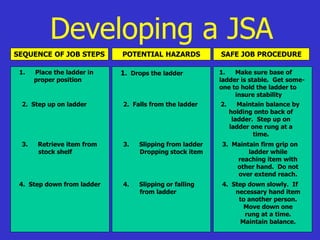
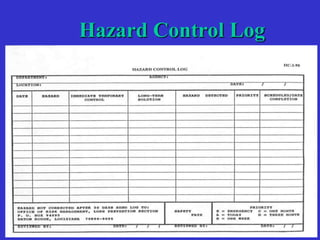
This document discusses supervisory responsibilities related to safety. It covers topics like conducting safety meetings and investigations, assisting with job safety analyses, maintaining equipment and work areas, providing training, and supervising employee tasks. It emphasizes the importance of safety training for supervisors and employees, conducting inspections, documenting meetings and investigations, and using tools like job safety analyses to improve safety. Supervisors are responsible for ensuring safety compliance and accident prevention through activities such as training, inspections, investigations, and documentation.