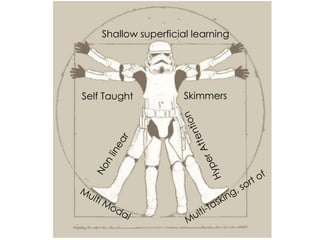
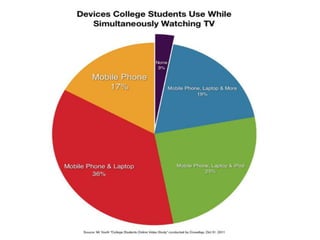
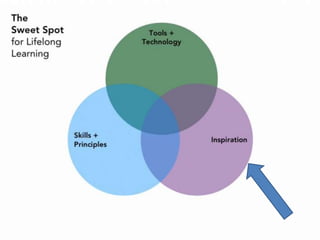
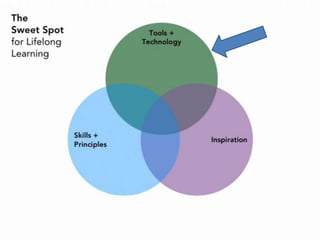
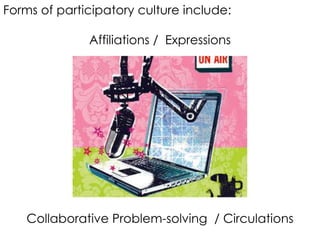
This document discusses how technology is changing the ways students interact, consume information, and learn. It notes that while technology is ubiquitous, it does not necessarily lead to digital or information literacy. It argues that educators must help students take control of technology and be critical consumers of information. The document promotes using participatory and student-centered and technologies in teaching to engage students and help them develop important literacy skills for a digital world.