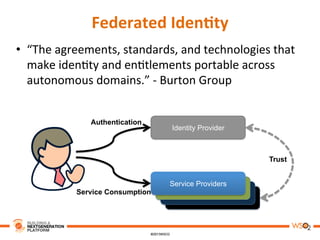
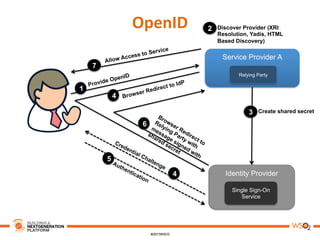
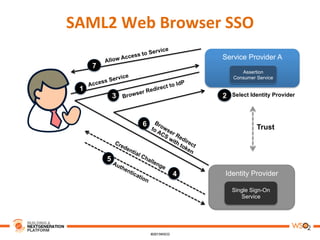
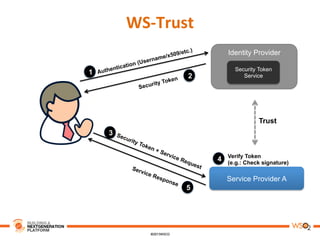
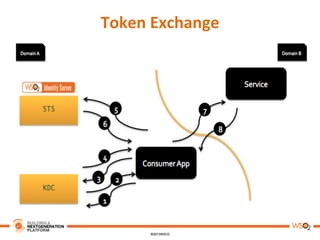
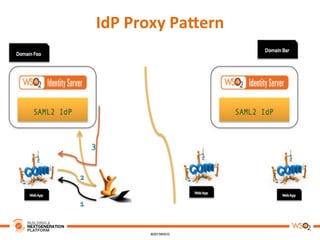
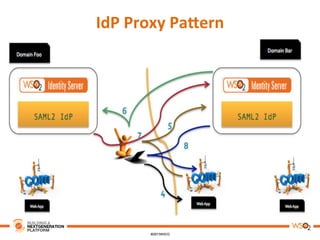
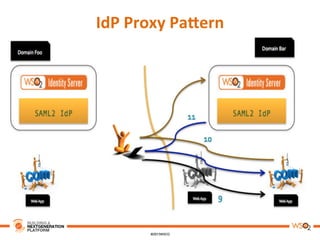
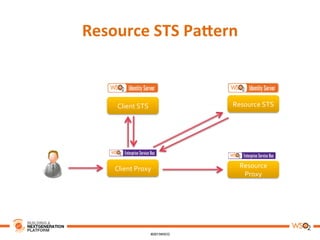
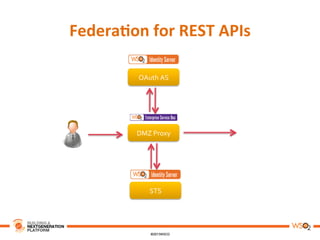
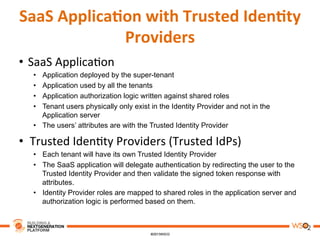
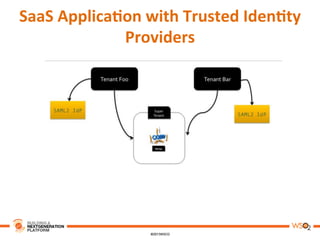
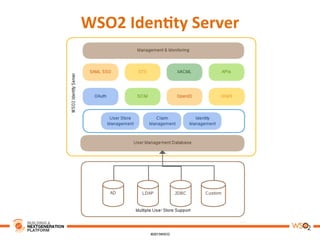
This document discusses practical use cases of federated identity in real world scenarios. It begins by defining identity and explaining problems with digital identity, such as having separate identities in different applications. It then introduces federated identity as a way to make identities portable across domains. Key requirements for federated identity include identity management, authentication, trust between domains, attribute mapping, and attribute exchange. Common protocols for federated identity include OpenID, SAML, and WS-Trust. The document provides examples of federated identity patterns using WSO2 Identity Server and discusses use cases such as a SaaS application with trusted identity providers.