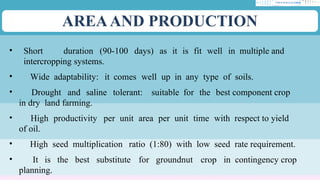
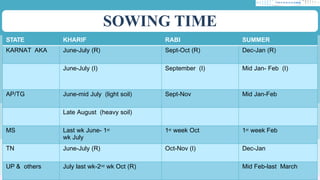
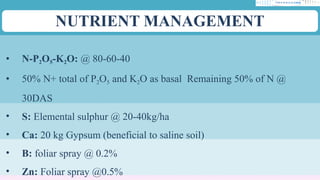
The document discusses the cultivation of sunflowers (Helianthus annuus), highlighting its economic importance as a significant oilseed crop that contributes to cooking oil and industrial products, with beneficial properties for health. It outlines agronomic practices, climatic and soil requirements, and harvest details, noting that sunflowers are drought and saline tolerant and suitable for various intercropping systems. Additionally, it covers seed management, nutrient requirements, and the overall yield rates in both rainfed and irrigated conditions.