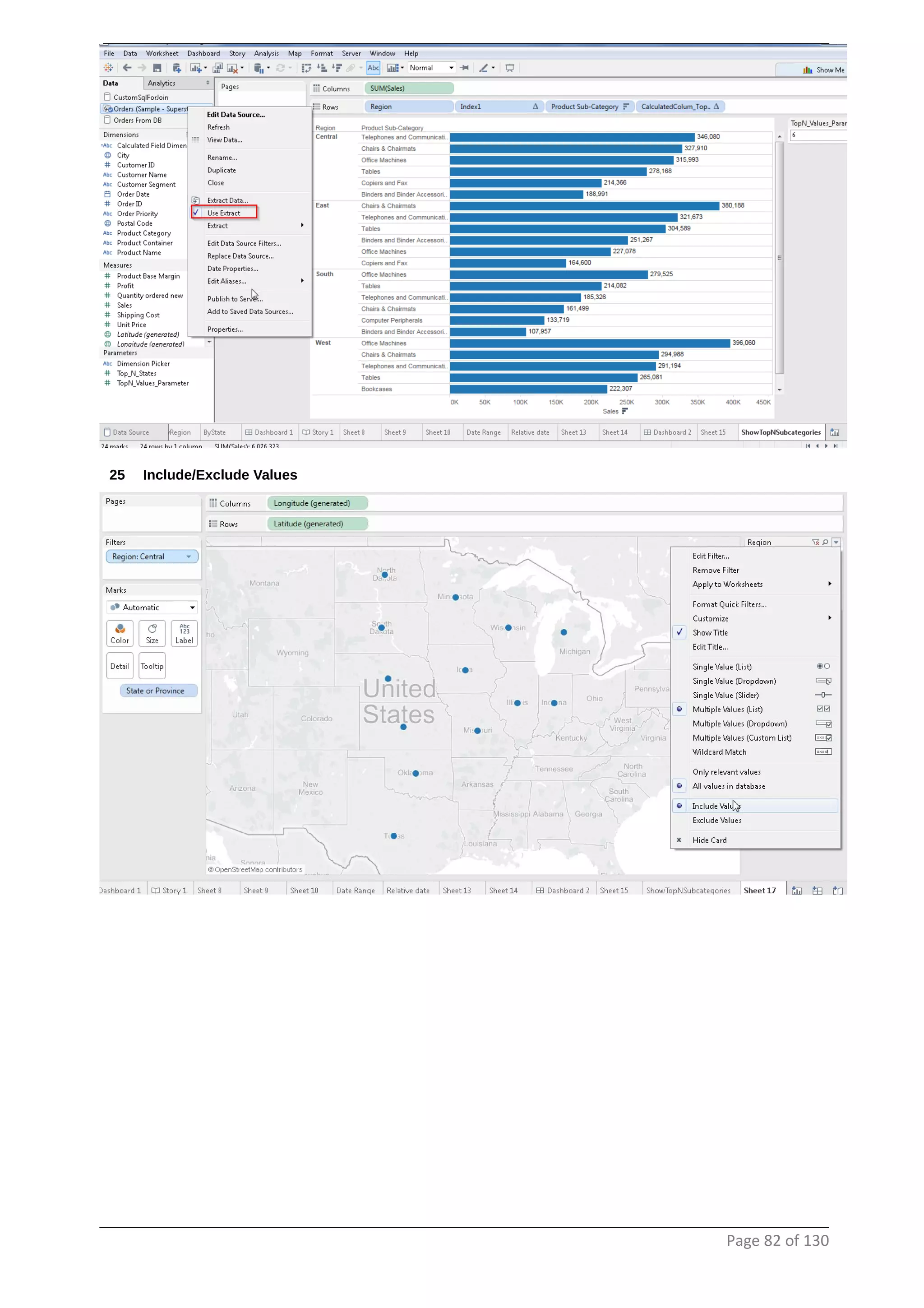
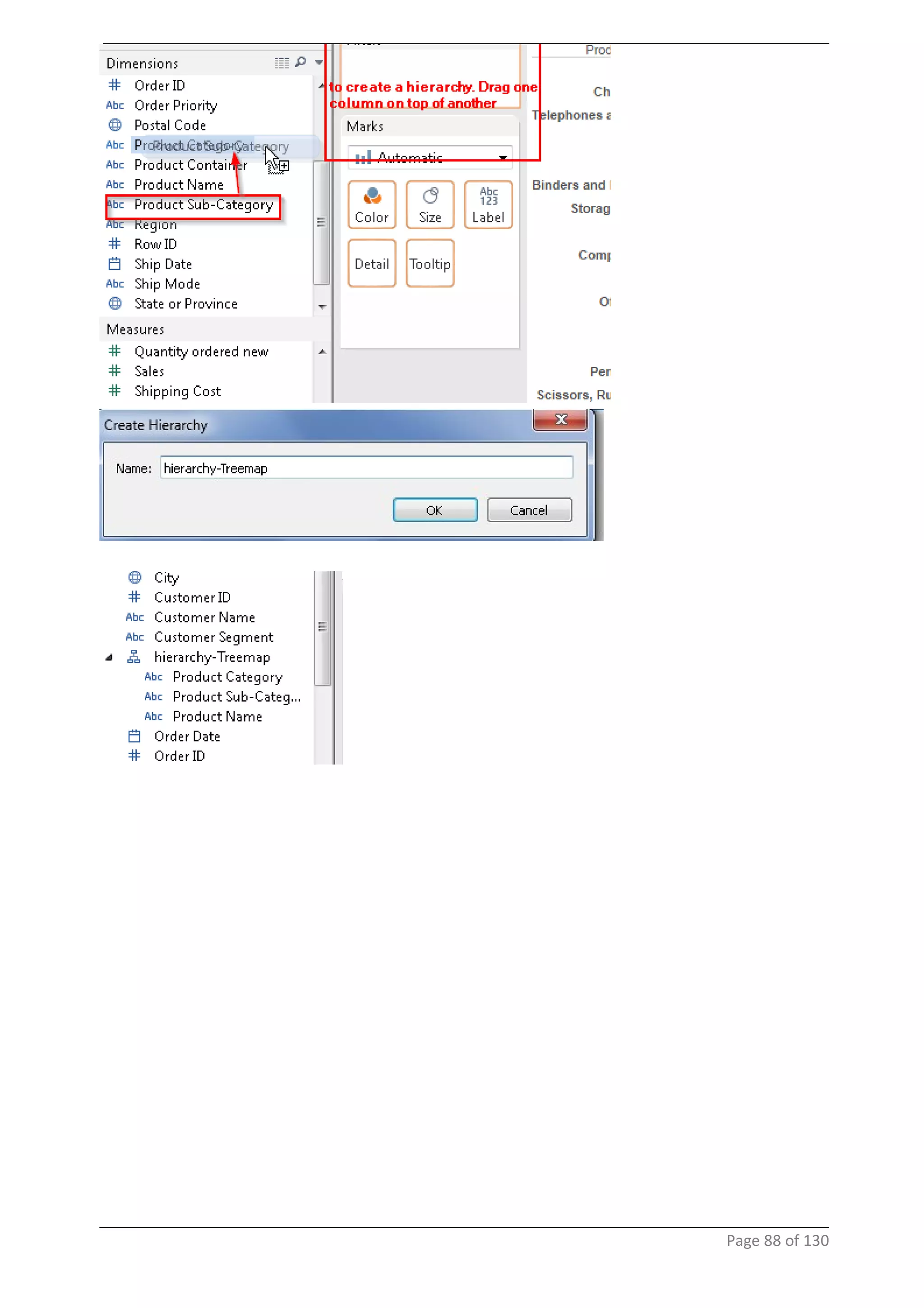
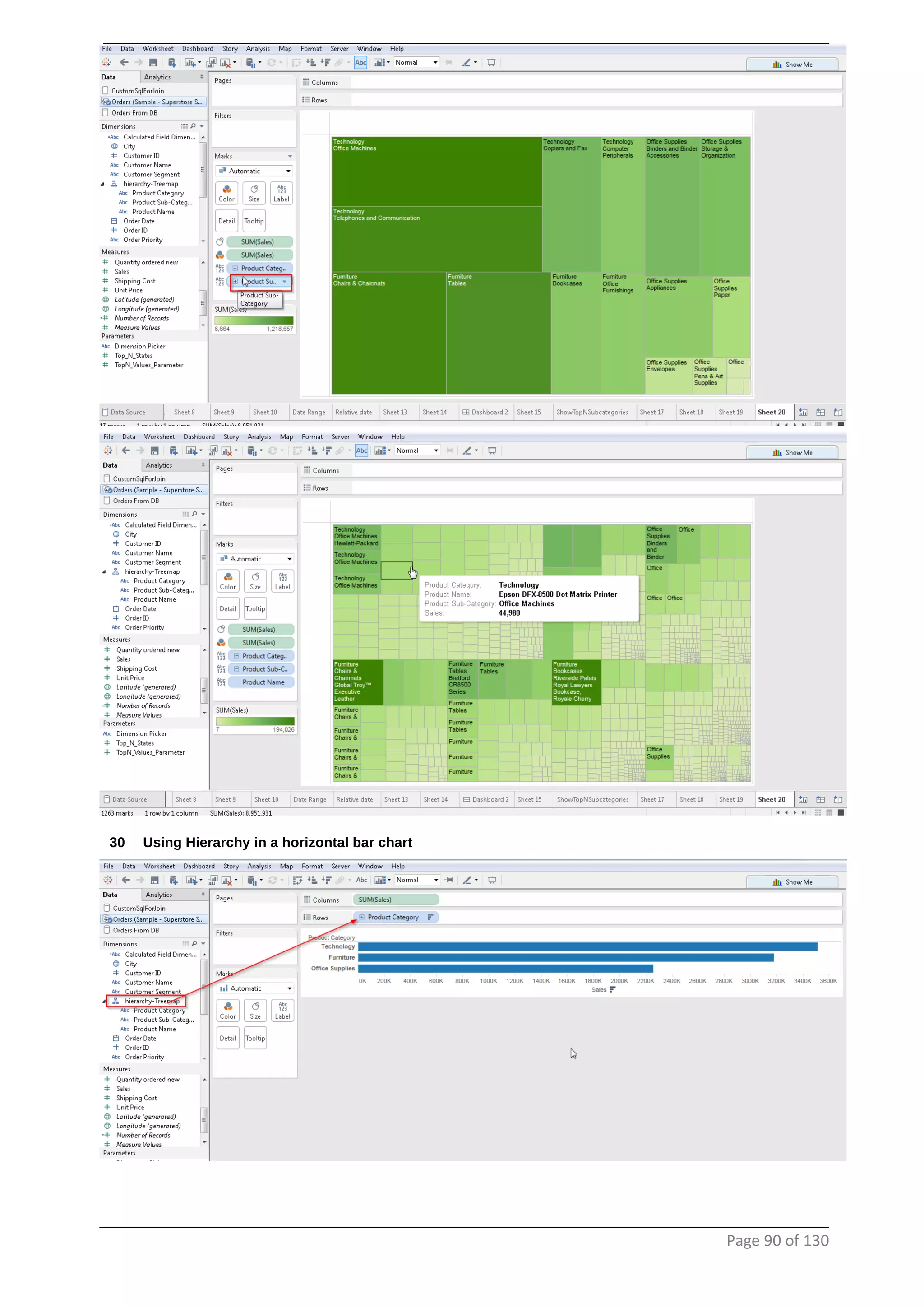
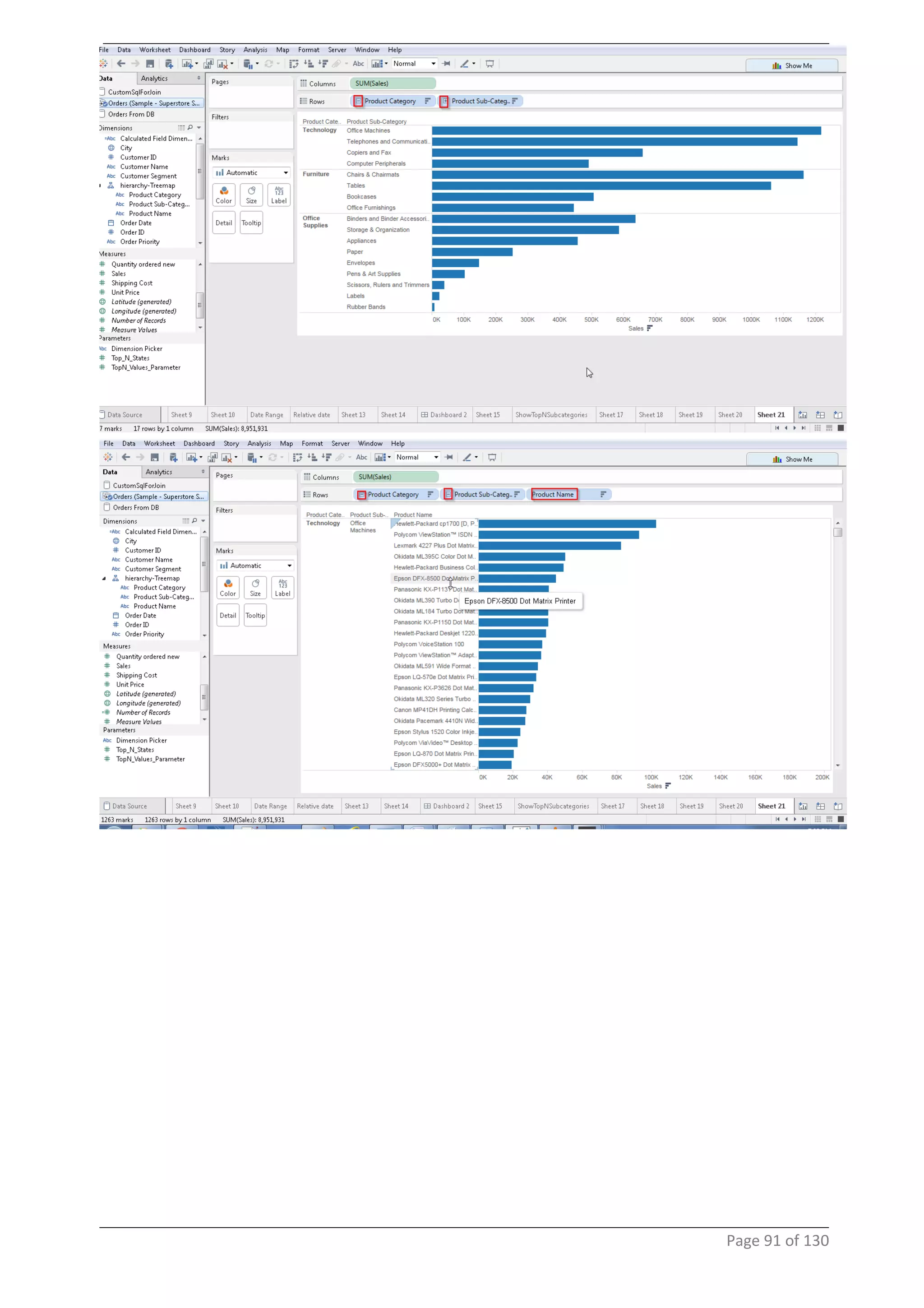
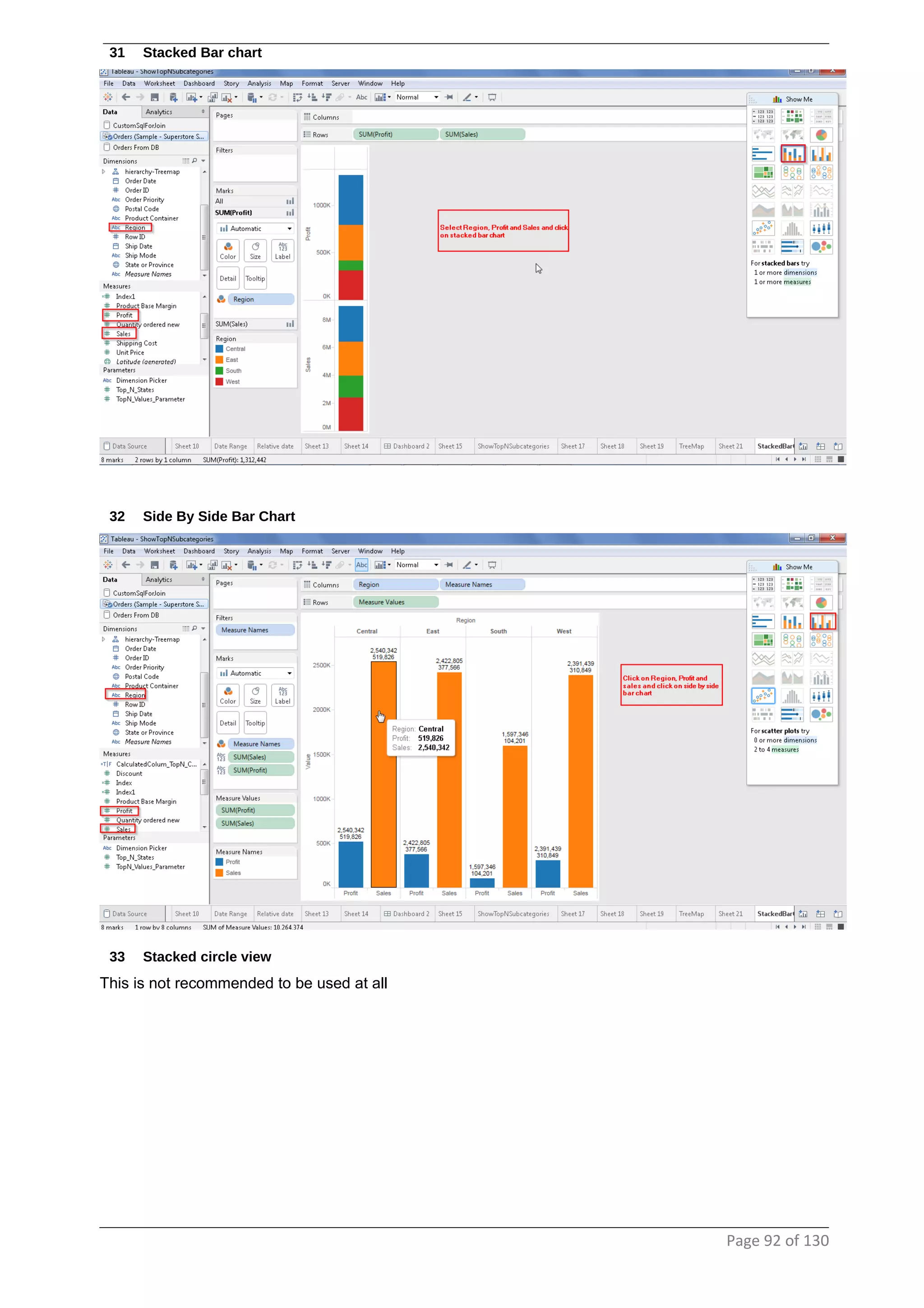
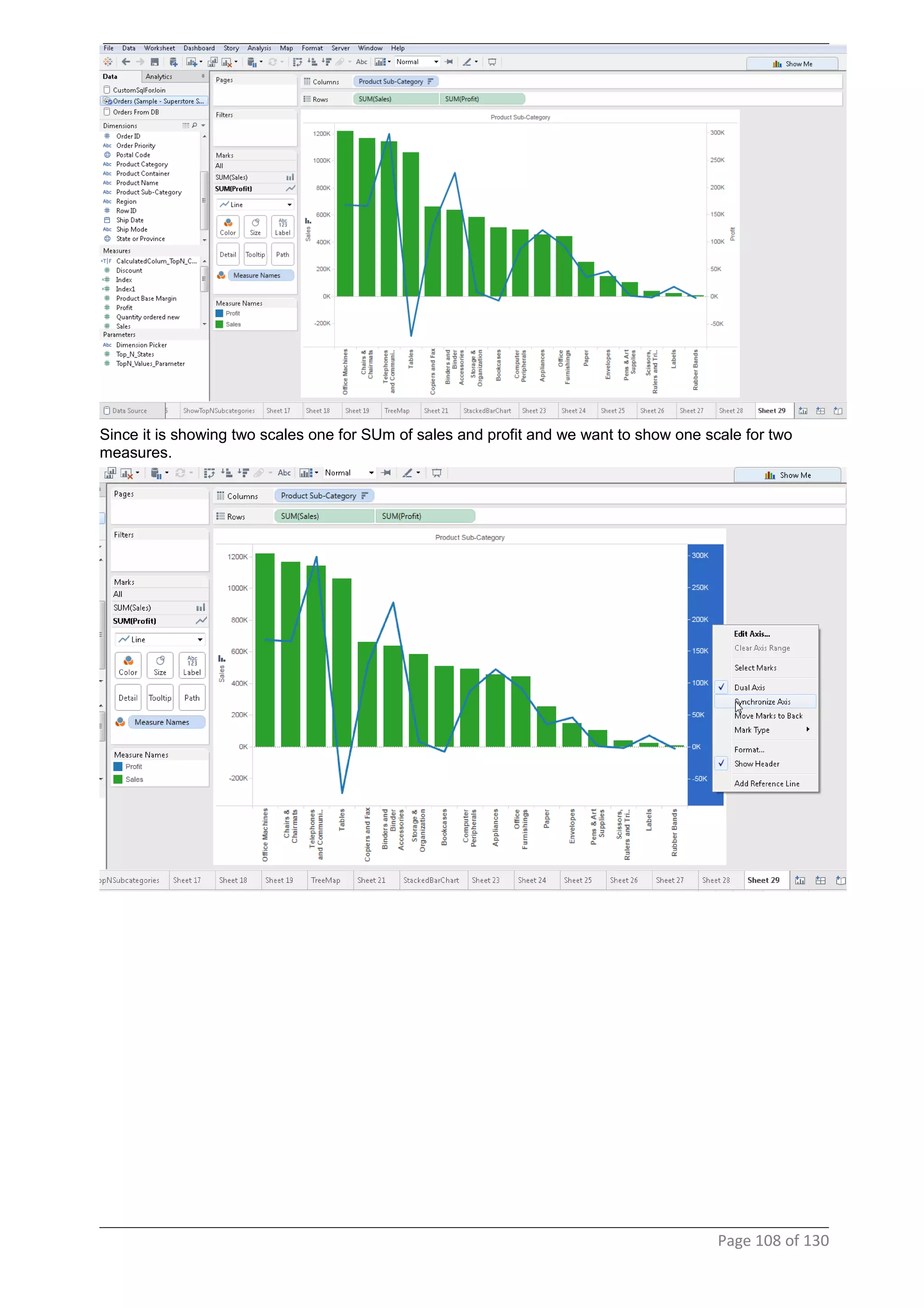
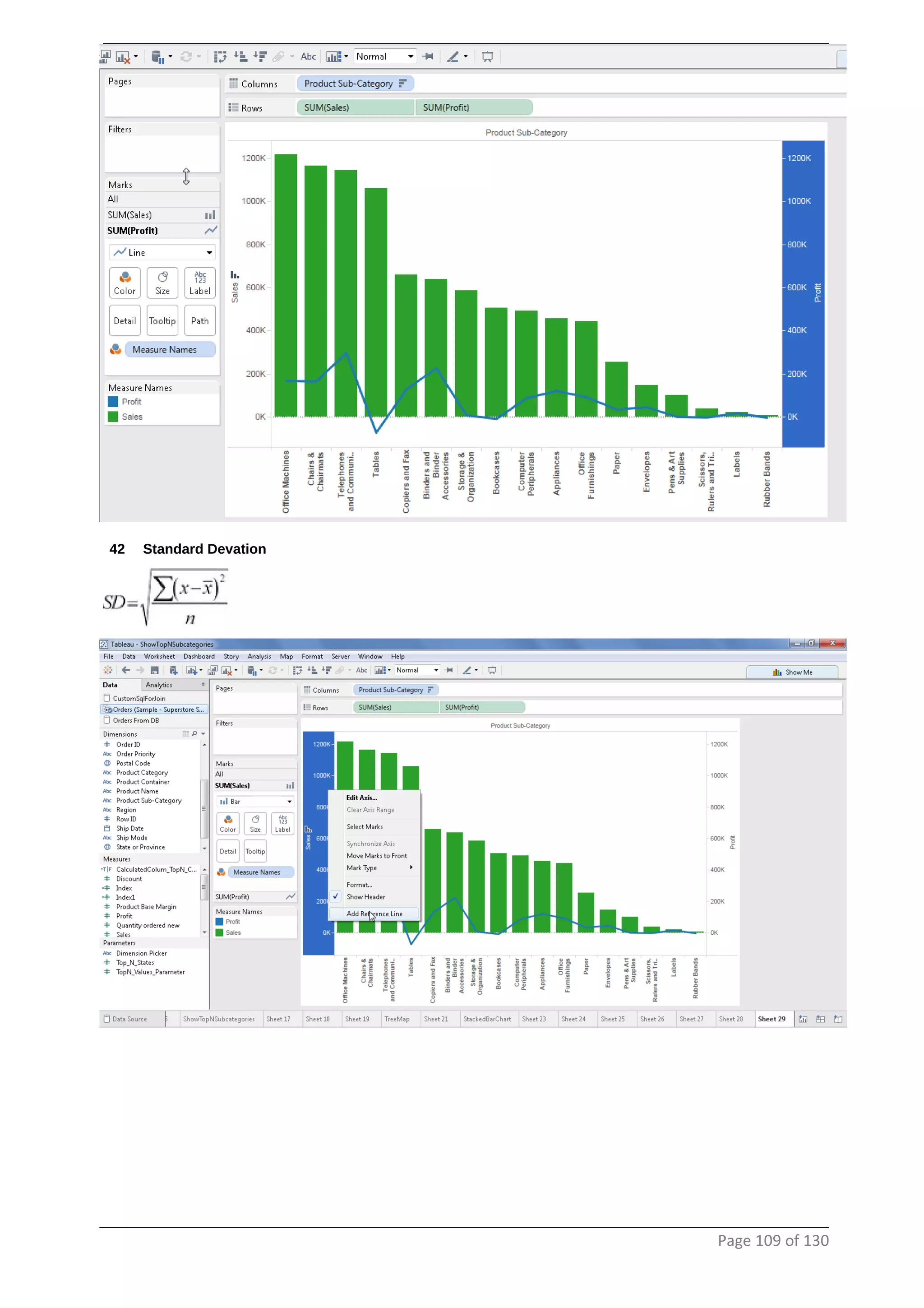
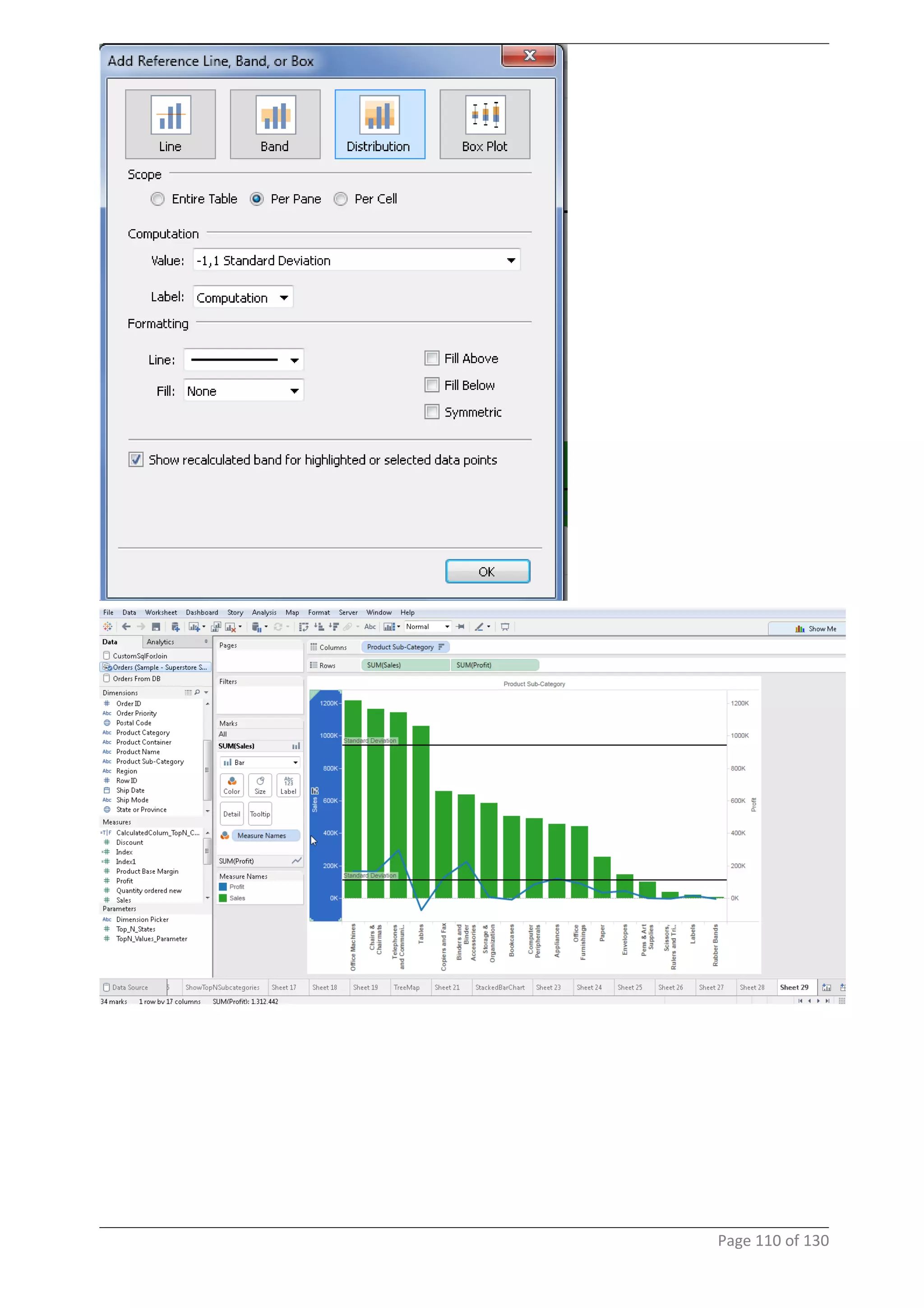
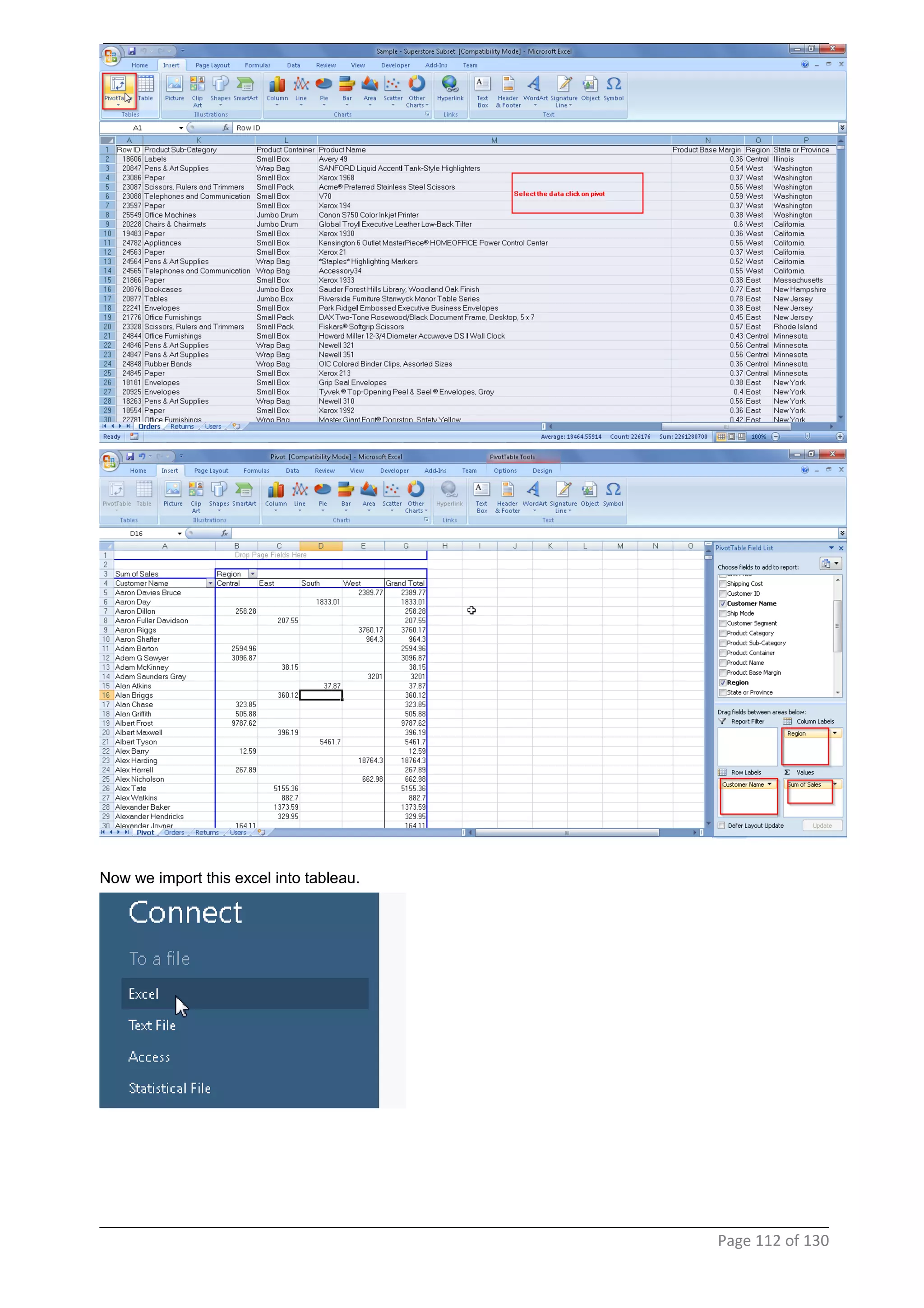
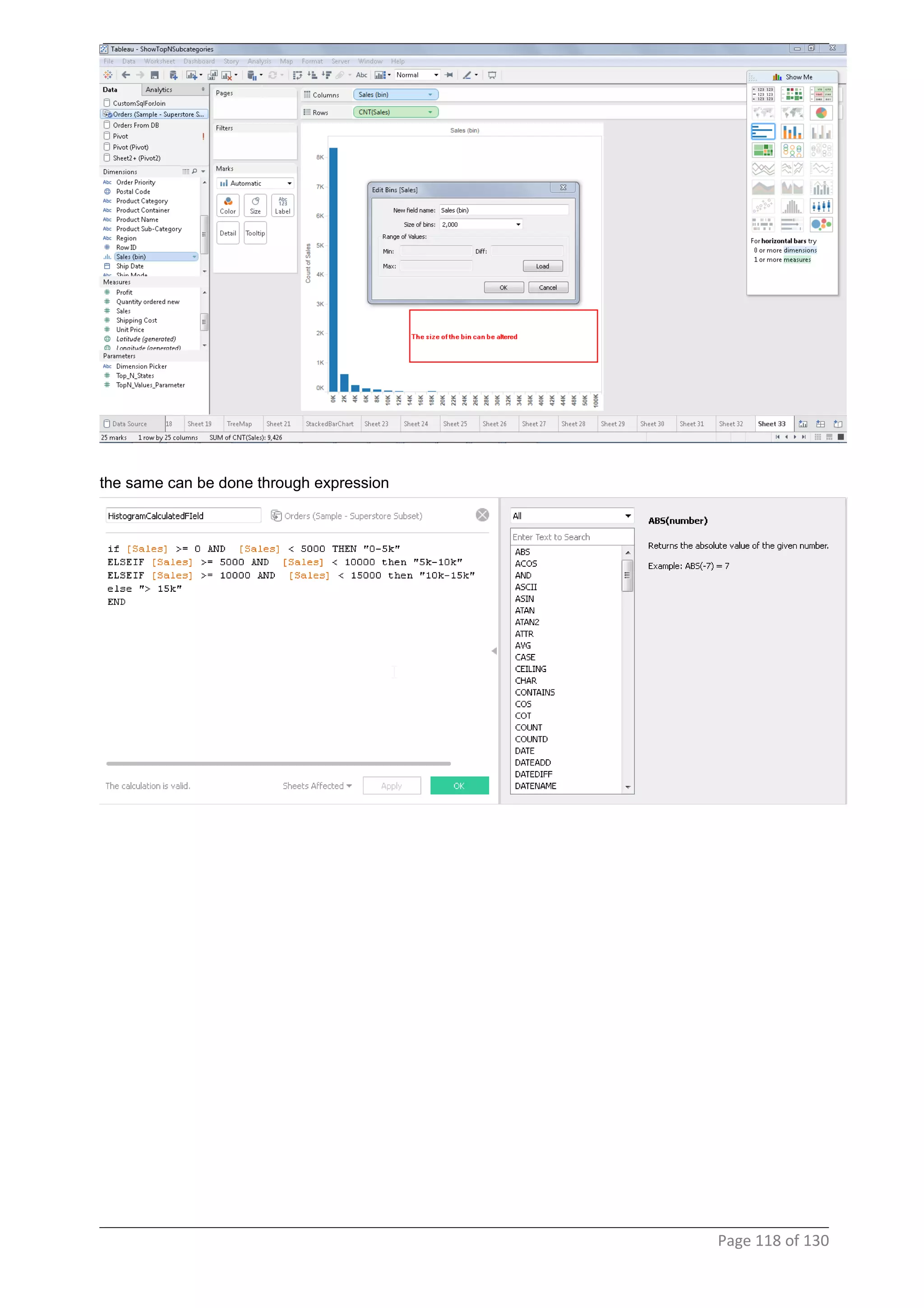
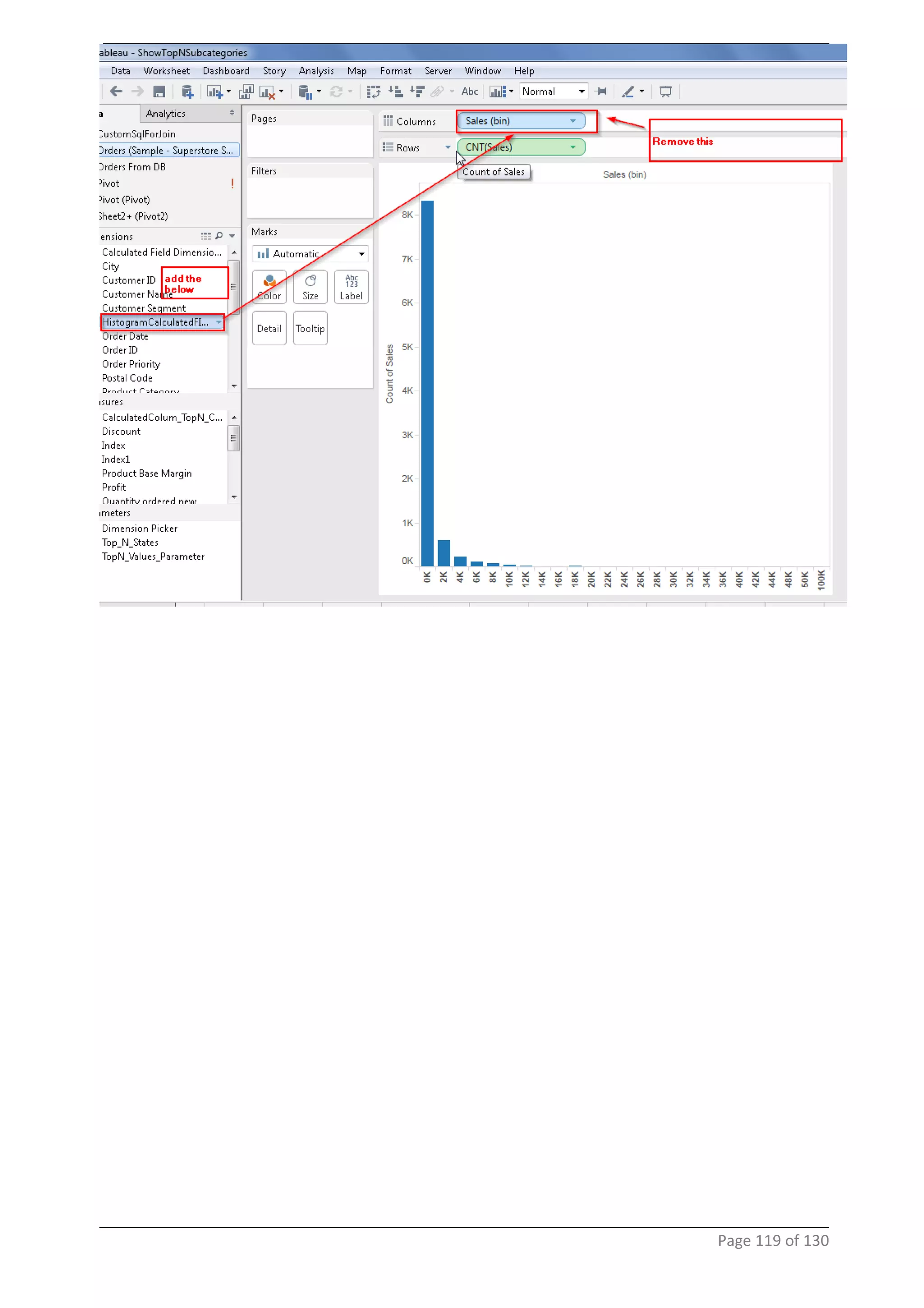
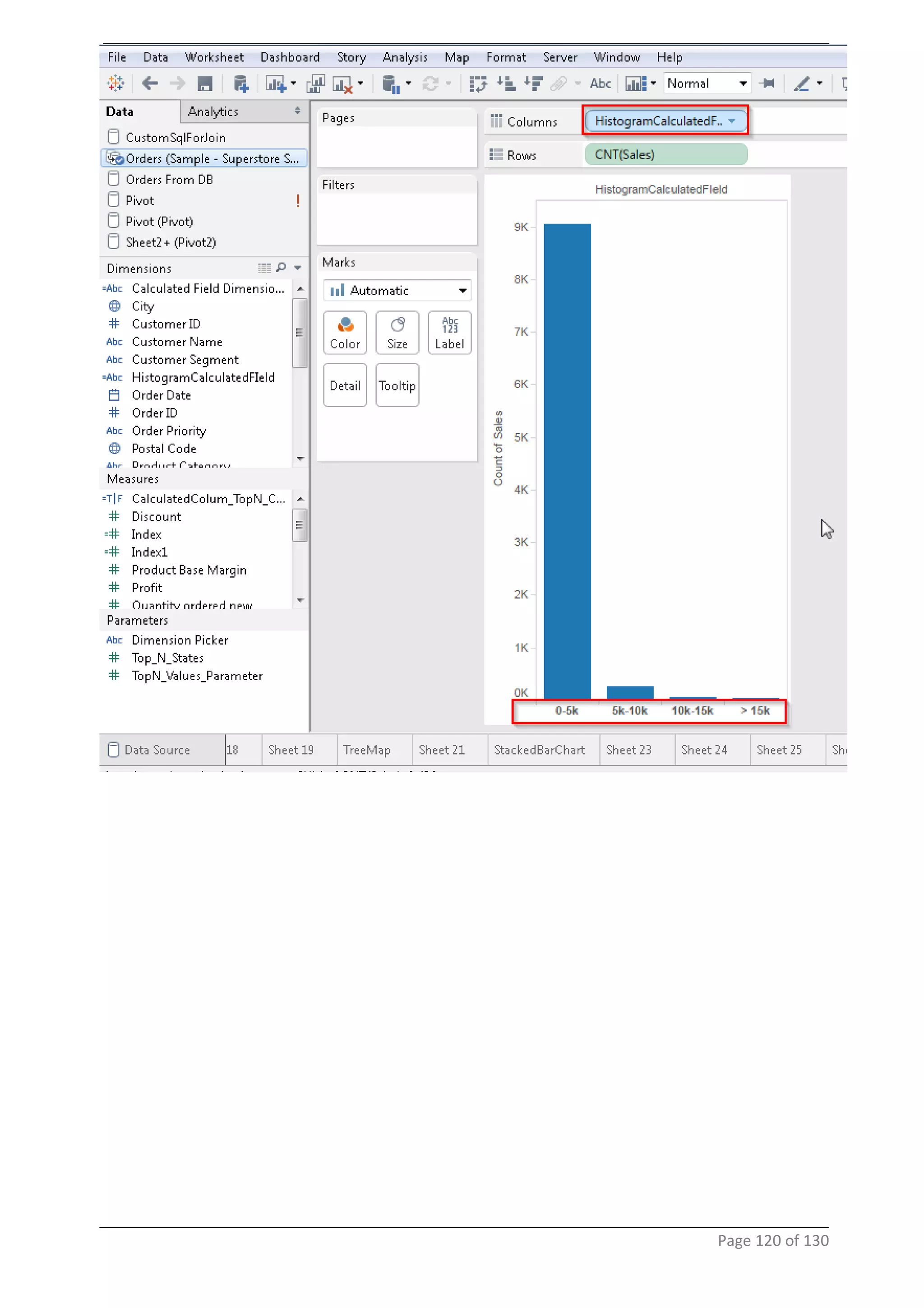
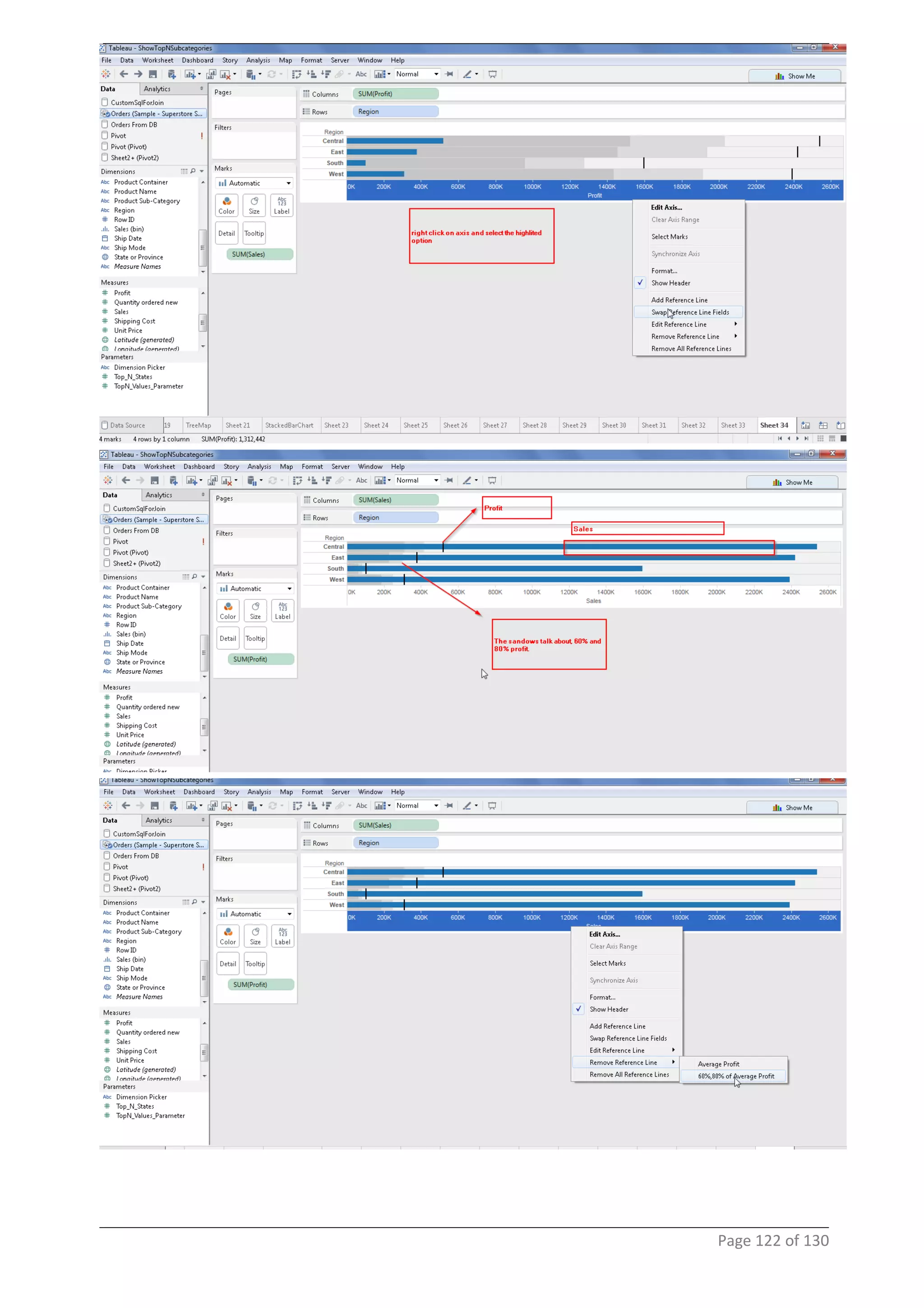
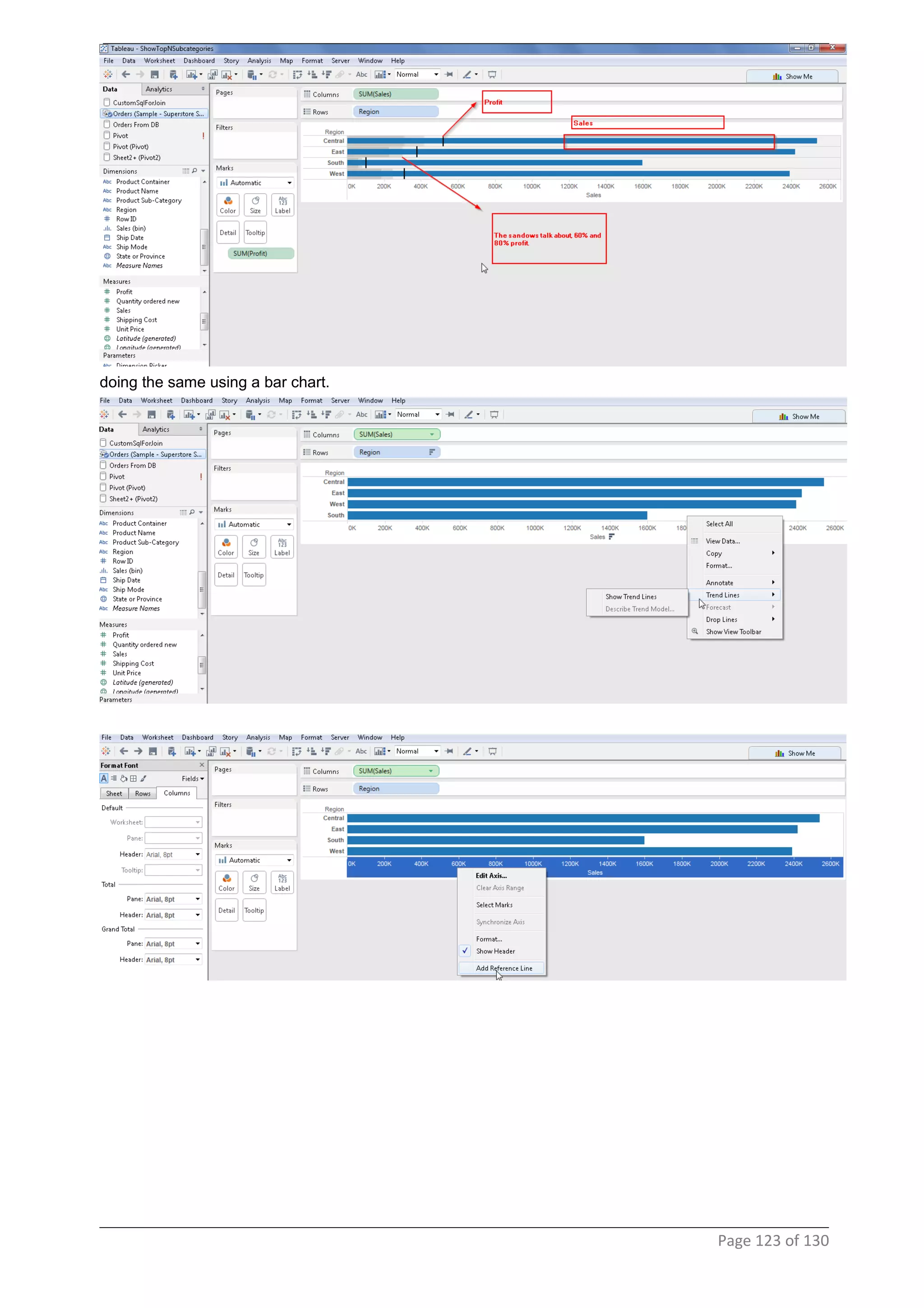
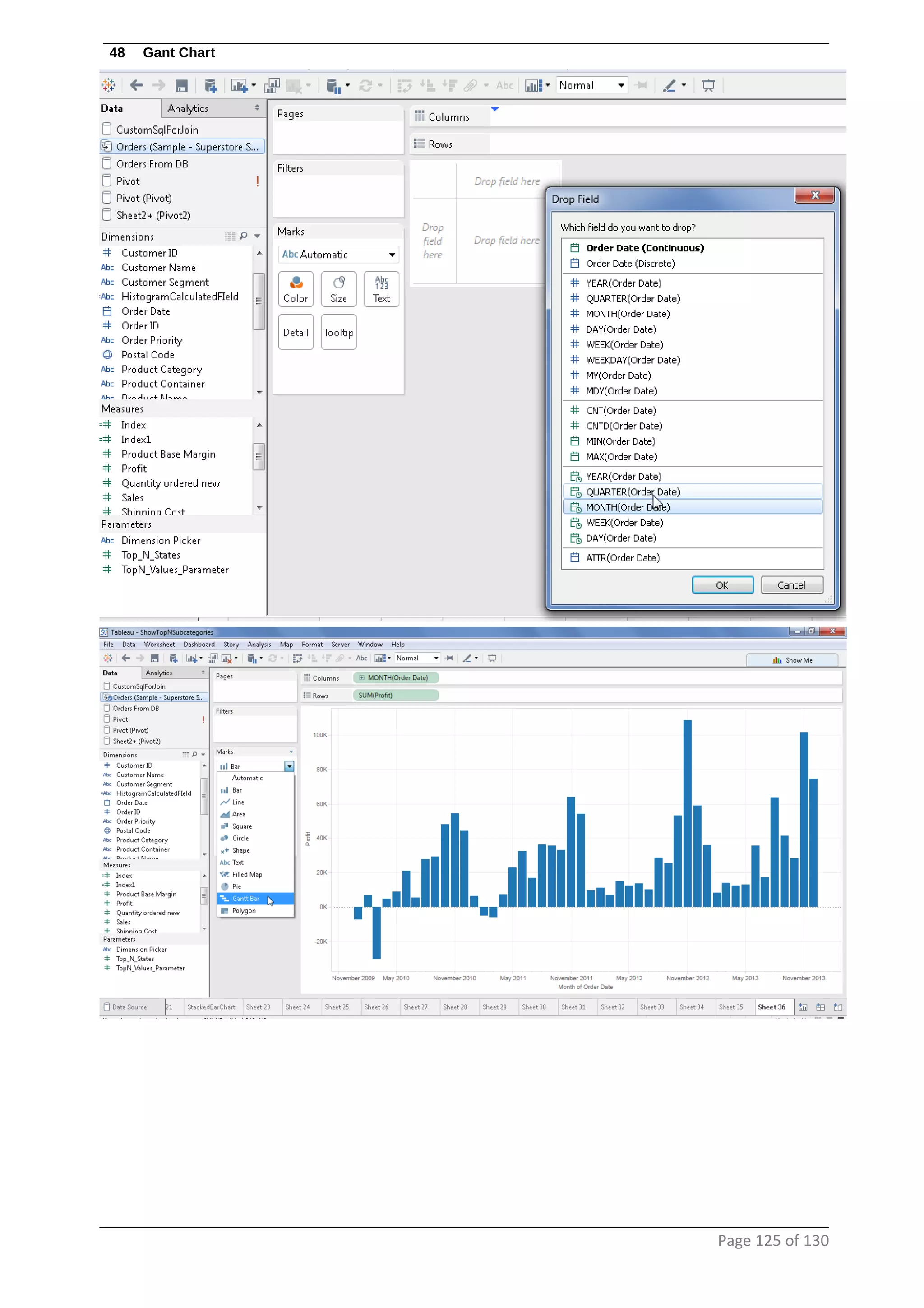
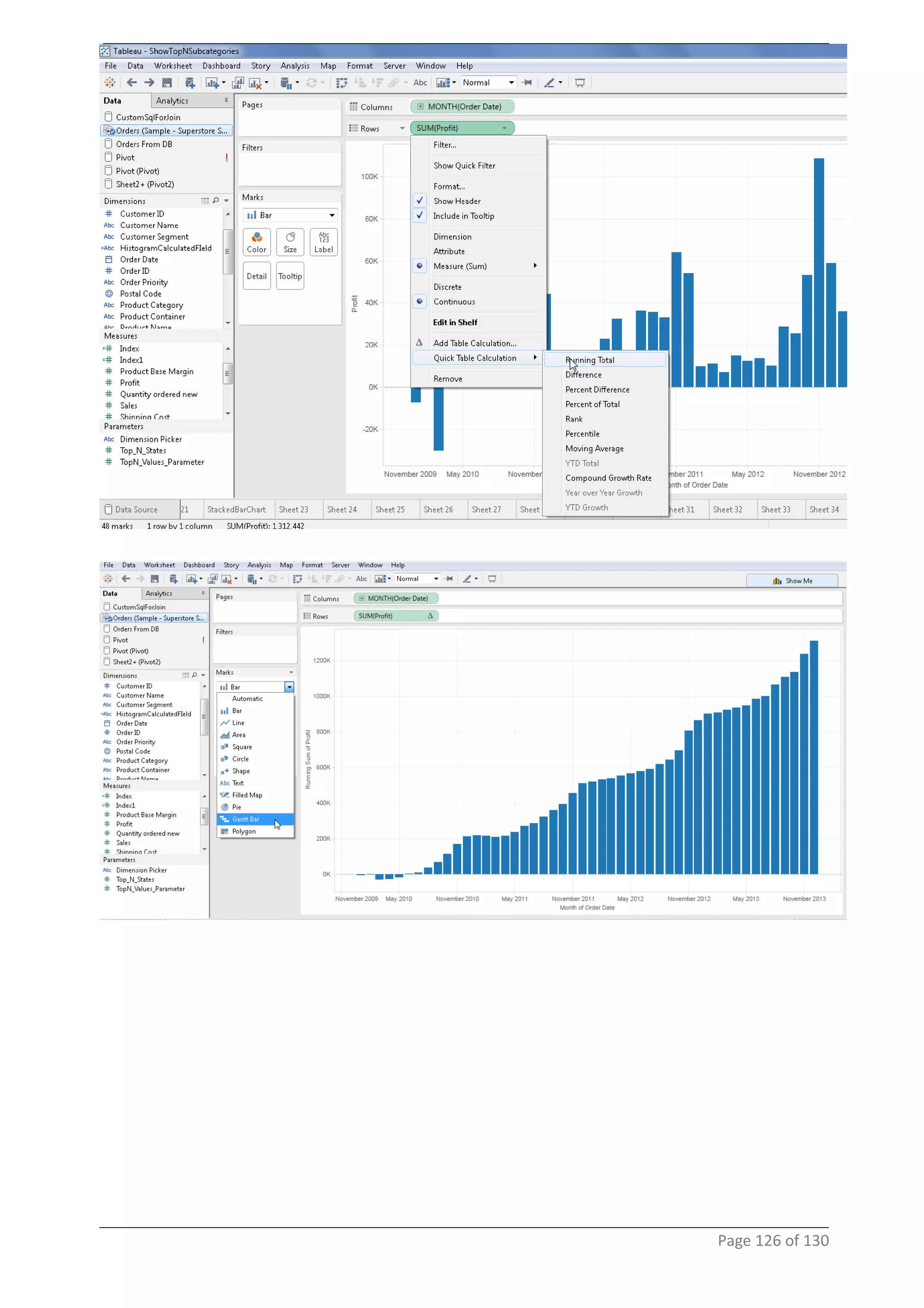
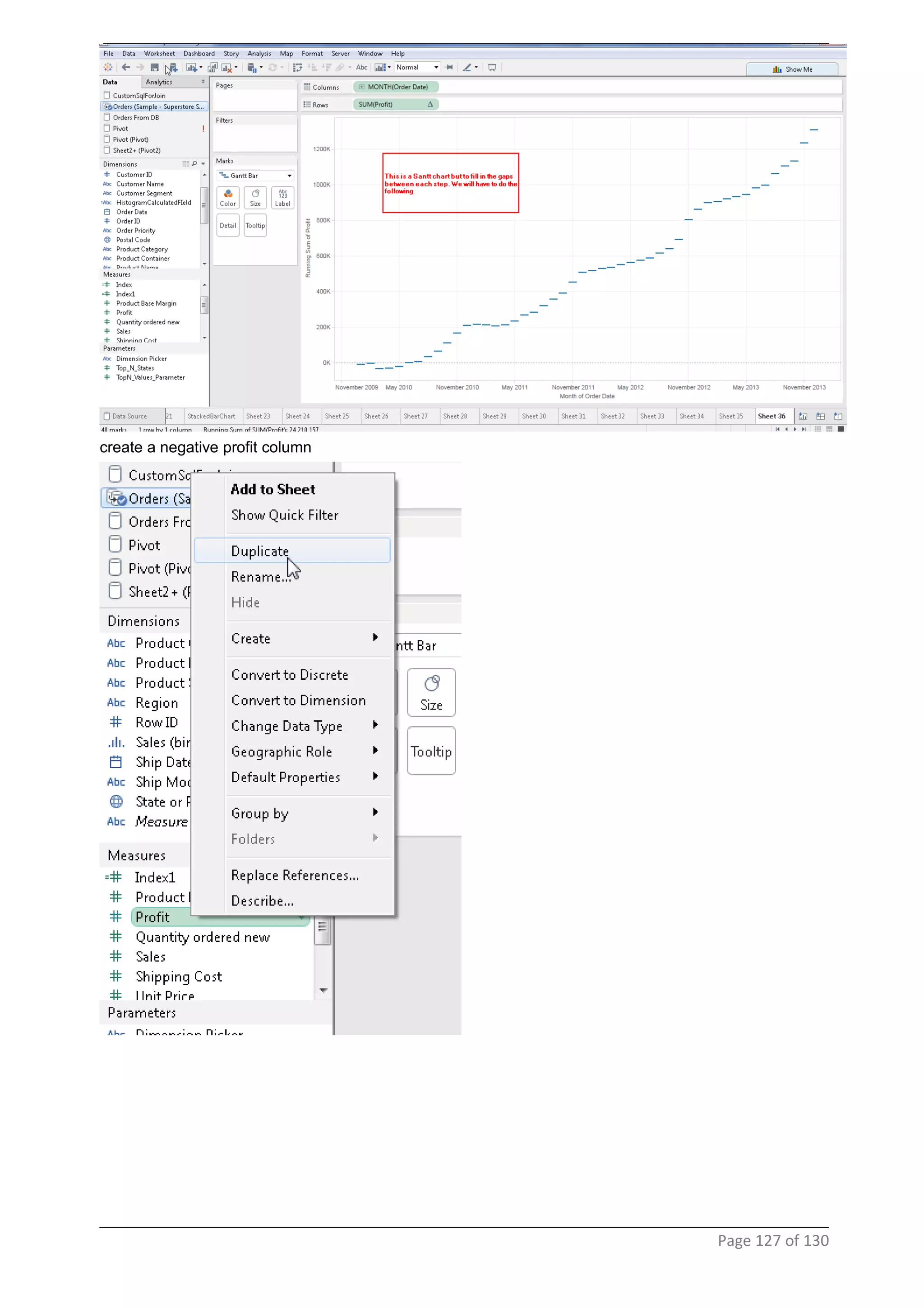
This document provides instructions and examples for creating dashboards and visualizations in Tableau. It covers connecting to data sources, basic visualization types like maps and bar charts, formatting options, filters, pages, dashboards, custom SQL, linking to web pages, and other advanced functions. The goal is to help users leverage the power of visual perception to communicate information clearly and efficiently through designed dashboards.