The document provides information on seed production technology for sunflower. It discusses the botany, cultivation practices including varietal selection, isolation distances, seed treatment, nutrient application, irrigation, pest and disease management, harvesting, processing, and storage. The key points are:
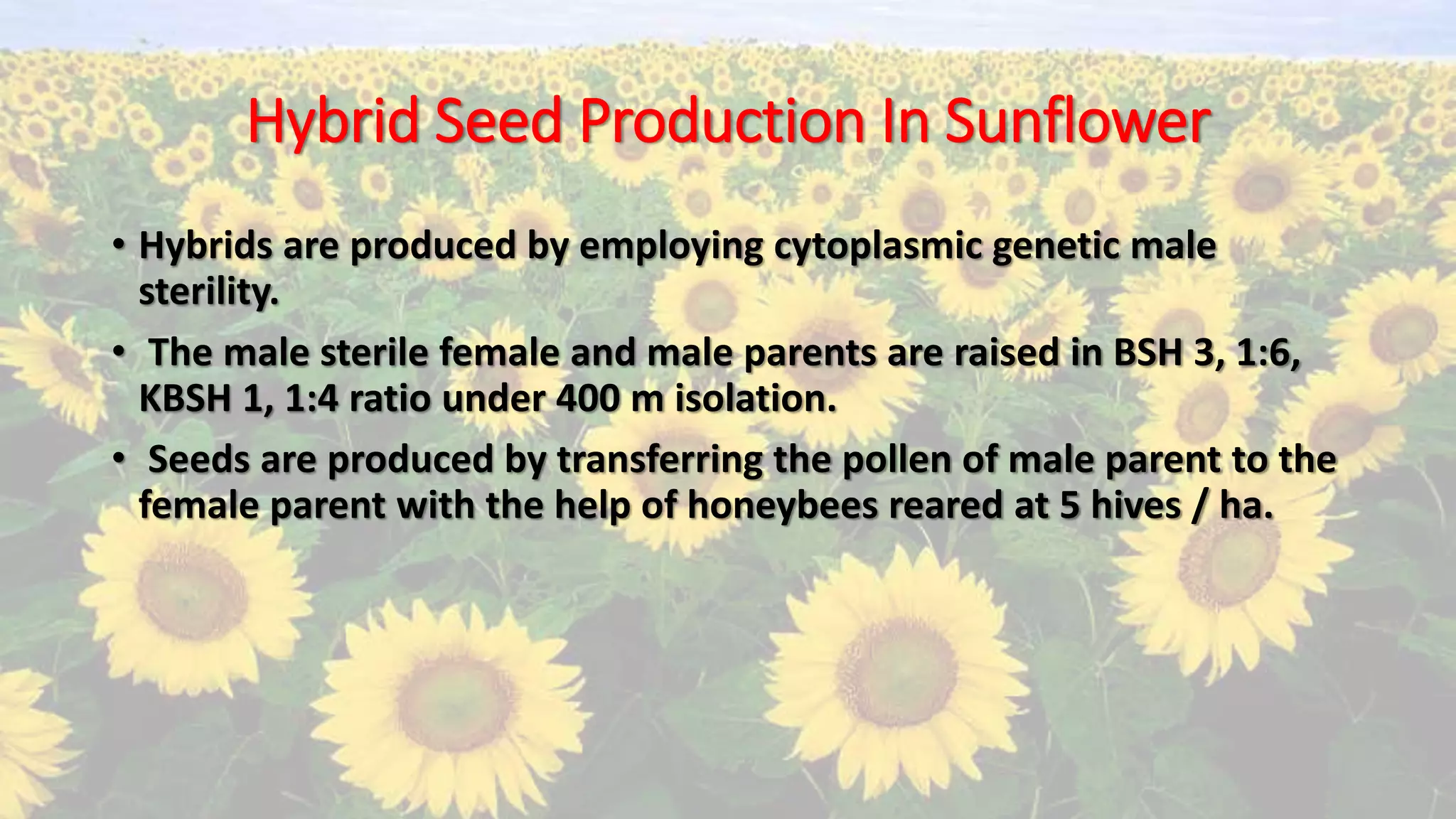
- Sunflower is a cross-pollinated crop pollinated by insects like honey bees. Varietal seed is produced using isolation and roguing to maintain purity.
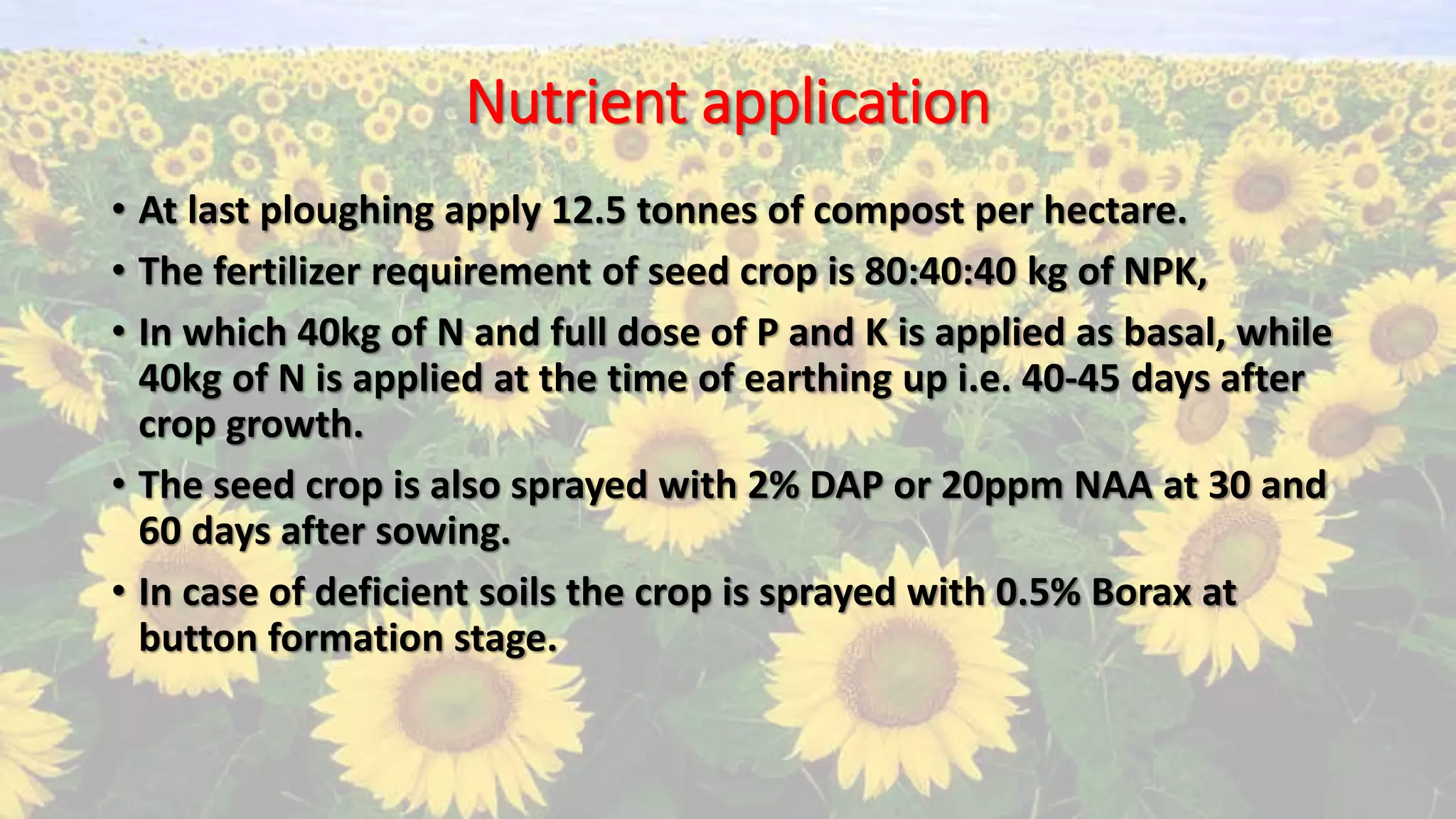
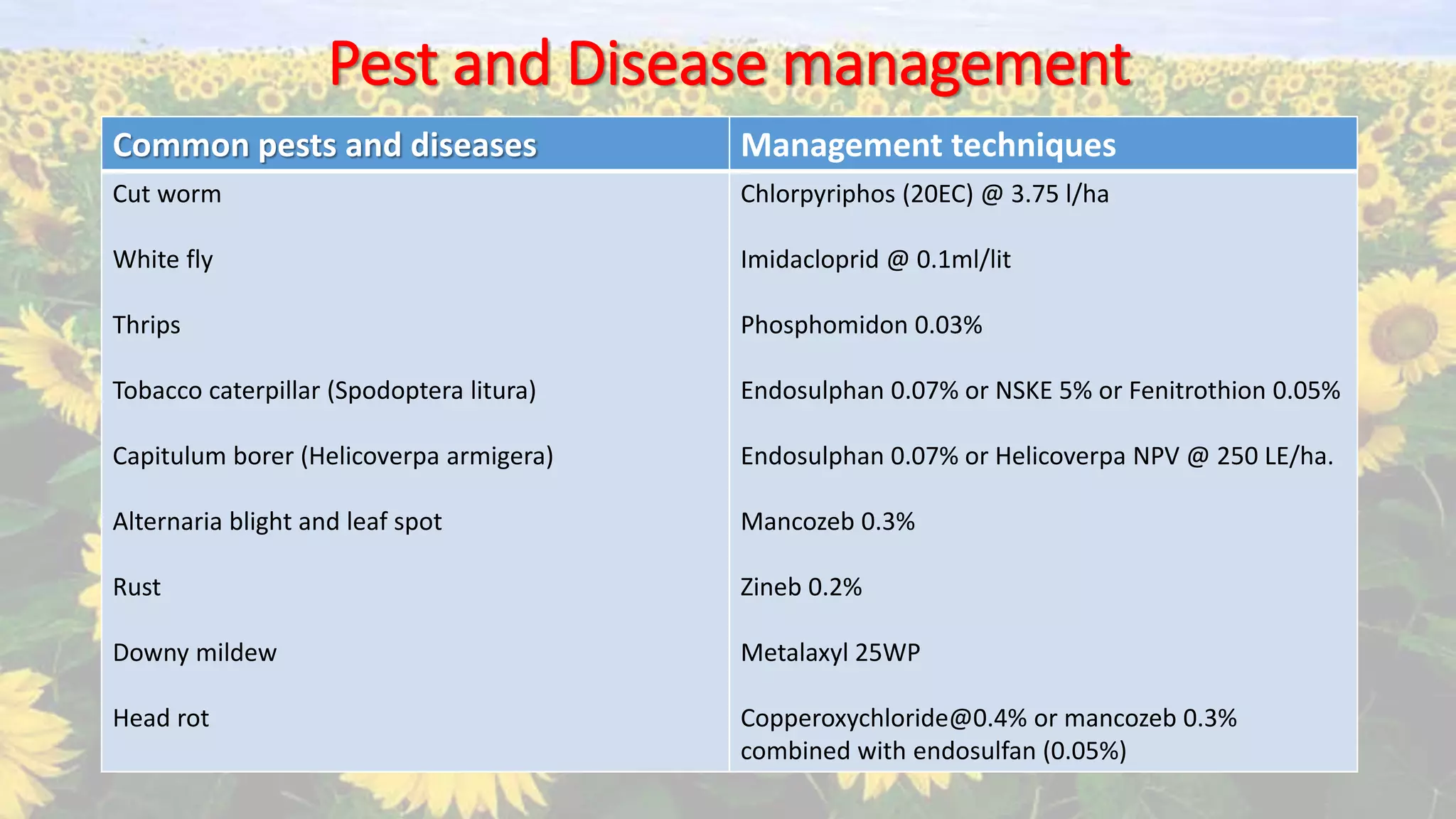
- Cultural practices include soil preparation, seed treatment, spacing, fertilizer application, irrigation, and pest/disease control.
- Fields must be isolated from other varieties and wild sunflowers by 400-600m for foundation and 200-400m for certified seed production.