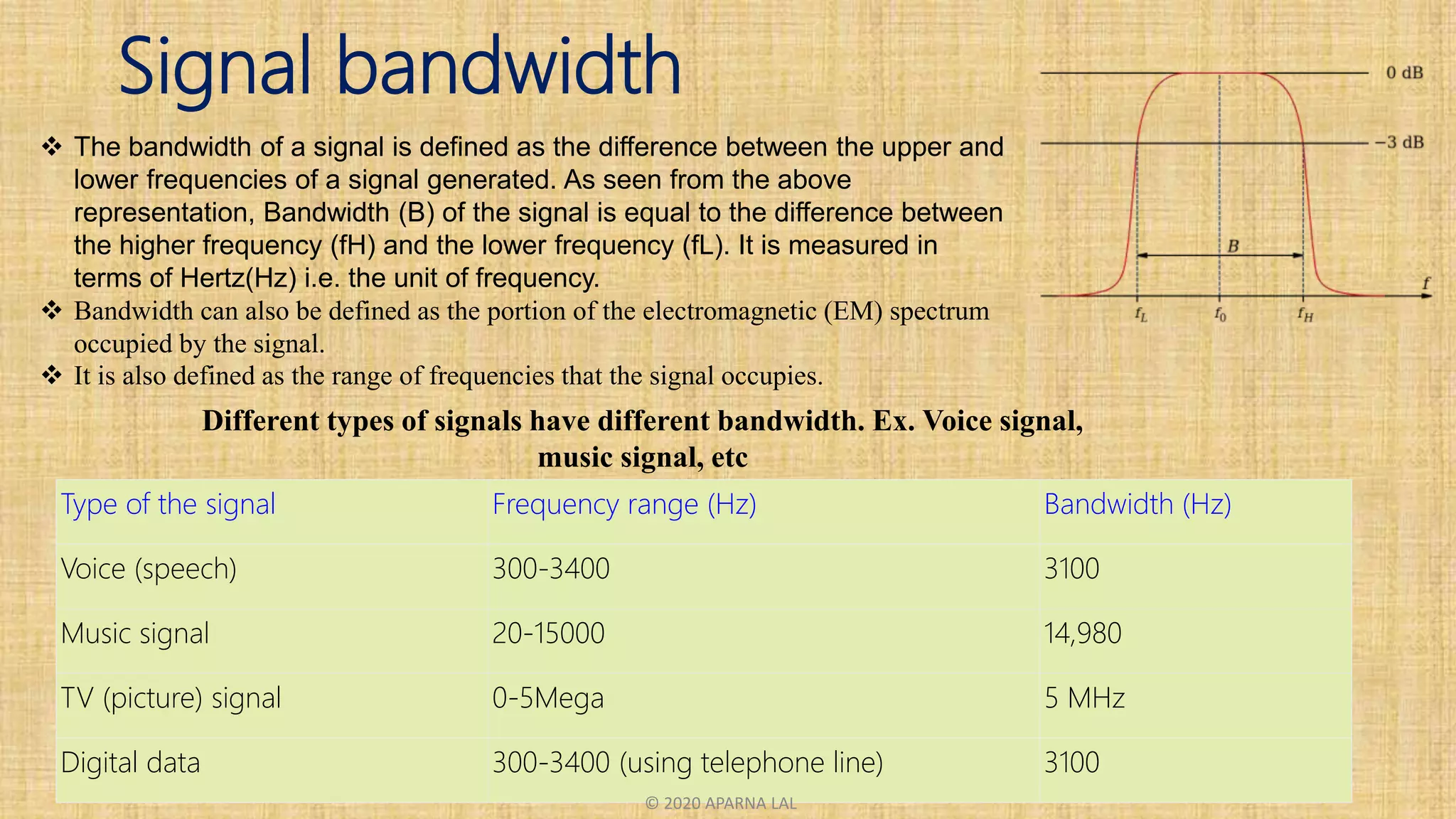
The bandwidth of a signal is defined as the difference between the upper and lower frequencies of the signal. It represents the range of frequencies occupied by the signal and is measured in Hertz (Hz). Different types of signals have different bandwidths. For example, the bandwidth of a voice signal is 300-3400 Hz, while the bandwidth of a music signal is 20-15000 Hz. Bandwidth is calculated differently for analog and digital signals, with analog bandwidth based on frequency and digital bandwidth on bit rate.