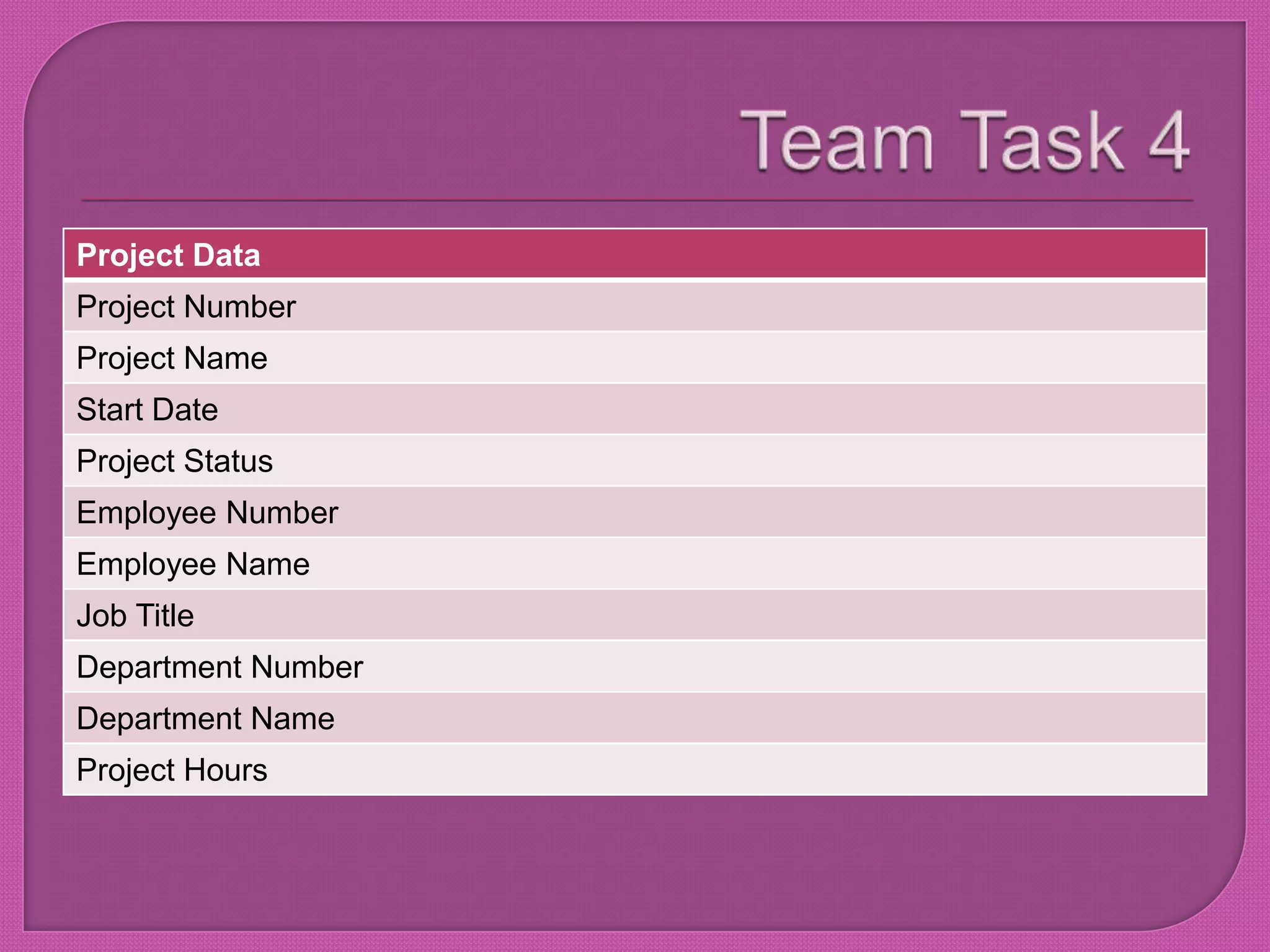
The document outlines tasks for managing a project involving database design. It discusses normalizing databases to eliminate repeating data and designing tables across multiple databases to improve efficiency. The tasks include identifying entities, creating an entity relationship diagram, explaining data design concepts, and describing database systems, data relationships, and data warehousing. Some tasks must be completed sequentially before others can start.