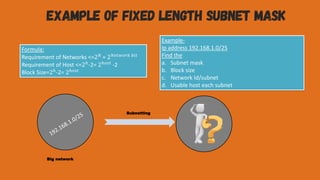
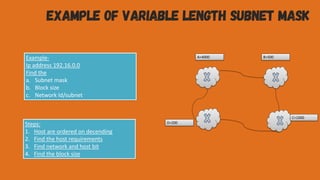
The document discusses subnetting a large network with the IP address 200.1.2.0 into four smaller subnets. It provides the subnet mask and IP address range for each of the four subnets created. It also discusses the differences between fixed length and variable length subnetting. In another example, it shows how to calculate the subnet mask, block size, usable hosts, and network IDs when given the IP address 192.168.1.0/25.