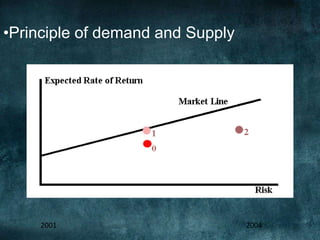
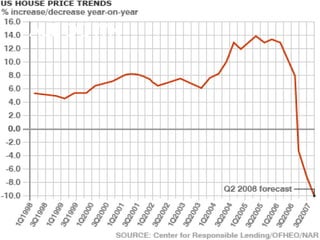
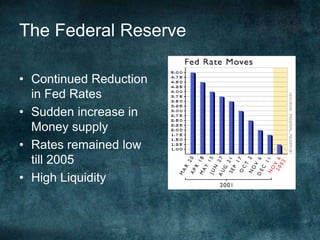
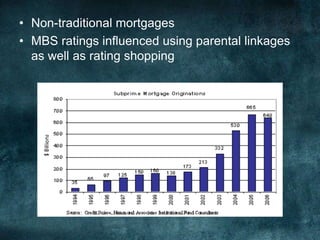
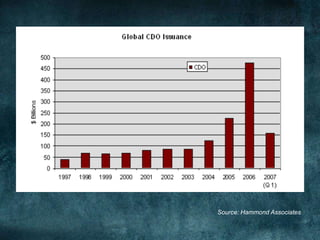
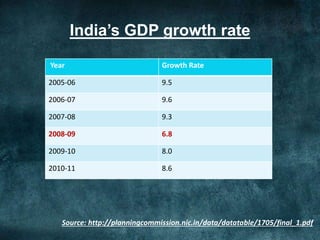
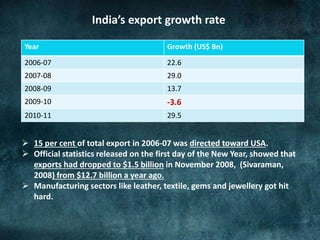
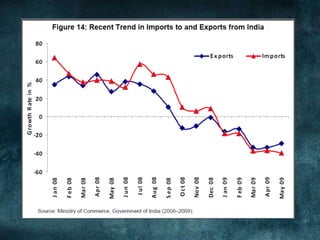
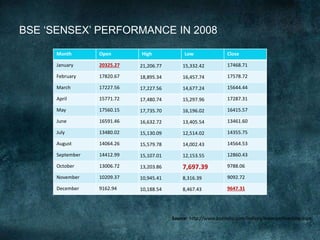
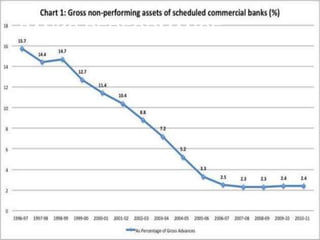
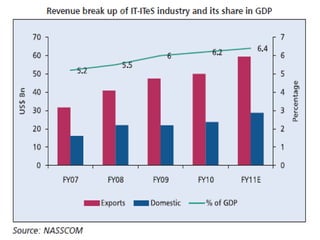
This document provides an overview of the 2008 subprime mortgage crisis in the United States. It defines subprime loans as high-risk loans given to borrowers with poor credit. In the early 2000s, low interest rates and rising home prices fueled increased subprime lending. However, starting in 2006, subprime borrowers began defaulting on mortgages as home prices declined. These mortgage defaults led to losses in mortgage-backed securities, hurting financial institutions and triggering a global recession. India was less impacted than other countries due to regulations that limited exposure of its financial system to global markets.