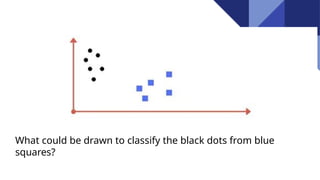
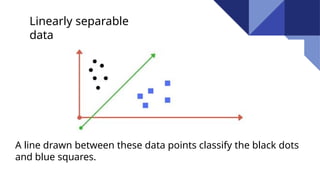
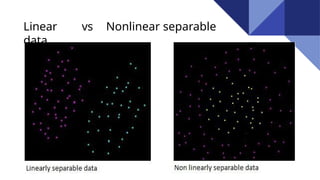
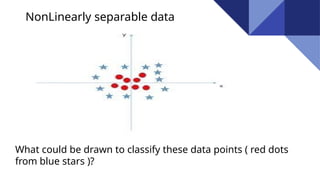
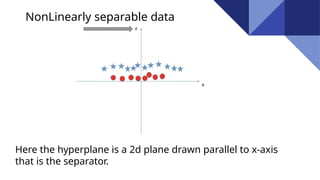
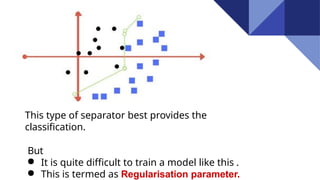
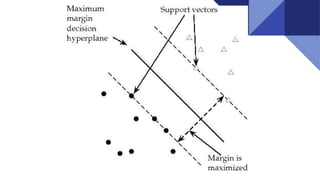
Support Vector Machines (SVM) are discriminative classifiers that utilize training data to create an optimal hyperplane for categorizing new examples. They effectively handle both linearly and non-linearly separable data, incorporating concepts like the margin and support vectors to achieve classification. SVMs are applied in various fields such as face detection, text categorization, and bioinformatics.