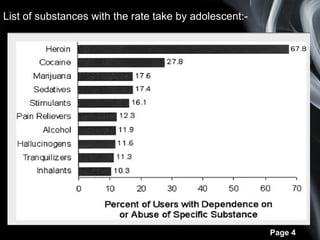
The document discusses substance abuse and its treatment. It defines substance abuse and dependence, and lists the DSM-IV criteria for substance abuse. Common substances abused by adolescents are discussed. Psychological factors, environment, peer pressure, and mental health issues can contribute to substance abuse. Consequences in academic settings include learning problems, reduced attention and focus. Prevention strategies and treatment methods like behavioral therapies and psychological interventions are important to address substance abuse issues.