Embed presentation
Download to read offline







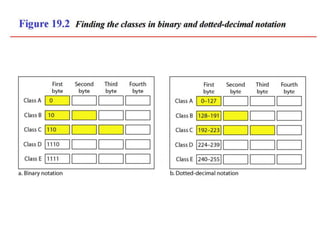

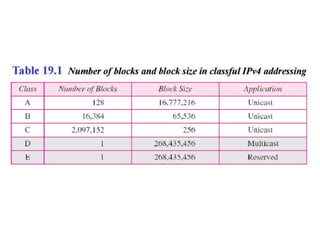

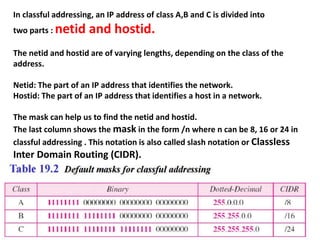



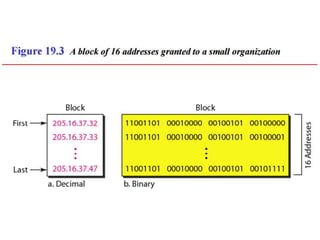










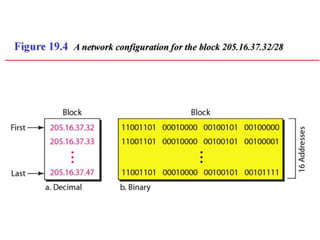

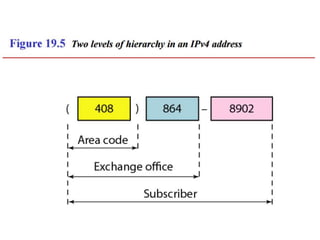
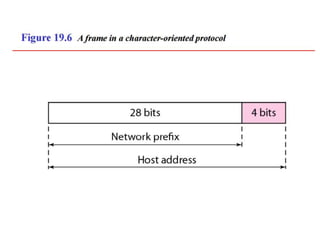

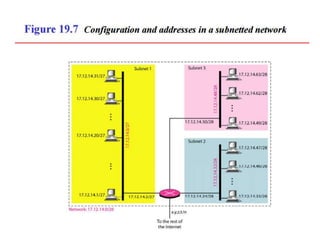
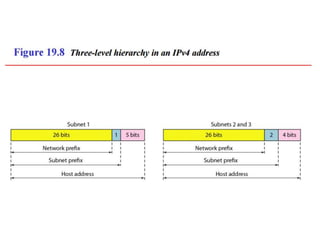




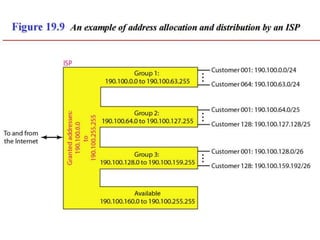
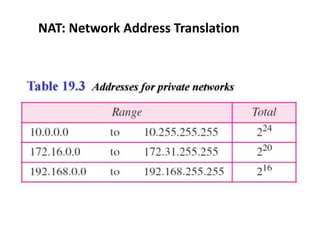
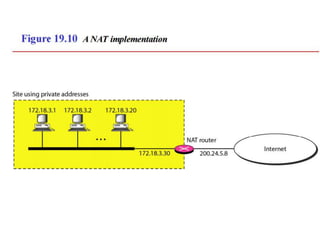
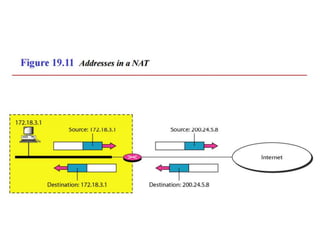
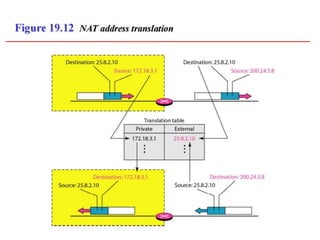
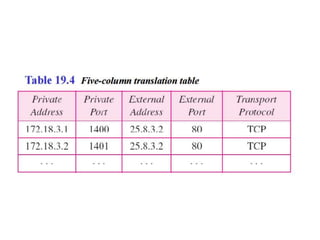
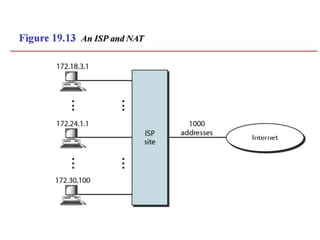

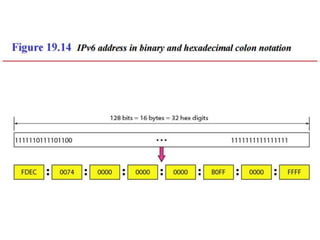
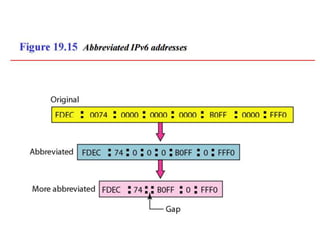

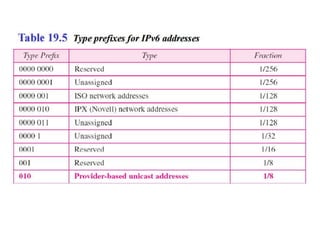
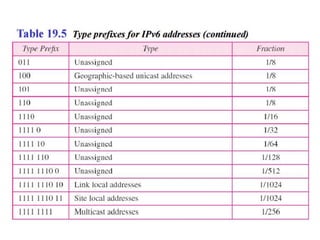
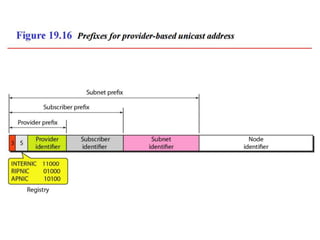
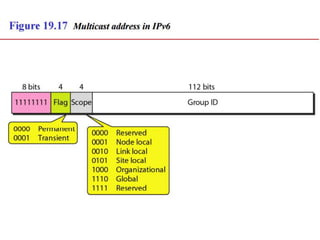
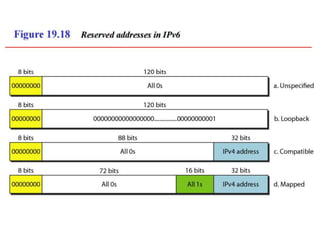
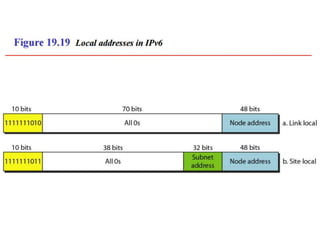


The document discusses IP addressing and subnetting. It explains that IP addresses are divided into a netid and hostid portion, with the lengths depending on the address class. Subnetting further divides the network portion from the host portion using CIDR notation such as 192.60.128.0/22. This separates the network prefix from the host identifier using a bitwise AND with the subnet mask. The document also mentions network address translation (NAT).






















































