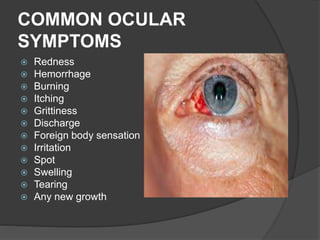
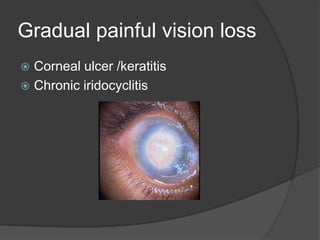
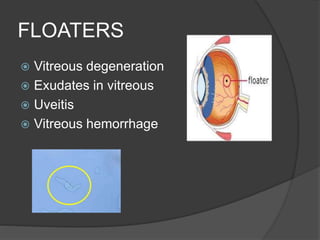
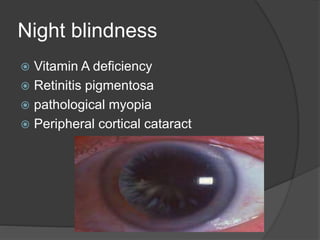
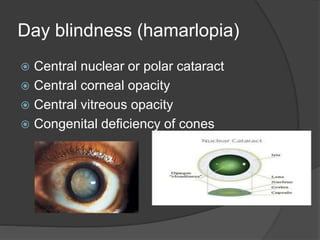
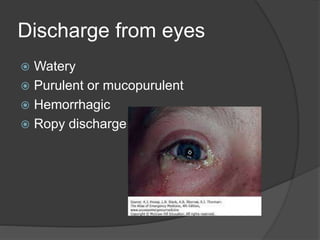
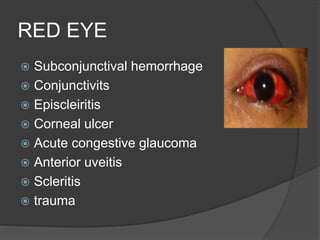
This document discusses ocular symptoms and their potential causes. It describes symptoms related to vision such as blurred vision, floaters, flashes of light, and diplopia that can indicate issues like retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, or optic neuritis. Symptoms involving the eyelids like lumps, swelling, or drooping may signal problems like entropion or ectropion. Common symptoms of redness, discharge, pain, irritation and burning are discussed in relation to conditions like conjunctivitis, uveitis, glaucoma and dry eyes. The document provides an overview of important symptoms in ophthalmology and their differential diagnoses.