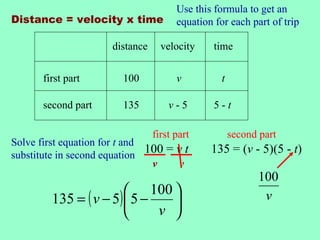
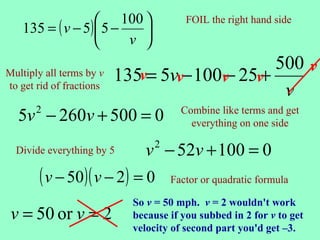
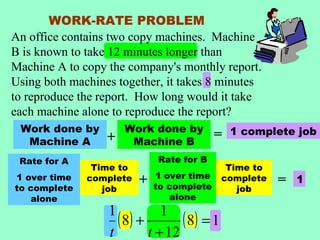
Machine A can copy the monthly report in 12 minutes and Machine B can copy it in 24 minutes. Using both machines together, they can copy the report in 8 minutes. To solve for the individual times, an equation was set up equating the work done by each machine over time to the total work done. This resulted in a quadratic equation that was factored and solved to find the times for each machine alone as 12 and 24 minutes.