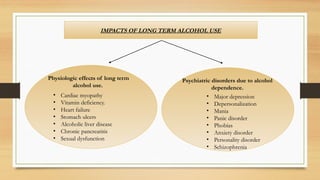
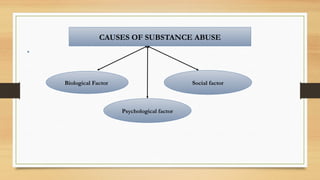
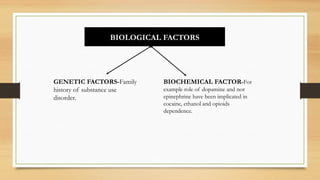
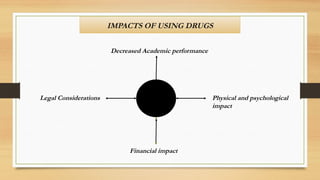
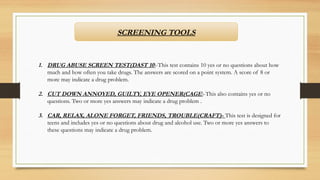
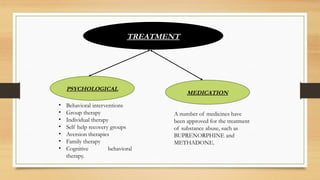
The document provides an overview of substance use disorders, defining key concepts like addiction, dependence, and tolerance, while outlining various criteria for substance use disorders as per DSM-5. It discusses different types of substance abuse including alcohol, opioids, cannabis, and cocaine, along with their psychological and physiological impacts. The document also covers causes, screening methods, treatment options, and statistical data on substance use and treatment in 2019.