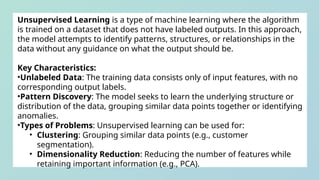
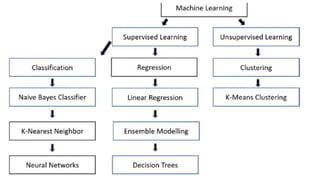
The document outlines the learning objectives for a machine learning course, focusing on the distinctions between classification and regression tasks. It explains the importance of machine learning, types of learning (supervised and unsupervised), and the processes involved in analyzing business problems. Additionally, it includes examples of problem statements related to classification and regression as well as a practical task involving centroid calculation.