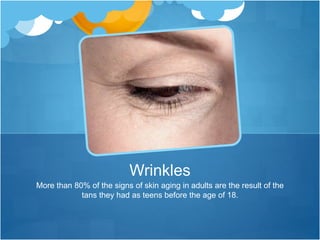
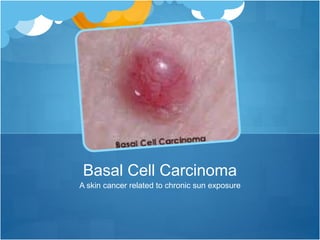
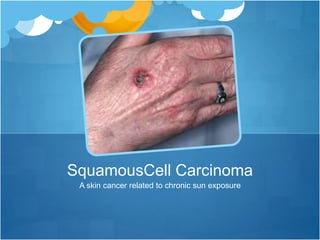
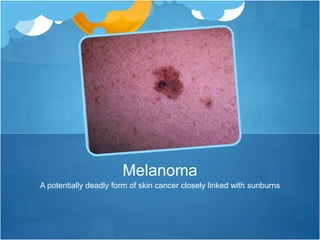
One blistering sunburn in childhood can double the risk of melanoma later in life. While basal cell cancer and squamous cell cancer risk increases with chronic sun exposure, melanoma risk increases even after a single severe sunburn. Other melanoma risks include fair skin, number of moles, and family history. It is important to apply sunscreen liberally, reapply every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating, use at least SPF 30, and seek shade during peak sun hours to prevent sun damage and skin cancer.

![1) Risk for Melanoma
Doubles if you’ve had five sunburns
Only takes ONE blistering sunburn in childhood to double
your risk of melanoma later in life!
As opposed to other more common types of skin cancer
(basal cell cancer [BCC] or squamous cell cancer [SCC])
risk for melanoma increases with even ONE bad sunburn
SCC and BCC are related to chronic sun accumulation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunscreenmeme-3-140710181957-phpapp02/85/Sunburn-The-Heat-Is-On-2-320.jpg)