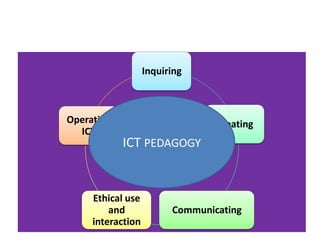
This document discusses syncing digital learning to key learning areas and ICT pedagogy in education. It notes that classroom teachers require flexible practices to engage modern students. ICT is seen as a catalyst for change that requires evaluation of its effectiveness. The document recommends that teachers integrate ICT based on pedagogical needs, to provide creative problem-solving opportunities. It also suggests that inquiry learning can be enhanced through ICT to create accelerated and personalized learning, while ethical issues around internet use need supervision and filtering. Professional development in ICT is most effective when contextual, collaborative, sustained and supports teachers' self-efficacy and system-based needs.