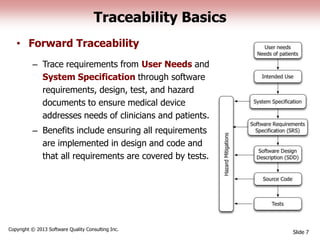
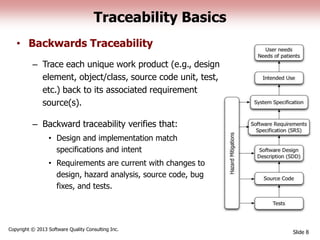
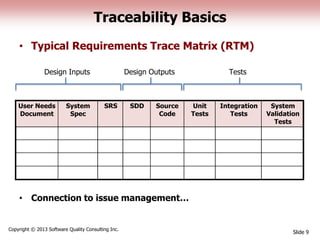
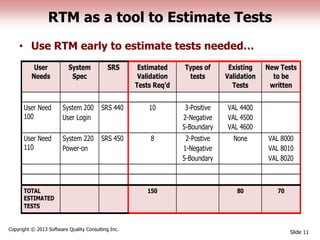
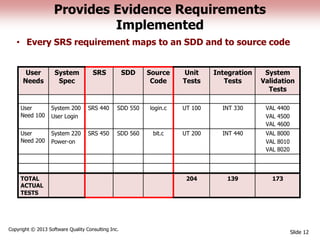
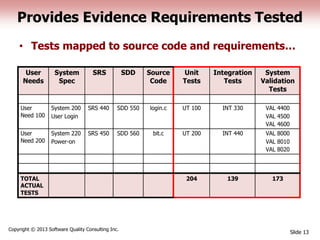
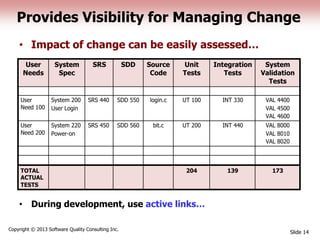
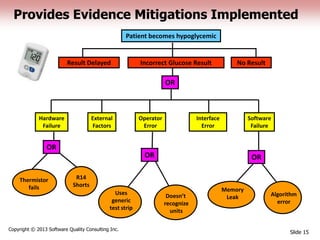
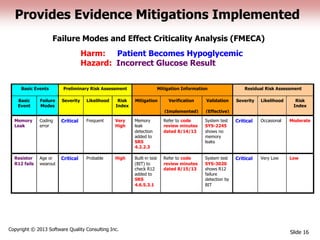
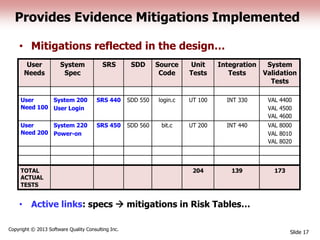
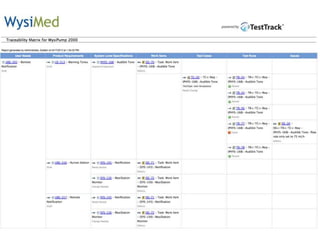
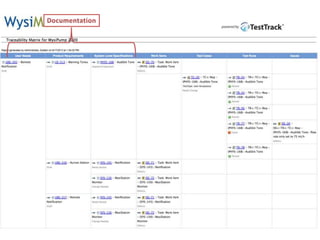
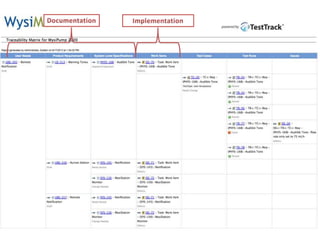
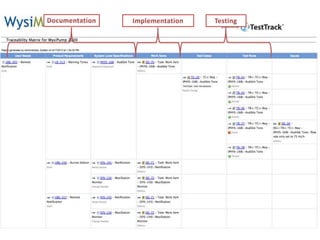
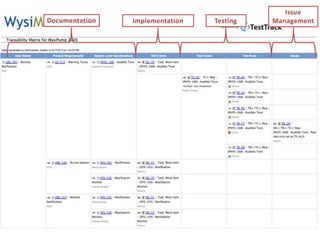
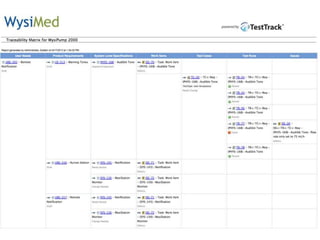
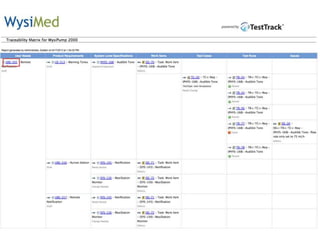
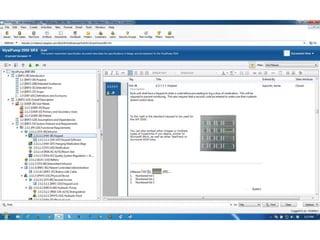
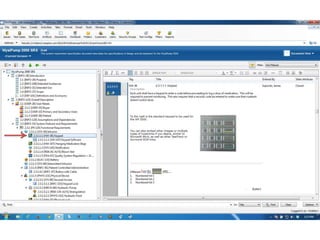
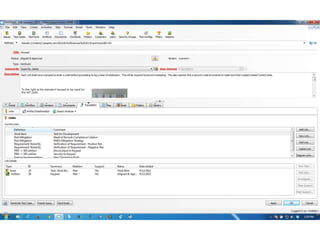
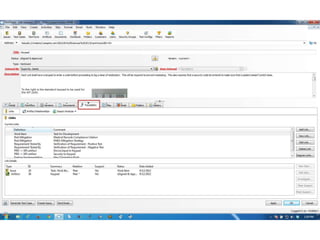
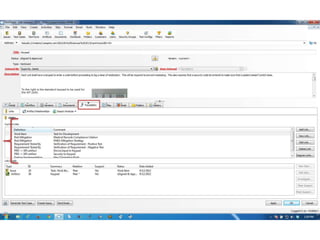
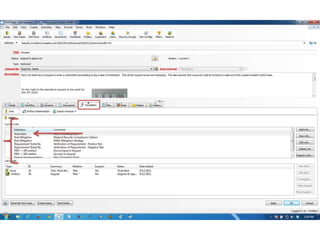
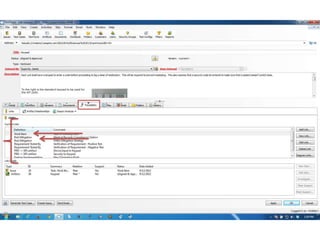
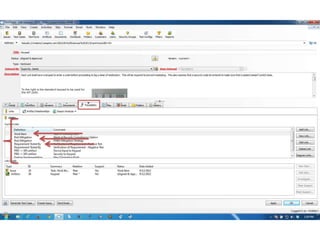
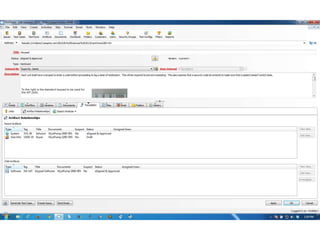
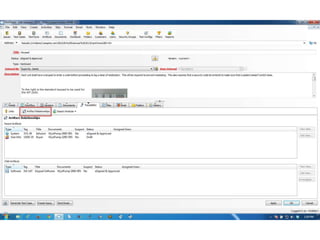
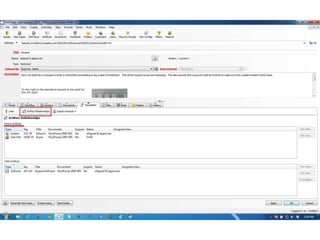
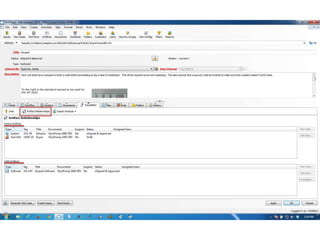
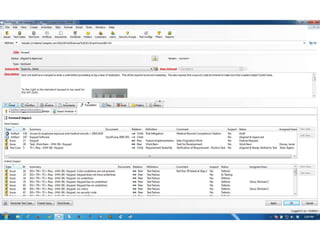
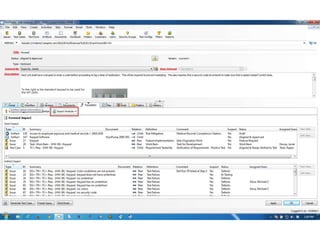
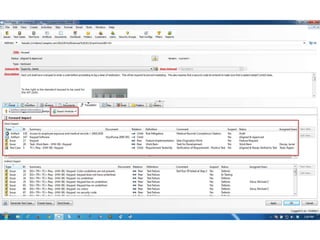
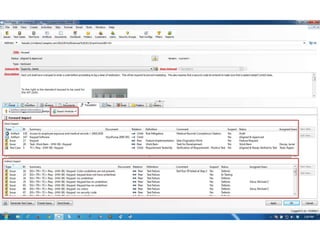
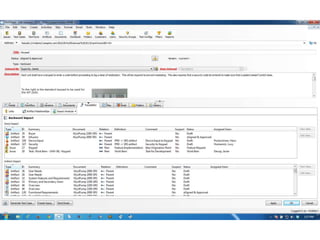
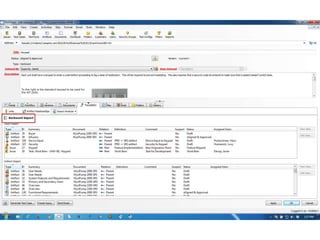
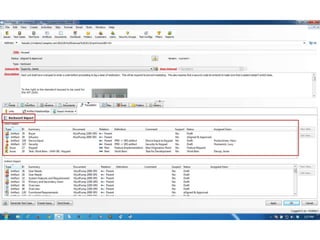
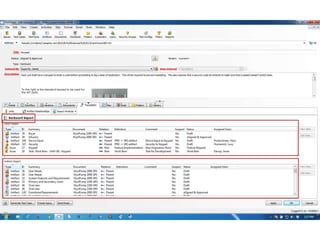
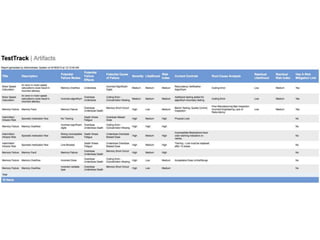
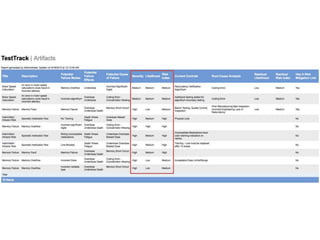
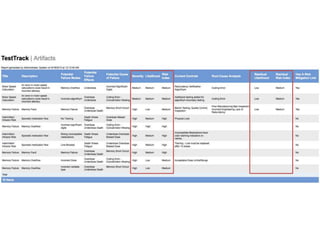
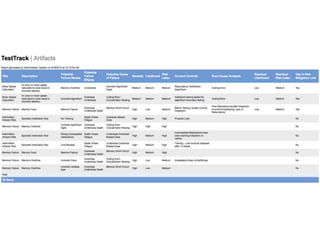
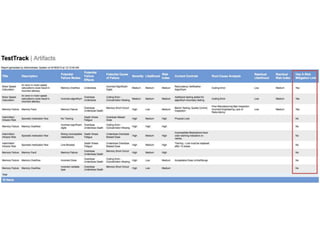
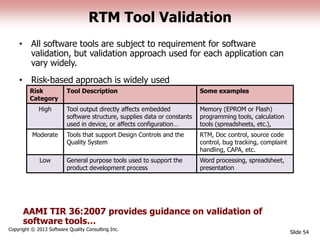
This document discusses the regulatory requirements for software traceability and the benefits of using a requirements trace matrix (RTM). It notes that traceability is required by FDA guidance to link requirements with design, implementation, testing and risk mitigation. An RTM provides benefits such as ensuring all requirements are implemented and tested, managing changes, and demonstrating that hazards are mitigated. The document provides an example of how an RTM can be used and validated as a software tool.