This document discusses the crankshaft component of internal combustion engines. It describes how a crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion. Crankshafts must withstand high stresses from engine forces over many load cycles. The document then focuses on modeling and analyzing a single cylinder engine crankshaft to identify stresses and find solutions to problems. It examines the crankshaft material, construction methods like forging and casting, and how features like radii and hardening increase fatigue strength to handle engine stresses.




![Uses:
A single-cylinder Villiers engine in the engine bay of a 1959 Bond Minicar
Motorbike Horex "Regina" with one-cylinder-four-stroke-engine
Early motorcycles, automobiles and other applications such as marine engines all tended to be
single-cylinder. The configuration remains in widespread use in Auto rickshaws, motor
scooters, mopeds, dirt bikes, go-karts, radio-controlled models and is almost exclusively used in
portable tools, along with garden machinery such as lawn mowers.
The bestselling motor vehicle of the world, the Honda Super Cub, has a very fuel-efficient 49 cc
single-cylinder engine and big-diameter 17-inch wheels. Some motorcycles with strong
single-cylinder engines are available today. There are sport bikes like the KTM 690 Duke
R[1] which has 70 hp 690 cc single-cylinder engine and reaches 125 mph (200 km/h) with a curb](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crankshaft-220121065421/85/Crank-shaft-5-320.jpg)
![weight of only 150 kg, dual-sport motorcycles like the BMW G650GS, as well as classics like
the Royal Enfield 500 Bullet with a long-stroke single-cylinder engine.[2]
Construction
Crankshafts can be monolithic (made in a single piece) or assembled from several pieces.
Monolithic crankshafts are most common, but some smaller and larger engines use assembled
crankshafts.
Forging and casting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crankshaft-220121065421/85/Crank-shaft-6-320.jpg)
![Forged Crankshaft
Crankshafts can be forged from a steel bar usually through roll forging or cast in ductile steel.
Today more and more manufacturers tend to favour the use of forged crankshafts due to their
lighter weight, more compact dimensions and better inherent damping. With forged
crankshafts, vanadium micro alloyed steels are mostly used as these steels can be air cooled after
reaching high strengths without additional heat treatment, with exception to the surface hardening
of the bearing surfaces. The low alloy content also makes the material cheaper than high alloy
steels. Carbon steels are also used, but these require additional heat treatment to reach the desired
properties. Iron crankshafts are today mostly found in cheaper production engines (such as those
found in the Ford Focus diesel engines) where the loads are lower. Some engines also use cast iron
crankshafts for low output versions while the more expensive high output version use forged steel.
Machining
Crankshafts canalso be machined out of a billet, often a bar of high quality vacuum remelted steel.
Though the fibre flow (local in homogeneities of the material's chemical composition generated
during casting) doesn’t follow the shape of the crankshaft (which is undesirable), this is usually not
a problem since higher quality steels, which normally are difficult to forge, can be used. These
crankshafts tend to be very expensive due to the large amount of material that must be removed
with lathes and milling machines, the high material cost, and the additional heat treatment
required. However, since no expensive tooling is needed, this production method allows small
production runs without high costs.
In an effort to reduce costs, used crankshafts may also be machined. A good core may often be
easily reconditioned by a crankshaft grinding [21] process. Severely damaged crankshafts may also](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crankshaft-220121065421/85/Crank-shaft-7-320.jpg)


![LITERATURE REVIEW
Yingkui and Zhibo [1] established three dimensional model ofa dieselengine crankshaft by using
Pro E software. Using ANSYS analysis tool, the finite element analysis for the crankshaft was
conducted under extreme operation conditions and stress distribution of the crankshaft was
presented. The crank stress change model and the crank stress biggest hazard point were found by
using finite element analysis, and the improvement method for the crankshaft structure design was
given. This shows that the high stress region mainly concentrates in the Knuckles of the crank arm
& the main journal, and the crank arm and the connecting rod journal, which is the area most easily
broken.
Jian et al. [2] analyzed three dimensional model of 380 diesel engine crankshaft. They used ProE
and ANSYS as FEA tools. First of all, the 380 diesel engine entity crankshaft model was created
by Pro E software. Next, the model was imported to ANSYS software. Material properties,
constraints boundary conditions and mechanical boundary conditions of the 380 diesel engine
crankshaft were determined. Finally, the strain and the stress figures of the 380 diesel crankshaft
were calculated combined with maximum stress point and dangerous area. This article checked the
crankshaft’s static strength and fatigue evaluations. That provided theoretical foundation for the
optimization and improvement of engine design. The maximum deformation occurs in the end of
the second cylinder balance weight.
Gu Yingkui et.al. [3] researched a three-dimensional model of a diesel engine crankshaft was
established by using PRO/E software. Using ANSYS analysis tool, it shows that the high stress
region mainly concentrates in the knuckles of the crank arm & the main journal and the crank arm
& connecting rod journal ,which is the area most easily broken.
Jian Meng et al. [4] analyzed crankshaft model and crank throw were created by Pro/ENGINEER
software and then imported to ANSYS software. The crankshaft deformation was mainly bending
deformation under the lower frequency. And the maximum deformation was located at the link
between main bearing journal, crankpin and crank cheeks.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crankshaft-220121065421/85/Crank-shaft-10-320.jpg)
![Xiaorong Zhou et al. [5] described the stress concentration in static analysis of the crankshaft
model. The stress concentration is mainly occurred in the fillet of spindle neck and the stress of the
crankpin fillet is also relatively large. Based on the stress analysis, calculating the fatigue strength
of the crankshaft will be able to achieve the design requirements. From the natural frequencies
values, it is known that the chance of crankshaft resonant is unlike. This paper deals with the
dynamic analysis of the whole crankshaft. Farzin H. Montazersadgh et al.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crankshaft-220121065421/85/Crank-shaft-11-320.jpg)



























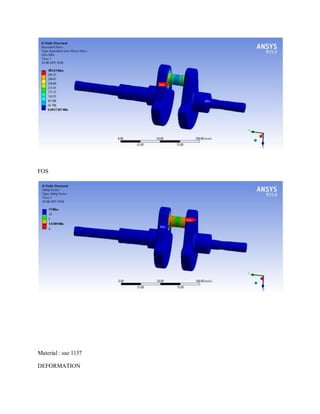
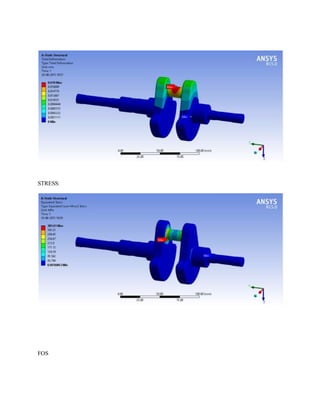
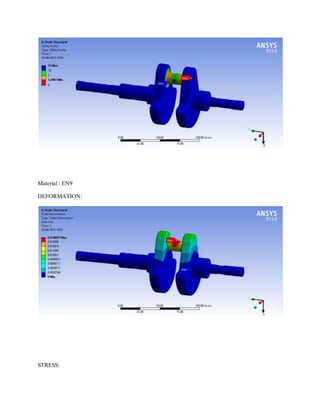
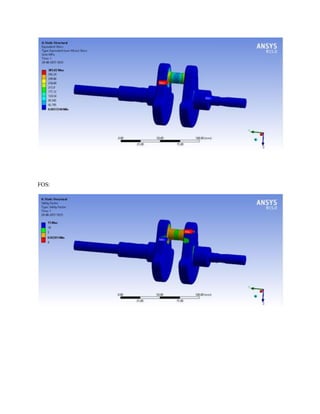
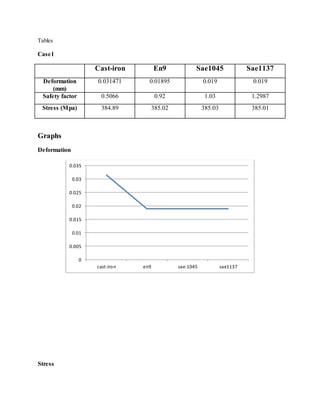
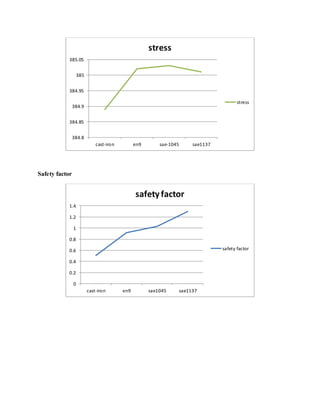
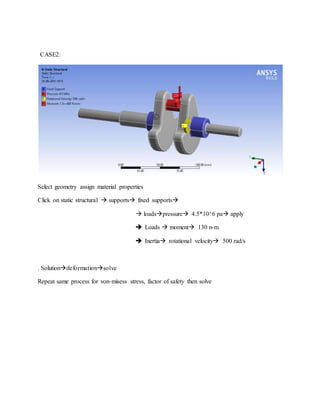
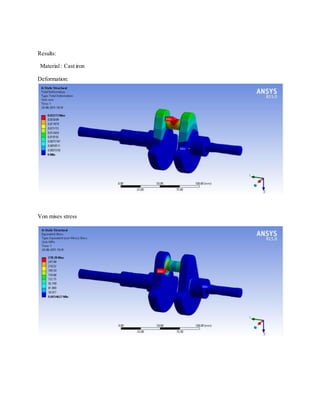
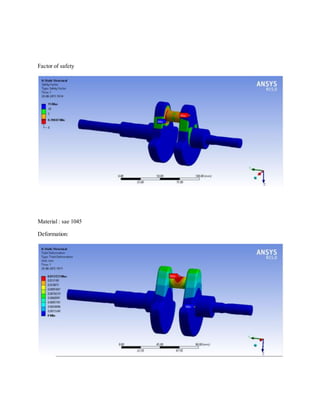
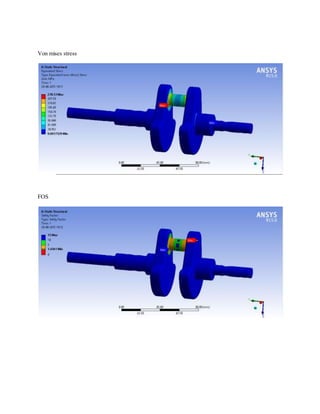
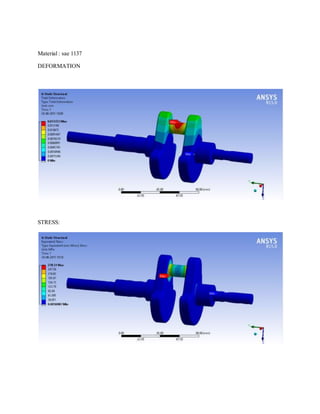
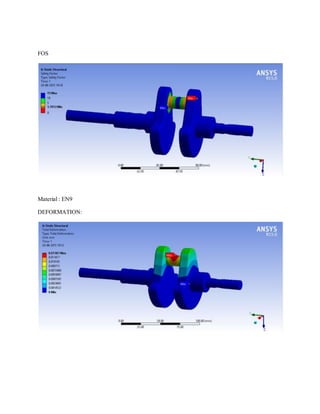
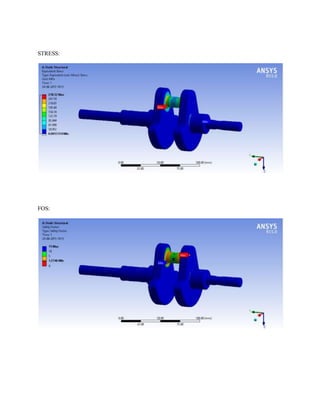
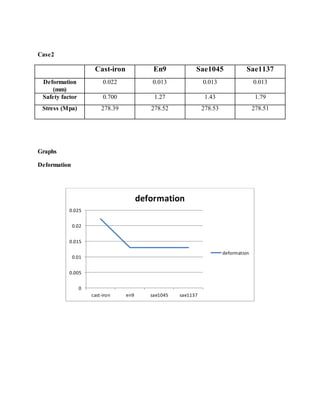


![1.Yu Ding and Xiaobo Li.,2011, “ Crankshaft Strength Analysis of a Diesel Engine Using Finite
Element Method,” Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference
2. Jian Meng., Yongqi Liu., Ruixiang Liu.,2011,“Finite Element Analysis of 4-Cylinder Diesel
Crankshaft, ” I.J. Image, Graphics and Signal Processing, 5, 22-29
3. MENG Jian., LIU Yong-qi., LIU Rui-xiang., and ZHENG Bin.,2011,“Intension Analysis of3-D
Finite Element Analysis on 380 diesel crankshaft,” International Conference on Computational
and Information Sciences
4.Mr.S.J Patil “ Modal analysis of compressor crankshaft”, International Journal of Scientific
Reasearch, vol-2, Issue:7, ISSN: 2277-8179, Pages: 155-158, July-2013.
[5] Momin Muhammad Zia Muhammad Idris “ Optimization of crankshaft using strength
analysis”, International Journal of Engineering Reasearch and applications, Vol-3, Issue-3,
ISSN:2248-9622, Pages: 252-258, May-Jun-2013.
[6] Rincle Garg, Sunil Baghla, “Finite element analysis and optimization of crankshaft”,
International Journal of Engineering and Management Reaserch, vol-2,Issue-6,ISSN: 2250-0758,
Pages:26-31, December 2012.
[7] BDNS Murthy “ Modeling analysis and optimization of crankshaft”, vol-2, Issue-9, ISSN:
2278-0181, Pages: 749-753, September-2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crankshaft-220121065421/85/Crank-shaft-63-320.jpg)