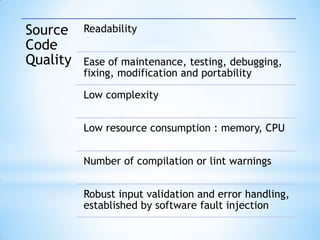
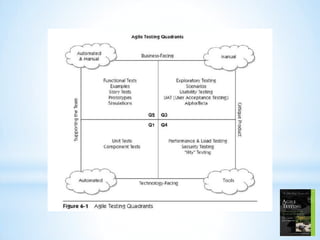
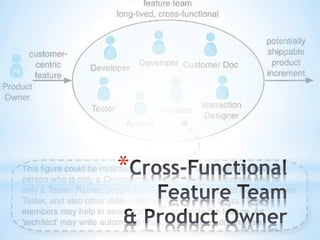
This document discusses software testing and quality from an agile perspective. It defines software testing as an empirical investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about product quality. Quality is defined as value to stakeholders, who can perceive quality differently. Testers must understand stakeholders and how the product may affect them. The document then discusses testing methods, levels, functional vs non-functional testing, and metrics for software product and source code quality. It advocates for scrum-based agile practices like identifying user roles, writing user stories, and test automation.