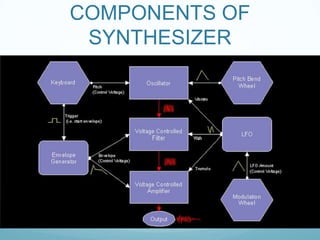
This document provides an overview of the graphical interfaces of 4 different synthesizers - ES1, ES2, ESP, and ESE. It describes the key sections and parameters of each synthesizer interface, including the oscillator, filter, amplifier, LFO, envelope, and other sections. It also reflects on learning about synthesizer interfaces from scratch and welcomes feedback to improve.