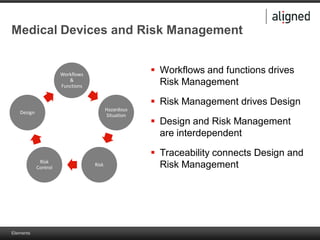
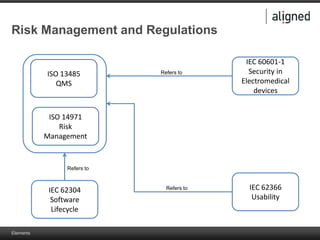
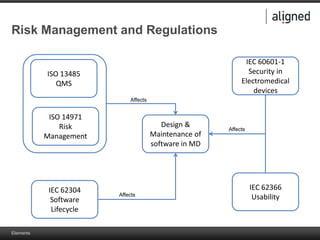
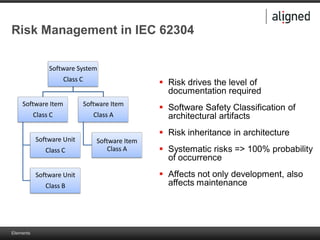
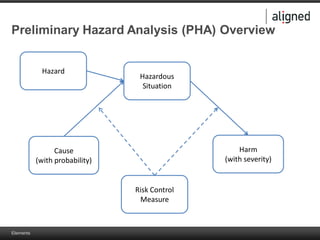
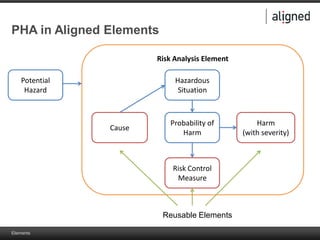
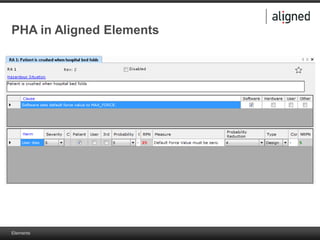
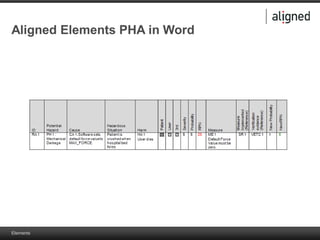
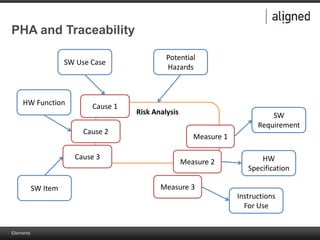
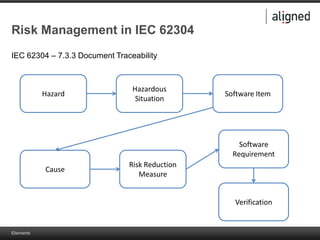
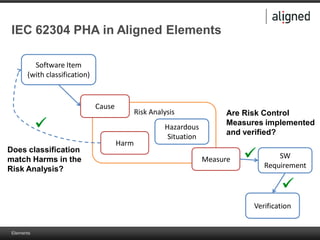
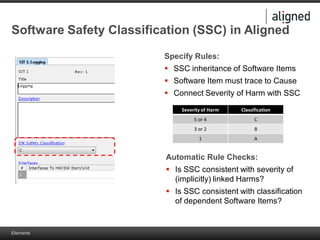
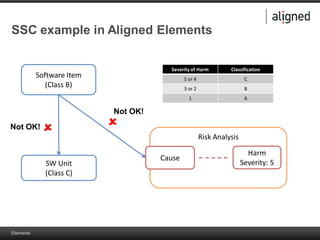
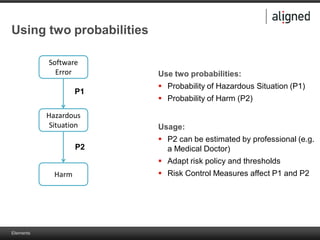
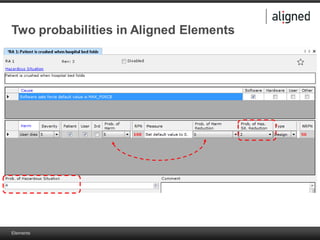
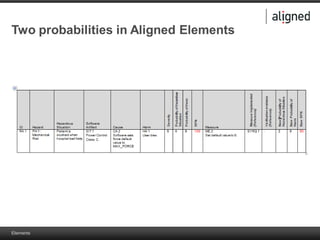
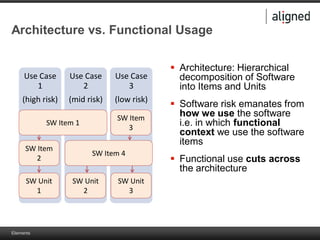
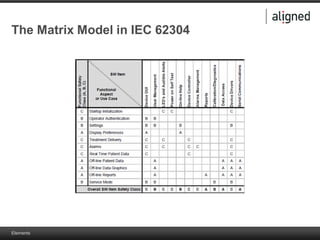
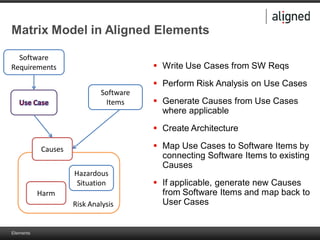
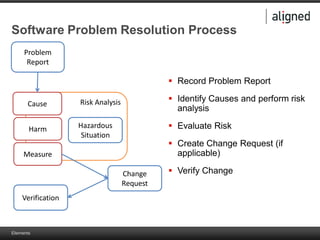
The document outlines the integration of risk management within the IEC 62304 framework, emphasizing the interdependence of design and risk management in medical devices. It discusses various risk management elements, including hazard identification, risk evaluation, and control measures, alongside regulatory standards like ISO 14971 and ISO 13485. Additionally, it introduces aligned elements as tools for consistent documentation and risk analysis throughout the software lifecycle.