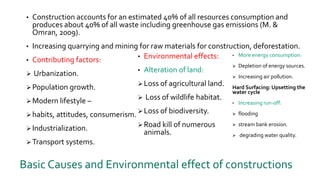
The document defines sustainable construction as construction practices that minimize negative environmental, social, and economic impacts. It discusses how construction accounts for 40% of resource use and waste. Sustainable construction methods outlined include reuse and recycling of materials, natural ventilation, and retrofitting existing structures. The summary highlights how sustainable construction conserves resources through various practices and represents an investment in the future.