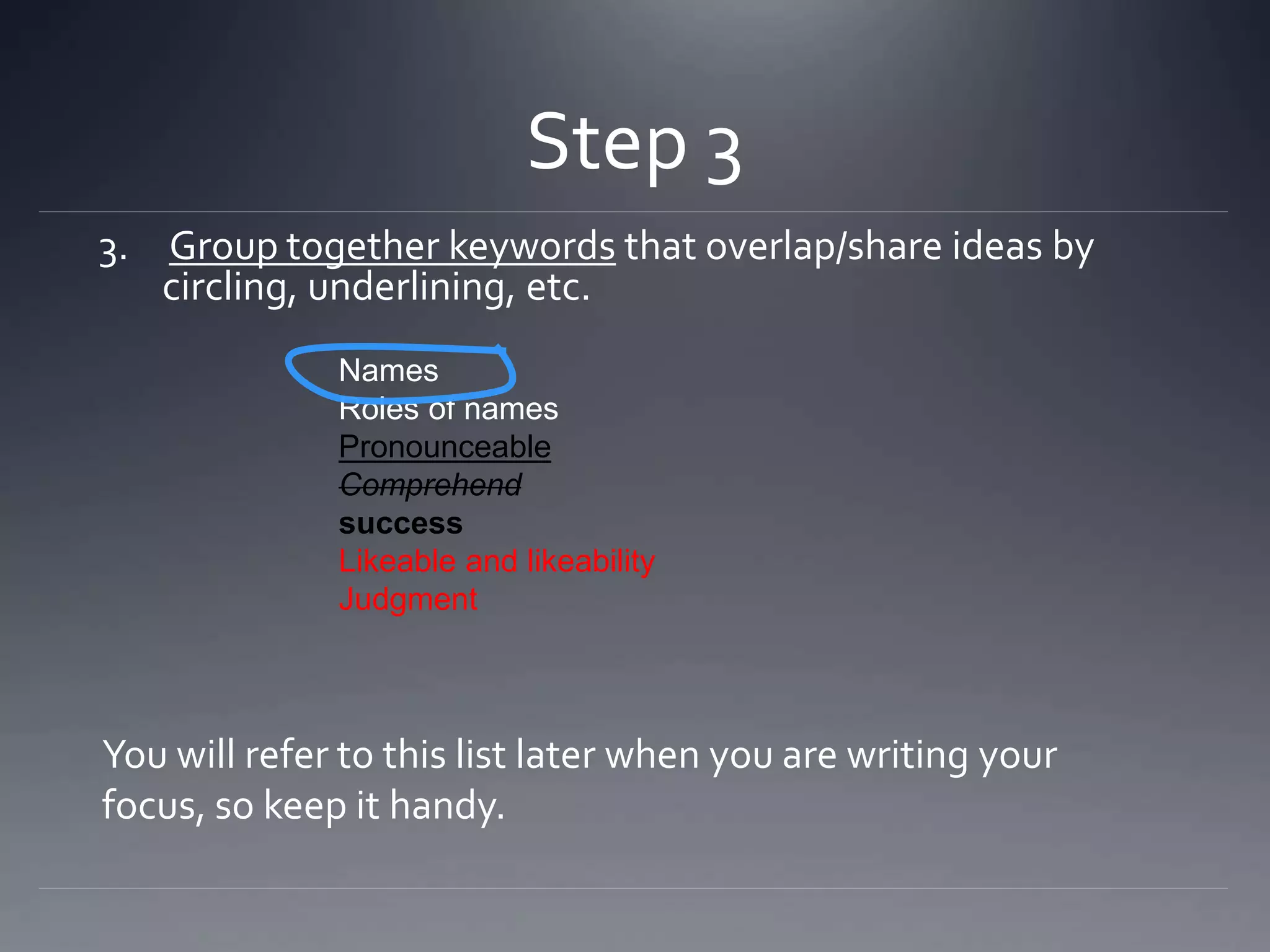
The document provides a detailed guide on how to summarize texts effectively, emphasizing the importance of writing in one's own words and focusing on the author's main points. It outlines a six-step process for creating a summary, including annotating the text, identifying keywords, and refining main ideas into a concise statement. The final summary should include the author's purpose along with 5-7 supporting sentences that encapsulate the main ideas from the text.