Embed presentation
Download to read offline
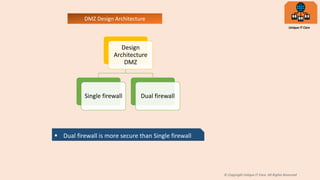
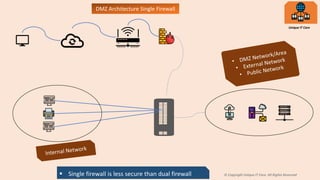
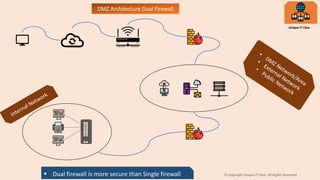




A DMZ, or demilitarized zone, is a network area between an internal trusted network and an external untrusted network like the internet. It improves security by acting as a buffer between the two networks. There are two common DMZ architectures - single firewall and dual firewall. A dual firewall configuration is considered more secure as it provides separation of the DMZ from both the internal and external networks, while a single firewall connects them all together. Common servers placed in the DMZ include web, mail, FTP, and proxy servers to allow access from outside while protecting the internal network.






