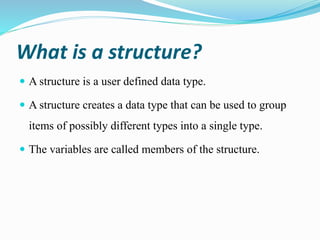
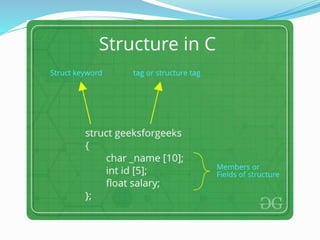
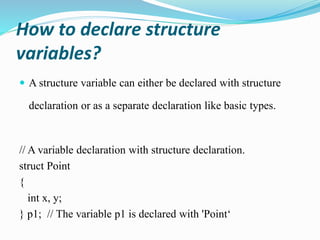
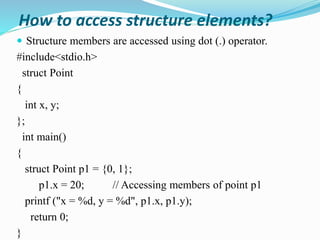
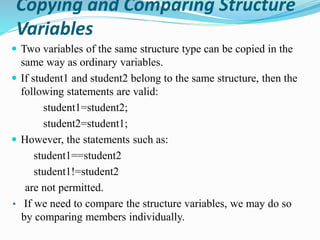
This document discusses structures in C programming. It defines a structure as a user-defined data type that groups different data types together under a single name. It provides examples of how to create, declare, initialize, access, copy, compare, and declare arrays of structures. Structures allow grouping of related data and make the code more organized and readable.

![How to create a structure?
‘struct’ keyword is used to create a structure.
Following is an example.
struct address
{
char name[50];
char street[100];
char city[50];
char state[20];
int pin;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-191209042542/85/Structures-in-c-4-320.jpg)



![What is an array of structures?
#include<stdio.h>
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point arr[10]; // Create an Array of Structures
arr[0].x = 10; // Access Array Members
arr[0].y = 20;
printf("%d %d", arr[0].x, arr[0].y);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structuresinc-191209042542/85/Structures-in-c-11-320.jpg)
