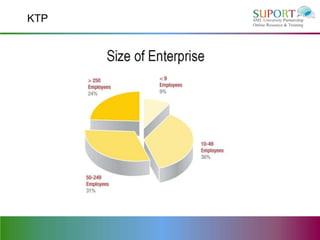
This document outlines the goals and content of a session on collaborating with public research organizations. The session aims to help participants learn how to identify potential public research partners, guidelines for selecting partners, good practice guidelines for collaboration, and information on relevant EU and national funding opportunities. The document provides sources for finding potential partners, what makes a good partnership, advice on collaboration best practices, and discusses small and large-scale collaboration examples. It also outlines the European Union's 7th Framework Programme for funding as well as some national funding sources from Northern Ireland.